Vietnamese philosophy
Last updated
Vietnamese philosophy includes both traditional Confucian philosophy, Vietnamese local religious traditions, Buddhist philosophy and later introducing French, Marxist and other influences.
Contents
Confucianism in Vietnam

Confucianism entered Vietnam and was later reinforced in the four Bắc thuộc periods of Chinese domination, beginning with the first Chinese domination of Vietnam from 111 BCE. [1] This was also the beginning of Taoism in Vietnam and Buddhism in Vietnam. Confucianism was reinforced in government by the Confucian court examination system in Vietnam, as well as the way family raised and taught children toward filial piety, through absolute obedience. [2]
Nationalism in Vietnam
Communism in Vietnam
Socialism in Vietnam
Ho Chi Minh Thought
Study of Vietnamese philosophy
Most research on Vietnamese philosophy is conducted by modern Vietnamese scholars. [3] The traditional Vietnamese philosophy has been described by one biographer of Ho Chi Minh (Brocheux, 2007) as a "perennial Sino-Vietnamese philosophy" blending different strands of Confucianism with Buddhism and Taoism. [4] Some researchers have found the empirical evidence of this "blending" and defined the socio-cultural phenomenon as "cultural additivity". [5] Another, Catholic, writer (Vu, 1966) [6] has analysed Vietnamese philosophy as constituted of tam tài ("three body" Heaven, Man, Earth) philosophy, yin-yang metaphysics, and agricultural philosophy. [7] Tran Van Doan, professor of philosophy at National Taiwan University (1996) [8] considers that Vietnamese philosophy is humanistic but not anthropocentric. [9]
Notable philosophers
The confucian poet-philosopher-scholar is typified by Lê Quý Đôn. Other confucianists include Chu Văn An (1292–1370) mandarin, Lê Quát a 14th Century anti-Buddhist Confucian writer, Mạc Đĩnh Chi (1280–1350), Nguyễn Trãi (1380–1442) a famous Đại Việt Confucian scholar, Nguyễn Khuyến (1835–1909). Notable modern Vietnamese philosophers include Cao Xuân Huy (vi, 1900–1983), Nguyễn Duy Quý (vi, born 1932), Nguyễn Đức Bình (vi, born 1927), Nguyễn Đăng Thục (vi, 1909–1999), Phạm Công Thiện (vi, 1941–2011), Trần Văn Giàu (vi, 1911–2010), modern marxist philosopher Trần Đức Thảo (noted in Paris in the 1960s) and Vietnamese Catholic philosopher Lương Kim Định.
Related Research Articles
Articles related to Vietnam and Vietnamese culture include:
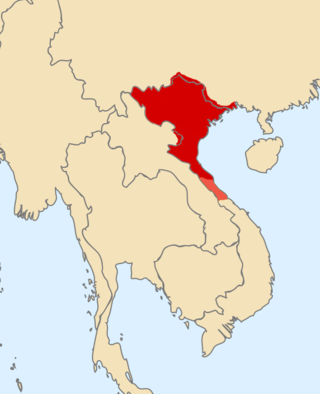
The Lý dynasty, officially Great Cồ Việt from 1009 to 1054 and Great Việt from 1054 to 1225, was a Vietnamese dynasty that existed from 1009 to 1225. It was established by Lý Công Uẩn when he overthrew the Early Lê dynasty. The dynasty ended when empress regnant Lý Chiêu Hoàng was pressured to abdicate the throne in favor of her husband, Trần Cảnh in 1225, the dynasty lasts for 216 years. During Lý Thánh Tông's reign, the official name of the state was changed from Đại Cồ Việt to Đại Việt, a name that would remain Vietnam's official name until the onset of the 19th century.
Lạc Sơn is a rural district of Hòa Bình province in the Northwest region of Vietnam. As of 2019, the district had a population of 136,652. The district covers an area of 580 km2. The district capital lies at Vụ Bản.

Paris By Night 91: Huế, Sài Gòn, Hà Nội is a Paris By Night program produced by Thúy Nga that was filmed at the Terrace Theater at the Long Beach Convention and Entertainment Center on January 12, 2008 and January 13, 2008.
2nd Corps or Hương Giang Corps was a regular army corps of the Vietnam People's Army. First organised in 1974 during the Vietnam War, 2nd Corps had a major role in the Ho Chi Minh Campaign that ended the war. Before disbanded on 21 November 2023, the corps was stationed in Lạng Giang District, Bắc Giang.
The 4th Military Region of Vietnam People's Army, is directly under the Ministry of Defence of Vietnam, tasked to organise, build, manage and command armed forces defending the North Central Vietnam. The predecessor, 4th War Zone was established by the order of Ho Chi Minh on 15 October 1945, and this day has become the traditional day of the Military Zone. On 3 June 1957, Ho Chi Minh signed the ordinance 17/SL to establish 4th Military Zones on the basis of 4th Joint Zone, simultaneously with other military zones: the North Vietnamese, North West, North East, Left Bank, Right Bank.

Paris By Night 99 – Tôi Là Người Việt Nam is a Paris By Night program produced by Thúy Nga Productions that was filmed at Knott's Berry Farm on 16 and 17 January 2010 and released DVD from 9 April 2010. The show was hosted by Nguyễn Ngọc Ngạn, Nguyễn Cao Kỳ Duyên and Trịnh Hội.
The 8th Politburo of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV), formally the 8th Political Bureau of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (Vietnamese: Bộ Chính trị Ban Chấp hành trung ương Đảng Cộng sản Việt Nam Khoá VIII), was elected at the 1st Plenary Session of the 8th Central Committee in the immediate aftermath of the 8th National Congress.

The 12th Politburo, formally the Political Bureau of the 12th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam, was elected at the 1st Plenary Session of the 12th Central Committee (CC) on 27 January 2016 during the 12th National Congress to serve for a five-year electoral term. Based on the principle that "the Party leads and the State manages", the Politburo is the highest decision-making institution in the CPV and Vietnam when the Party's National Congress and the Central Committee are adjourned. According to Party rules, the Politburo directs the general orientation of the government; it convenes meetings several times a month to discuss and decide policy, which is then implemented by the relevant state or party bodies, such as the National Assembly of Vietnam if the policy concerns law-making, or the Party's Central Organisation Commission if it concerns cadre policy. The total number of meetings the 12th Politburo convened has not been publicly disclosed to the media. Some have been publicly reported, however, and are listed below.

The 10th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam was elected at the 10th National Congress of the Communist Party of Vietnam. The 10th Central Committee elected the 10th Politburo and the 10th Secretariat.
Story of Nhô village is a 1997 Vietnamese telefilm adapted from Nguyễn Quang Thiều's 1994 novel The assassin of the fields. The film was produced by Vietnam Television Film Center and directed by Đặng Lưu Việt Bảo.

The abdication of Bảo Đại took place on 25 August 1945 and marked the end of the 143-year reign of the Nguyễn dynasty over Vietnam ending the Vietnamese monarchy. Emperor Bảo Đại abdicated in response to the August Revolution. A ceremony was held handing power over to the newly established Democratic Republic of Vietnam, which was established during the end of World War II in Asia as Vietnam had been occupied by French and later Japanese imperialists.

The government of the Nguyễn dynasty, officially the Southern dynasty and commonly referred to as the Huế Court, centred around the emperor as the absolute monarch, surrounded by various imperial agencies and ministries which stayed under the emperor's presidency. Following the signing of the Patenôtre Treaty the French took over a lot of control and while the government of the Nguyễn dynasty still nominally ruled the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin, in reality the French maintained control over these territories and the Nguyễn government became subsidiary to the administration of French Indochina. During World War II the Japanese launched a coup d'état outsting the French and establishing the Empire of Vietnam which was ruled by the Nguyễn government. During the August Revolution the Nguyễn government was abolished in the aftermath of World War II.

Conscription in Vietnam has existed since 1975 and requires male citizens between the ages of 18 and 25 to perform compulsory military service. Women are not required to perform military service, but they may voluntarily join the military.

During the Nguyễn dynasty period (1802–1945) of Vietnamese history its Ministry of Education was reformed a number of times, in its first iteration it was called the Học Bộ, which was established during the reign of the Duy Tân Emperor (1907–1916) and took over a number of functions of the Lễ Bộ, one of the Lục Bộ. The Governor-General of French Indochina wished to introduce more education reforms, the Nguyễn court in Huế sent Cao Xuân Dục and Huỳnh Côn, the Thượng thư of the Hộ Bộ, to French Cochinchina to discuss these reforms with the French authorities. After their return the Học Bộ was established in the year Duy Tân 1 (1907) with Cao Xuân Dục being appointed to be its first Thượng thư (minister). Despite nominally being a Nguyễn dynasty institution, actual control over the ministry fell in the hands of the French Council for the Improvement of Indigenous Education in Annam.

The 8th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) was elected at the 8th CPV National Congress. It elected the 8th Politburo and the 8th Secretariat.

The 7th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) was elected at the 7th CPV National Congress. It elected the 7th Politburo and the 7th Secretariat.

The 6th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) was elected at the 6th CPV National Congress. It elected the 6th Politburo and the 6th Secretariat.

The 5th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) was elected at the 5th CPV National Congress. It elected the 5th Politburo and the 5th Secretariat.
References
- ↑ John R. Jones Guide to Vietnam 1994 - Page 29 "Confucianism. Confucianism entered Vietnam from China during the Bac Thuoc era (111 BC - AD 938) when the country was under the yoke.."
- ↑ Napier, Nancy K.; Vuong, Quan Hoang. What we see, why we worry, why we hope: Vietnam going forward. Boise, ID: Boise State University CCI Press, October 2013. ISBN 978-0985530587.
- ↑ Teaching and research in philosophy: Asia and the Pacific Unesco - 1986 Page 363 "On matters relating to national traditions in philosophy, the Vietnamese philosophers will continue to study the history of national philosophy, to write books on the history of Vietnamese philosophy, to do research on the typical characteristics ..."
- ↑ Pierre Brocheux, Ho Chi Minh: A Biography 2007 - Pages 204,205 “Ho was also steeped in the perennial Sino-Vietnamese philosophy that blended Confucianism (in its plural form incorporating Confucius, Mencius, Xunzi, and Wang Yang Ming)7 with Buddhism and Taoism."
- ↑ Vuong, Quan-Hoang (2018). "Cultural additivity: behavioural insights from the interaction of Confucianism, Buddhism and Taoism in folktales". Palgrave Communications. 4 (1): 143. doi: 10.1057/s41599-018-0189-2 . S2CID 54444540.
- ↑ Vu Dinh Trac, "Triet ly truyen thong Viet Nam don duong cho Than Hoc Viet Nam," Dinh Huong 11 (1966)
- ↑ Peter C. Phan Vietnamese-American Catholics 2005 Page 27 "Vu Dinh Trac believes that traditional Vietnamese philosophy is constituted by tam tai philosophy, yin-yang metaphysics, and agricultural philosophy. These three strands are illustrated by the various symbols on the upper surface of the Dong ..."
- ↑ "Tu Viet triet toi Viet than," Dinh Huong 11 (1996)
- ↑ Fumitaka Matsuoka, Eleazar S. Fernandez, Realizing the America of Our Hearts: Theological Voices of Asian Americans, St. Louis, Mo: Chalice Press 2003, ISBN 0827232519, page 178: "Another important contributor to the retrieval and elaboration of Vietnamese philosophy is Tran Van Doan, professor of ... For Tran Van Doan, Vietnamese philosophy is humanistic (vi nhan) but not anthropocentric (day nhan) in so far as ...
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.