The number of trends and innovations in the field of construction aim at making construction faster and deliver higher and better performance. However, construction is not restricted to a structure made of concrete and bricks; aesthetics cannot be ignored. The interior design is key to have a blissful life inside the building. Therefore, more than ever people are paying keen attention to the way their homes are designed but it is a myth that one has to spend a bomb to beautify it. In this article, whether you are building a new house from scratch or remodelling the existing one and we are going to tell you about a simple material that will go a long way in aesthetically improving your home! And that is POP (plaster of paris).
Plaster of Paris is a building material which is used for plastering the internal walls as well as making the false ceilings of the house. It is also used to cast decorative elements like mouldings, Cornish, etc.

Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating gypsum crystals. It is a cheaper solution to the time-consuming and ecologically straining process of sand cement plaster. It is used extensively in many countries for general building operations which have the specific requirements for light weight and high fire resistance.
What is Plaster of Paris?
According to ‘M.G. Goyal’ (Author of Construction Handbook for Civil Engineer & Architect, Vol 2) Gypsum, a rocklike mineral (IS: 1290) known chemically as hydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO42H2O) is found in many parts of the world, usually combined with impurities such as clay, limestone, and iron oxides. In its pure form gypsum is white, a chalk like material but in combination with impurities, it may be gray, brown or pinkish. Relatively pure calcined gypsum is known as Plaster of Paris, after the huge beds of it that underlie the city of Paris where it was mined in abundance in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.
The origins of plaster of Paris can be traced to Montmartre in North Paris where it was extensively mined from. It is also known as POP.
As described by ‘S.C. Rangwala’ (Author of Engineering Materials book), Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating gypsum crystals at the temperature of 160–170 °C (248–356 °F). It loses about 14.7% of its water content in the form of steam. The resulting product is the hemihydrate of calcium sulphate and it is known as first settle plaster or the “Plaster of Paris”.

According to ‘Walter Scarborough et al’ (Author of Building Construction – Principles, Materials, System), when POP is heated to remove 75% of its water, the resulting product is calcium sulphate hemihydrate (Hemi means “half”), referred to as plaster of Paris. The chemical notation of Plaster of Paris is CaSO4– ½ H2O. (Chemical name of POP is calcium Sulphate where Ca is the symbol for calcium and SO4 is the symbol for sulphate, so CaSO4 stands for calcium sulphate). When water is added to plaster of paris, it returns to its original hard, rocklike form gypsum containing calcium sulphate and two molecules of water.
Also Read:
Gypsum Board: All You Need to Know!
Types of Gypsum Board | All you Need to Know
POP is manufactured as a dry powder and is mixed with water to make a paste when used. It was used to create some of the most important artworks of the Renaissance period, including Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel ceiling, which was painted on a thin layer of wet Plaster of Paris.
Uses of Plaster of Paris
Plaster of Paris is being used from the ancient times in the following fields till date,
- Construction Work
- Medical field
(a) POP use in Construction Work
01. Art work

The artists use Plaster of Paris for producing sculptures and decorative metal castings. These are famous for making plaster moulds. We can create our desired shapes using plaster mouldings. pour the mouldings into it, wait for it to become solid and voila!
02. Architecture Design

Plaster of Paris (POP) is also known as gypsum plaster. It is mainly used in architectures in historical monuments starting from the 16th century. It is specially meant for decorative purposes. The modern gypsum plaster is used in the repair works of historic monuments.
03. Fireproofing
Plaster of Paris has been deemed as a very effective tool in combating real estate fires for a long time. Since plaster of paris is a wet mixture, when set on fire, it releases all the trapped water as water vapour, thus reducing the spread of fire in a building. Hence, the plaster of Paris has preferred building material for fireproofing purposes.
(b) POP in Medical Use

As said by ‘Borrelli J. et al’ (Publish in PubLMed.gov – US National Library of Medicine National Institute of Health), Plaster of Paris is widely used as bone graft substitute and to fill up bones defects. It is used to create safety soft bandages. A bandage along with plaster is wrapped around the injured part. This will hold the damaged part until it is recovered.
Following are the Different Uses of Plaster of Paris
The advantage of POP plaster is that it expands very slightly on setting and is not, therefore, likely to cause cracking of surfaces as happens in the case of cement plaster. On drying out POP forms a sufficiently dense surface to resist normal knocks. POP plaster is comparatively easy to spread and level. Besides, the POP plasters have no appreciable chemical action on paint and do not cause alkali attack as in case of lime or cement plasters. This plaster is generally used as a finishing touch to cement and sand plaster undercoat. Mixed with water the plaster is spread and finished to a thickness of about 2 to 3 mm and sets in about 1 to 2 hours.
Because plaster of pairs reverts to gypsum with the addition of water and its subsequent setting, plaster of Paris expands on setting. This is unlike Portland cement, which shrinks on setting due to the evaporation of water. Thus, plaster of Paris is used for casting in moulds because it accurately assumes the shape of the mould.
- Plaster of Paris is used for ceiling and walls as a protective coating. It gives a smooth, shining surface.
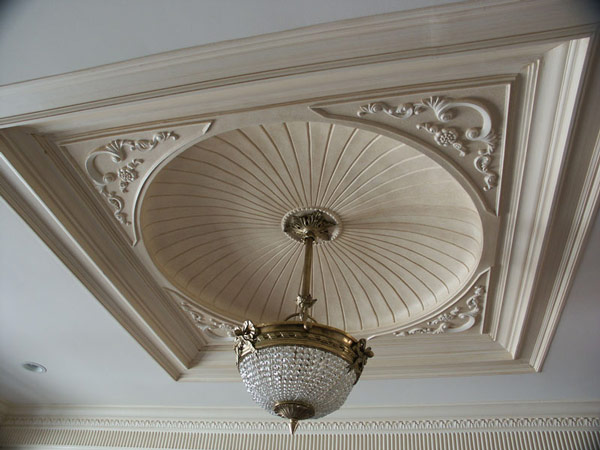

- POP is also used as a moulding and casting agent for decorative elements.

- In the medical department, plaster is used in orthopaedics to put casts around fractured bones. This stiff casts will help the bone recover and become like original one.
- To make sculptures and metal castings Plaster of Paris is used for decoration in buildings.

Also Read:
Fire Resistance of Concrete | Fire Resistive Construction
Acrylic Wall Putty: Increases the Life of Paint for Years to Come!
- A small repair works in wooden materials can be repaired using plaster of paris.
- It is used as a coating on wood and metal structures to prevent any fire accidents.
- POP is used in dentistry to make moulds of the teeth to be replaced.
If water is completely removed from gypsum, the resulting product, which is pure calcium sulphate, is called anhydrite. Anhydrite has a longer setting time than plaster of paris and is marketed as Keene’s cement, used as a finish coat in interior plaster.
Advantages of Plaster of Paris
Below are some of its advantages of POP to give you an idea whether you should use it in your dream home or not.
- It is light in weight and more durable.
- It has low thermal conductivity.
- It is very good fire resistant and hence a very good heat insulating material.
- It does not shrink while setting. Therefore, it does not develop cracks on heating or setting like conventional cement plaster.
- It forms a thick surface to resist normal knocks after drying.
- It mixes up easily with water and is easy to spread and level.
- It has good adhesion on fibrous materials.
- It gives a firm surface on which the colours can settle.
- It has no appreciable chemical action on paint and does not cause alkali attack.
- Plaster of Paris gives a decorative interior finish. Its gypsum content provides it a lot of shine and smoothness.
- It can easily be moulded into any shape.
Disadvantages of Plaster of Paris
- Gypsum plaster is not suitable for exterior finish as it is slightly soluble in water.
- It is more expensive than cement or cement lime plaster.
- It cannot be used in moist situations. So, if you are living in a humid climate, better not use POP!
- Skilled labour is required for precise application and thus labour cost for applying plaster of paris is high.
To summarise, it can be said that this plaster remains soft (to some extent) even after drying, it can be easily manipulated (shaped) by using sandpaper or metal. Hence, it is used for construction purposes, either by mixing with other substances or as a finishing material. However, it is widely used in home decors. Various designs can be made on the walls and ceilings. Apart from use in construction, it has an artistic use such as being used for sculptures. Many modern sculptors’ go for plaster of paris as moulding material, mainly because of its easy occurrence and settling speed. In addition to art and architecture, it is also used in orthopaedics to make smooth casts for broken limbs. So, if you are planning to remodel your home without burning a hole in your pocket, opt for plaster of paris and give a new shine to your old home!
Also Read:
Home Interior: False Ceiling Types!
Home Wallpaper: All You Need to Know






