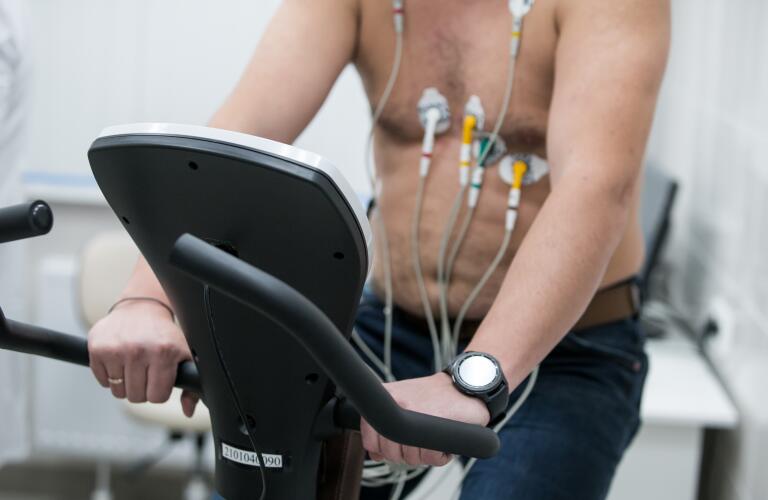
There are several types of cardiac stress tests. They all use one of two types of stress to increase your heart’s workload. Exercise stress tests use physical activity to accomplish this. Chemical or pharmacological stress tests use drugs to stimulate the heart to work harder.
Doctors use stress tests to assess heart health and diagnose heart conditions. The most common reason for recommending a stress test is suspected coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD causes blockages in the arteries supplying blood to the heart tissue. Stress tests can detect these blockages. Other diagnostic reasons for a stress test include potential heart arrhythmias and heart valve problems. Stress tests can also help evaluate treatment effectiveness and determine the amount and type of exercise that is safe.
When doctors recommend a stress test, they have a choice of testing techniques. Here’s a look at the different types of cardiac stress test procedures and why doctors may choose one over the other.
Stress ECG (Electrocardiogram) Testing
The most basic type of stress test is a stress ECG. It’s also the most common type. An ECG, or EKG, measures your heart’s electrical activity. To take the ECG, medical staff will connect painless electrodes to your chest and body. They will also monitor your blood pressure and breathing during the test.
After taking a resting ECG, you will begin exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike. Staff will look for changes in your blood pressure or ECG as your heart works harder. They will also want to know if you start having any symptoms, such as chest pain or trouble breathing.
Doctors may recommend a stress ECG for the following reasons:
- Assessing heart damage after a heart attack
- Diagnosing CAD, arrhythmias, or valve disease
- Determining the kind and amount of exercise that is safe for you, especially when starting cardiac rehabilitation
- Evaluating how well treatment for a heart condition is working
- Planning the type and timing of heart surgery or assessing the outcome
Stress Echo Testing
Stress echo—or echocardiogram—testing uses ultrasound heart imaging. Medical staff take an ultrasound image of the heart at rest. They take another image after the stress of either exercise or after administering a drug that stimulates the heart. Ultrasound is a fast and relatively inexpensive form of imaging. It’s often possible to get heart stress test results quickly after a stress echo.
A stress echo can show your doctor structures inside the heart, such as the valves. It will also show areas of the heart muscle with poor blood flow or even dead tissue. Your doctor will be able to physically observe the heart contracting and working. Comparing this motion before and after stress can more accurately show blockages and other problems.
Doctors may recommend a stress echo in the following circumstances:
- You are unable to exercise.
- You had an abnormal stress ECG.
- You have baseline ECG abnormalities.
- You have a pacemaker, bundle branch block, or enlarged heart.
- You take certain medicines, such as digoxin.
Nuclear Stress Testing
Nuclear stress testing also uses heart imaging. Like stress echo testing, medical staff will take an image of your heart at rest and again after stress. But instead of ultrasound, it uses an IV (intravenous) radioactive tracer solution. The tracer releases gamma rays that a special camera can detect.
Heart muscle cells take up the tracer from the blood. Heart cells with poor blood flow will not be able to absorb as much of the tracer as healthy cells. And dead tissue, such as scar tissue from a heart attack, will not take it up at all. These differences give your doctor a very clear image of blood flow to your heart tissue. Another name for this test is MPI (myocardial perfusion imaging). Because it is a more complex test than ultrasound, results can take longer.
There are advantages of MPI over both stress echo and stress ECG testing. Doctors may recommend MPI when these advantages are appropriate for your situation. Advantages include:
- It is the most accurate type of stress test for finding CAD. A stress ECG gives a falsely abnormal result in about 15% of cases. In contrast, an abnormal MPI is very highly indicative of CAD.
- It can find modest changes in blood flow. A stress ECG detects severe blockages of 70% or more. It is possible to have a normal stress ECG and have a heart attack due to smaller blockages. In contrast, there is less than a 1% chance of having a heart attack in the next five years after a normal MPI.
- It is easier to interpret the images in people with baseline heart problems.
- It is rare for images to be inadequate for interpretation.
In some cases, a stress echo may still be the right test for you. A stress echo does not use radiation. So, it is safe for people who need to avoid radiation exposure. It is also faster and less expensive than MPI. Stress echo results may be available more quickly than MPI as well.
Cardiac Stress Test Preparation
Your doctor will give you specific instructions to prepare for a cardiac stress test. This may involve not eating for a few hours before the test. You will also need to avoid caffeine and nicotine for several hours beforehand. They can affect the heart and cause problems with the test. Come to the test wearing comfortable clothes and shoes. If you take medications or supplements, ask your doctor whether to take them or not the day of your test.
Cardiac Stress Test Results
Regardless of the type of stress test, there are two main types of results. The first is abnormal, meaning the test was positive for changes during stress. The other is normal or negative, meaning the test showed normal responses during stress. It is possible for the test to come back as equivocal or inconclusive. This can mean the test showed changes, but they aren’t diagnostic. It’s also possible for the test to be uninterpretable. This usually means the test was incomplete for some reason. Your doctor will review the results with you and help you understand your options going forward.