107th United States Congress
Last updated| 107th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
106th ← → 108th | |
 United States Capitol (2002) | |
January 3, 2001 – January 3, 2003 | |
| Members | 100 senators 435 representatives 5 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Democratic (until January 20, 2001) Republican (Jan 20, 2001 – Jun 6, 2001) Democratic (from June 6, 2001) |
| Senate President | Al Gore (D) [lower-alpha 1] (until January 20, 2001) Dick Cheney (R) (from January 20, 2001) |
| House majority | Republican |
| House Speaker | Dennis Hastert (R) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 3, 2001 – December 20, 2001 2nd: January 23, 2002 – November 22, 2002 | |




The 107th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 2001, to January 3, 2003, during the final weeks of the Clinton presidency and the first two years of the George W. Bush presidency. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the 1990 United States census.
Contents
- Major events
- Major legislation
- Party summary
- Senate
- House of Representatives
- Leadership
- Senate 2
- House of Representatives 2
- Members
- Senate 3
- House of Representatives 3
- Changes in membership
- Senate 4
- House of Representatives 4
- Committees
- Senate 5
- House of Representatives 5
- Joint committees
- Caucuses
- Employees
- Legislative branch agency directors
- Senate 6
- House of Representatives 6
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
The House of Representatives had a Republican majority throughout the session, while the Senate was tied 50–50 for only the third time in history resulting in numerous changes in the majority. Vice President Al Gore gave Democrats a majority for 17 days, then a Republican majority after Dick Cheney became Vice President on January 20, 2001. Senator Jim Jeffords (R-VT) became an independent who caucused with the Democrats on June 6, 2001, giving the party a 51–49 majority for the rest of the Congress.
When Bush was sworn in as president on January 20, the Republicans held a federal trifecta for the first time since the 83rd Congress in 1955.
Major events
A rare even split in the United States Senate, the defection of a Senator, and the inauguration of a new Vice President, led to three changes in majorities.
- January 3, 2001: The 107th Congress officially begins, with the Senate split 50–50. Democrat Al Gore — the outgoing Vice President — briefly gives the Democrats a majority.
- January 3, 2001: First Lady Hillary Clinton, wife of outgoing President Bill Clinton, became the first, and, to date, only presidential spouse to hold political office (briefly serving as both First Lady and Senator).
- January 20, 2001: George W. Bush was sworn in as the 43rd President of the United States; simultaneously, Dick Cheney was sworn in as the 46th Vice President, giving Republicans a Senate majority.
- February 27, 2001: President Bush addressed a joint session of Congress.
- May 24, 2001: Senator Jim Jeffords left the Republican Party, becoming an independent who caucused with the Democrats, giving them a majority from June 6. [1]
- September 11, 2001: The September 11 attacks occurred.
- September 20, 2001: President Bush addressed a joint session of Congress, announcing the investigation into the September 11 attacks.
- October 7, 2001: Operation Enduring Freedom began with airstrikes against the Taliban.
- October 9, 2001: Anthrax spores were mailed to, among others, two Senators, Majority Leader Tom Daschle (D-SD) and Patrick Leahy (D-VT).
- December 2001: Accounting scandals arise from the financial practices of Enron and WorldCom.
- June 12, 2002: John Howard, the Prime Minister of Australia, addressed a joint session of Congress. The address was originally scheduled for September 12, 2001, but was postponed after the September 11 attacks.
- October 25, 2002: Senator Paul Wellstone (D-MN), dies in a plane crash, and non-caucusing Independence Party member Dean Barkley is appointed to hold the seat until a special election was held.
- November 23, 2002: Jim Talent wins the United States Senate special election for a Missouri seat, giving Republicans the majority once again (though formal reorganization was delayed until the 108th United States Congress convened).
Major legislation
- June 7, 2001: Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act, Pub. L. 107–16 (text) (PDF), 115 Stat. 38
- September 18, 2001: Authorization for Use of Military Force of 2001, Pub.L. 107-40
- September 22, 2001: Air Transportation Safety and System Stabilization Act, Pub.L. 107-42
- September 28, 2001: United States-Jordan Free Trade Area Implementation Act, Pub.L. 107-43
- October 26, 2001: "USA PATRIOT" Act, Pub. L. 107–56 (text) (PDF), 115 Stat. 272
- October 27, 2001: International Money Laundering Abatement and Financial Anti-Terrorism Act of 2001, Pub.L. 107-57
- November 19, 2001: Aviation and Transportation Security Act, Pub.L. 107-71
- December 18, 2001: MD-Care Act, Pub.L. 107-84
- December 21, 2001: Zimbabwe Democracy and Economic Recovery Act of 2001, Pub.L. 107-99
- January 8, 2002: No Child Left Behind Act, Pub. L. 107–110 (text) (PDF), 115 Stat. 1425
- January 8, 2002: District of Columbia Police Coordination Amendment Act of 2001, Pub.L. 107-113
- January 11, 2002: Small Business Liability Relief and Brownfields Revitalization Act, Pub. L. 107–118 (text) (PDF), 115 Stat. 2356
- March 9, 2002: Job Creation and Worker Assistance Act, Pub. L. 107–147 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 21
- March 27, 2002: Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act (McCain-Feingold), Pub. L. 107–155 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 81
- May 13, 2002: Farm Security and Rural Investment Act of 2002, Pub. L. 107–171 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 134
- May 14, 2002: Hematological Cancer Research Investment and Education Act, Pub.L. 107-172
- May 14, 2002: Enhanced Border Security and Visa Entry Reform Act of 2002, Pub.L. 107-173
- May 15, 2002: Notification and Federal Employee Antidiscrimination and Retaliation (No-FEAR) Act of 2002, Pub.L. 107-174
- July 30, 2002: Sarbanes–Oxley Act, Pub. L. 107–204 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 745
- August 5, 2002: Born-Alive Infants Protection Act of 2002, Pub.L. 107-207
- August 6, 2002: Trade Act of 2002, Pub. L. 107–210 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 933
- October 1, 2002: National Construction Safety Team Act, Pub.L. 107-231
- October 16, 2002: Authorization for Use of Military Force Against Iraq, Pub. L. 107–243 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 1497
- October 21, 2002: Sudan Peace Act, Pub. L. 107–245 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 1504
- October 29, 2002: Help America Vote Act, Pub. L. 107–252 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 1666
- November 6, 2002: Rare Diseases Act of 2002, Pub.L. 107-280
- November 25, 2002: Maritime Transportation Security Act of 2002, Pub.L. 107-295
- November 25, 2002: Homeland Security Act, Pub. L. 107–296 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 2135
- November 26, 2002: Terrorism Risk Insurance Act of 2002, Pub.L. 107-297
- December 17, 2002: E-Government Act of 2002, Pub. L. 107–347 (text) (PDF), 116 Stat. 2899
Party summary
Senate
| Party (Shading indicates party control) | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (D) | Independent (I) | Independence (IPM) | Republican (R) | Vacant | |||
| caucused with Democrats | |||||||
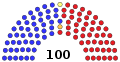
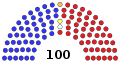
| End of previous Congress | 46 | 0 | 0 | 54 | 100 | 0 | |
| Begin [lower-alpha 2] | 50 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 100 | 0 | |
| January 20, 2001 [lower-alpha 3] | 50 | 50 | |||||
| June 6, 2001 [lower-alpha 4] | 50 | 1 | 49 | ||||
| October 25, 2002 [lower-alpha 5] | 49 | 99 | 1 | ||||
| November 4, 2002 [lower-alpha 5] | 1 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| November 23, 2002 [lower-alpha 6] | 48 | 1 | 50 | ||||
| November 30, 2002 [lower-alpha 7] | 49 | 99 | 1 | ||||
| December 2, 2002 [lower-alpha 7] | 50 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| Final voting share | 49% | 1% | 50% | ||||
| Beginning of the next Congress | 48 | 1 | 0 | 51 | 100 | 0 | |
House of Representatives
| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Independent | Republican | Vacant | |||
| caucused with Democrats | caucused with Republicans | |||||
| End of previous Congress | 208 | 1 | 1 | 222 | 432 | 3 |
| Begin | 211 | 1 | 1 | 221 | 434 | 1 |
| January 31, 2001 | 220 | 433 | 2 | |||
| March 30, 2001 | 210 | 432 | 3 | |||
| May 15, 2001 | 221 | 433 | 2 | |||
| May 28, 2001 | 209 | 432 | 3 | |||
| June 5, 2001 | 210 | 433 | 2 | |||
| June 19, 2001 | 222 | 434 | 1 | |||
| August 5, 2001 | 221 | 433 | 2 | |||
| August 16, 2001 | 220 | 432 | 3 | |||
| September 6, 2001 | 219 | 431 | 4 | |||
| October 16, 2001 | 211 | 220 | 433 | 2 | ||
| November 20, 2001 | 221 | 434 | 1 | |||
| December 18, 2001 | 222 | 435 | 0 | |||
| July 24, 2002 | 210 | 434 | 1 | |||
| August 1, 2002 | 0 | 223 | ||||
| September 9, 2002 | 209 | 433 | 2 | |||
| September 28, 2002 | 208 | 432 | 3 | |||
| November 30, 2002 | 209 | 433 | 2 | |||
| Final voting share | 48.5% | 51.5% | ||||
| Beginning of the next Congress | 205 | 1 | 0 | 229 | 435 | 0 |
Leadership
Senate
(until January 20, 2001)
(from January 20, 2001)
(January 20 – June 6, 2001)
- President: Al Gore (D), until January 20, 2001
- Dick Cheney (R), from January 20, 2001
- President pro tempore: Robert Byrd (D), until January 20, 2001
- Strom Thurmond (R), January 20 – June 6, 2001
- Robert Byrd (D), from June 6, 2001
Republican leadership
- Minority Leader: Trent Lott (R), until January 20, 2001, and from June 6, 2001
- Majority leader January 20 – June 6, 2001
- Minority Whip: Don Nickles (R), until January 20, 2001, and from June 6, 2001
- Majority whip January 20 – June 6, 2001
- Republican Conference Chairman: Rick Santorum
- Republican Conference Secretary: Kay Bailey Hutchison
- Republican Campaign Committee Chair: Bill Frist
- Republican Policy Committee Chairman: Larry Craig
Democratic leadership
- Majority Leader: Tom Daschle (D), until January 20, 2001, and from June 6, 2001
- Minority leader January 20 – June 6, 2001
- Majority Whip: Harry Reid (D), until January 20, 2001, and from June 6, 2001
- Minority whip January 20 – June 6, 2001
- Democratic Policy Committee Chairman: Byron Dorgan
- Democratic Conference Secretary: Barbara Mikulski
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Patty Murray
- Democratic Chief Deputy Whip: John Breaux
House of Representatives
- Speaker: Dennis Hastert (R)
Majority (Republican) leadership
- Majority Leader: Dick Armey
- Majority Whip: Tom DeLay
- Chief Deputy Whip: Roy Blunt
- Republican Conference Chairman: J. C. Watts
- Republican Conference Vice-Chairman: Deborah Pryce
- Republican Conference Secretary: Barbara Cubin
- Policy Committee Chairman: Christopher Cox
- Republican Campaign Committee Chairman: Thomas M. Davis
- House Rules Committee Chairman: David Dreier
Minority (Democratic) leadership
- Minority Leader: Dick Gephardt
- Minority Whip: David E. Bonior, until January 15, 2002
- Nancy Pelosi, from January 15, 2002
- Chief Deputy Minority Whips: John Lewis, Ed Pastor, Max Sandlin & Maxine Waters
- Democratic Caucus Chairman: Martin Frost
- Democratic Caucus Vice Chairman: Bob Menendez
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Nita Lowey
Members
Senate
Senators are listed by their class. In this Congress, Class 2 meant their term ended with this Congress, facing re-election in 2002; Class 3 meant their term began in the previous Congress, facing re-election in 2004; and Class 1 meant their term began in this Congress, facing re-election in 2006.
House of Representatives
Congressional district numbers are linked to articles describing the district itself.
Changes in membership
Senate
| State (class) | Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation [lower-alpha 9] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vermont (1) | Jim Jeffords (R) | Incumbent changed party and joined the Democratic caucus. | Jim Jeffords (I) | June 6, 2001 |
| Minnesota (2) | Paul Wellstone (D) | Incumbent died October 25, 2002. Successor appointed to serve the remaining two months of the term. | Dean Barkley (IMN) | November 4, 2002 |
| Missouri (1) | Jean Carnahan (D) | Interim appointee lost election. Successor elected November 5, 2002. | Jim Talent (R) | November 23, 2002 |
| Texas (2) | Phil Gramm (R) | Incumbent resigned November 30, 2002, to give successor seniority advantages. Successor appointed on December 2, 2002, having already been elected to the next term. [3] [4] | John Cornyn (R) | December 2, 2002 |
| Alaska (3) | Frank Murkowski (R) | Incumbent resigned December 2, 2002, to become Governor of Alaska. Successor appointed to remainder of the term ending January 3, 2005. | Lisa Murkowski (R) | December 20, 2002 |
House of Representatives
| District | Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation [lower-alpha 9] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California 32nd | Vacant | Incumbent Julian Dixon (D) had died December 8, 2000, before the beginning of this Congress. A special election was held June 5, 2001. | Diane Watson (D) | June 5, 2001 |
| Pennsylvania 9th | Bud Shuster (R) | Incumbent resigned, effective January 31, 2001. A special election was held May 15, 2001. | Bill Shuster (R) | May 15, 2001 |
| Virginia 4th | Norman Sisisky (D) | Incumbent died March 30, 2001. A special election was held June 19, 2001. | Randy Forbes (R) | June 19, 2001 |
| Massachusetts 9th | Joe Moakley (D) | Incumbent died May 28, 2001. A special election was held October 16, 2001. | Stephen Lynch (D) | October 16, 2001 |
| Arkansas 3rd | Asa Hutchinson (R) | Incumbent resigned August 5, 2001, to head the Drug Enforcement Administration. A special election was held November 20, 2001. | John Boozman (R) | November 20, 2001 |
| South Carolina 2nd | Floyd Spence (R) | Incumbent died August 16, 2001. A special election was held December 18, 2001. | Joe Wilson (R) | December 18, 2001 |
| Florida 1st | Joe Scarborough (R) | Incumbent resigned, effective September 6, 2001. A special election was held October 16, 2001. | Jeff Miller (R) | October 16, 2001 |
| Oklahoma 1st | Steve Largent (R) | Incumbent resigned, effective February 15, 2002, to concentrate on his campaign for governor. A special election was held January 8, 2002. | John Sullivan (R) | February 15, 2002 |
| Ohio 17th | Jim Traficant (D) | Incumbent expelled July 24, 2002, for criminal conviction of 10 counts of bribery, racketeering, and tax evasion. | Vacant | Not filled for remainder of Congress |
| Virginia 5th | Virgil Goode (I) | Incumbent changed party. | Virgil Goode (R) | August 1, 2002 |
| Ohio 3rd | Tony P. Hall (D) | Incumbent resigned September 9, 2002, after he was appointed to be the U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization. | Vacant | Not filled for remainder of Congress |
| Hawaii 2nd | Patsy Mink (D) | Incumbent died September 28, 2002, but was elected posthumously on November 5, 2002. | Ed Case (D) | November 30, 2002 |
Committees
Lists of committees and their party leaders for members of the House and Senate committees can be found through the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of this article. The directory after the pages of terms of service lists committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and, after that, House/Senate committee assignments. On the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
Joint committees
- Economic (Chair: Rep. Jim Saxton, Vice Chair: Sen. Jack Reed)
- Taxation (Chair: Rep. Bill Thomas, Vice Chair: Sen. Max Baucus)
- The Library (Chair: Rep. Vernon J. Ehlers, Vice Chair: Sen. Chris Dodd)
- Printing (Chair: Sen. Mark Dayton, Vice Chair: Rep. Robert W. Ney)
Caucuses
Employees
Legislative branch agency directors
- Architect of the Capitol: Alan M. Hantman
- Attending Physician of the United States Congress: John F. Eisold
- Comptroller General of the United States: David M. Walker
- Director of the Congressional Budget Office: Dan Crippen
- Librarian of Congress: James H. Billington
- Public Printer of the United States: Michael F. DiMario, until 2002
- Bruce James, from 2002
Senate
- Chaplain: Lloyd John Ogilvie (Presbyterian)
- Curator: Diane K. Skvarla
- Historian: Richard A. Baker
- Parliamentarian: Bob Dove, until May 2001
- Alan Frumin, May 2001 - end
- Secretary: Gary Lee Sisco, until July 11, 2001
- Jeri Thomson, July 12, 2001 - end
- Librarian: Greg Harness
- Sergeant at Arms: James W. Ziglar, until August 2, 2001
- Alfonso E. Lenhardt, September 4, 2001 - end
- Secretary for the Majority / Minority:
- Martin P. Paone (Democrats)
- Elizabeth B. Letchworth (Republicans)
- David J. Schiappa (Republicans)
House of Representatives
See also
- List of new members of the 107th Congress
- 2000 United States elections (elections leading to this Congress)
- 2002 United States elections (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
Notes
- ↑ U.S. Vice President Al Gore's term as President of the Senate ended at noon on January 20, 2001, when Dick Cheney's term began.
- ↑ Al Gore (D) was U.S. Vice President until January 20, 2001, with the tie-breaking vote.
- ↑ Dick Cheney (R) became U.S. Vice President January 20, 2001, with the tie-breaking vote.
- ↑ In Vermont, Senator Jim Jeffords switched June 6, 2001, from Republican to Independent and caucused with Democrats.
- 1 2 In Minnesota, Paul Wellstone (D) died October 25, 2002. Dean Barkley (IMN), who did not caucus with either party, was appointed November 4, 2002, to Wellstone's seat.
- ↑ In the November 5, 2002 Missouri special election, Jim Talent (R) took Jean Carnahan (D)'s seat and became senator November 23, 2002, but there was no reorganization because Senate was out of session. [2]
- 1 2 In Texas, Phil Gramm (R) resigned November 30, 2002, to give his successor advantageous office space. Senator-elect John Cornyn (R) was appointed December 2, 2002, to finish Gramm's term.
- ↑ In Missouri, Senator-elect Mel Carnahan (D) died October 16, 2000, but had won the 2000 Senate election posthumously.
- 1 2 When seated or oath administered, not necessarily when service began.
Related Research Articles

The 82nd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1951, to January 3, 1953, during the last two years of President Harry S. Truman's second term in office.

The 108th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives from January 3, 2003, to January 3, 2005, during the third and fourth years of George W. Bush's presidency.

The 101st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1989, to January 3, 1991, during the final weeks of Ronald Reagan's presidency and the first two years of George H. W. Bush's presidency.

The 95th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1977, to January 3, 1979, during the final weeks of Gerald Ford's presidency and the first two years of Jimmy Carter's presidency.

The 92nd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1971, to January 3, 1973, during the third and fourth years of Richard Nixon's presidency.

The 91st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1969, to January 3, 1971, during the final weeks of the presidency of Lyndon Johnson and the first two years of the first presidency of Richard Nixon.

The 85th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1957, to January 3, 1959, during the fifth and sixth years of Dwight Eisenhower's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1950 United States census.

The 84th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1955, to January 3, 1957, during the third and fourth years of Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1950 United States census.

The 83rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the federal government of the United States in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1953, until January 3, 1955, during the last two weeks of the Truman administration, with the remainder spanning the first two years of Dwight Eisenhower's presidency. It was composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The apportionment of seats in the House was based on the 1950 U.S. census.

The 90th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1967, to January 3, 1969, during the last two years of President Lyndon B. Johnson's second term in office.

The 81st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1949, to January 3, 1951, during the fifth and sixth years of Harry S. Truman's presidency.

The 80th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1947, to January 3, 1949, during the third and fourth years of Harry S. Truman's presidency. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the 1940 United States census.

The 74th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1935, to January 3, 1937, during the third and fourth years of Franklin D. Roosevelt's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1930 United States census.

The 87th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1961, to January 3, 1963, during the final weeks of Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidency and the first two years of John Kennedy's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1950 United States census, along with two seats temporarily added in 1959.

The 89th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1965, to January 3, 1967, during the second and third years of Lyndon B. Johnson's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1960 United States census.

The 77th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1941, to December 16, 1942, during the ninth and tenth years of Franklin D. Roosevelt's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1930 United States census.

The 79th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1945, to January 3, 1947, during the last months of Franklin D. Roosevelt's presidency, and the first two years of Harry Truman's presidency. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the 1940 United States census.

The 112th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, from January 3, 2011, until January 3, 2013. It convened in Washington, D.C., on January 3, 2011, and ended on January 3, 2013, 17 days before the end of the presidential term to which Barack Obama was elected in 2008. Senators elected to regular terms in 2006 completed those terms in this Congress. This Congress included the last House of Representatives elected from congressional districts that were apportioned based on the 2000 census.

The 113th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, from January 3, 2013, to January 3, 2015, during the fifth and sixth years of Barack Obama's presidency. It was composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives based on the results of the 2012 Senate elections and the 2012 House elections. The seats in the House were apportioned based on the 2010 United States census. It first met in Washington, D.C., on January 3, 2013, and it ended on January 3, 2015. Senators elected to regular terms in 2008 were in the last two years of those terms during this Congress.

The 114th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States of America federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 2015, to January 3, 2017, during the final two years of Barack Obama's presidency. The seats in the House were apportioned based on the 2010 United States census.
References
- ↑ "Leaving Republican Party: Jeffords' 2001 speech". Burlington Free Press. August 18, 2014. Retrieved January 10, 2019.
- ↑ "Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present" – via Senate.gov.
- ↑ Associated Press (November 21, 2002). "Cornyn Gets Early Start in Senate". The Edwardsville Intelligencer. Retrieved November 3, 2020.
- ↑ "SENATORS OF THE UNITED STATES > 1789-present > A chronological list of senators since the First Congress in 1789" (PDF). United States Senate – via Senate.gov.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Biographical Directory of the United States Congress
This article incorporates public domain material from the Biographical Directory of the United States Congress
External links
- United States 107th Congress Web Archive from the U.S. Library of Congress
- Congress.gov
- History, Art and Archives from the United States House of Representatives
- Statistics & Lists from the United States Senate
- Booknotes interview with Tom Daschle on Like No Other Time: The 107th Congress and the Two Years That Changed America, November 30, 2003.
- "Videos of House of Representatives Sessions for the 107th Congress from www.C-SPAN.org".
- "Videos of Senate Sessions for the 107th Congress from www.C-SPAN.org".
- "Videos of Committees from the House and Senate for the 107th Congress from www.C-SPAN.org".
- House of Representatives Session Calendar for the 107th Congress (PDF).
- Senate Session Calendar for the 107th Congress (PDF).
- Congressional Pictorial Directory for the 107th Congress. S. PRT. 1967.
- Congressional Pictorial Directory for the 107th Congress (Revised). S. PRT. 1967.
- "Official Congressional Directory for the 107th Congress". Congressional Directory. 1991/1992- : S. Pub. 1887.
- Official Congressional Directory for the 107th Congress (Revised) (PDF).
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.