What Is the Scientific Method? 7 Steps To Test Conclusions
Updated July 31, 2023
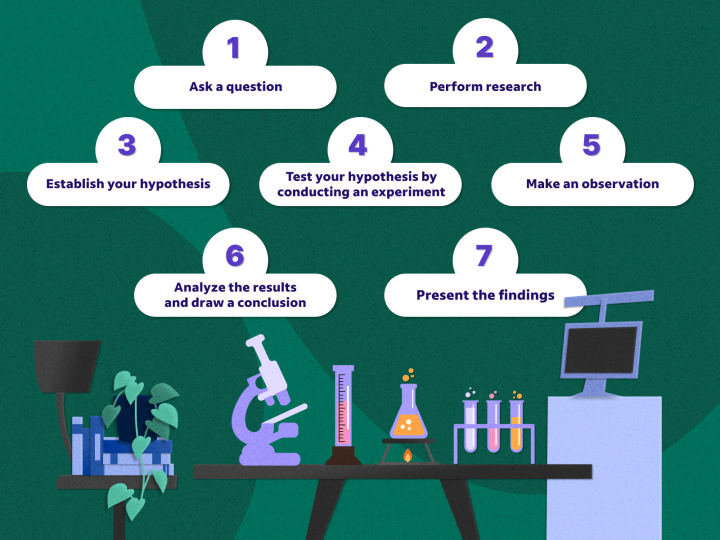
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a process used when conducting experiments and exploring observations. Some areas of science rely more heavily on this method to answer questions, as they are more easily tested than other areas. This method aims to discover the relationships between cause and effect in various situations and applications.When following the scientific method, scientists must ask questions, gather and look at the evidence and determine whether the answers to their questions can be found through that evidence. Scientists also use the method to determine whether all information presented and found can combine to create a logical answer. The scientific method provides a way to apply logical and rational problem-solving methods to scientific questions.Related: What Is a Scientist? Definition and Types of Scientists
Get recommendations for your resume in minutes
The 7 steps of the scientific method
Based on the type of question being asked, the type of science being applied and the laws that apply to that particular branch of science, you may need to modify the method and alter or remove one or several of the steps. Here are the seven steps of the scientific method illustrated by an example scientific hypothesis:1. Ask a question
The first step in the scientific method is asking a question you want to answer. This question will include one of the key starters: how, what, when, why, where, who or which. The question you ask should also be measurable and answerable through experimentation. It is often something that can be measured with a numerical result, although behavioral results are also part of the scientific method.Example: Perhaps, you want to test an experiment about the causal relationship between music and certain domesticated animals. A good question to begin with might be: ”Does music impact the behavior of certain species of domestic animals, such as canines and felines?”2. Perform research
With your question formulated, conduct preliminary background research to prepare yourself for the experiment. You can find information through online searches or in your local library, depending on the question you are asking and the nature of the background data. You may also find previous studies and experiments that can help with your process and conclusions.In this case, you might start by reviewing previous scientific studies for animal experiments related to their reactions to music. Key to finding pertinent information might be looking at studies about animal behavior concerning art or domestic animals directly affected by music.Related: How To Become a Research Scientist3. Establish your hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess that seeks to answer a question that can be systematically tested. Your hypothesis should also include predictions that you can measure through experimentation and research.Example: Based on your research, you start to fine-tune your thoughts about what will probably happen: “If I play classical music, my dog and cat will remain in the room with me. If I play rock-and-roll music, my dog and cat will leave the room.”4. Test your hypothesis by conducting an experiment
Next, test your hypothesis by experimenting. Your experiment is a way to quantifiably test your predictions and should be able to be repeated by another scientist.Example: You decide to test it out: You bring the cat and dog into the same room where a sound system is available. You play classical music at a low volume. Both animals remain in the room. Then, you change scientist the music to rock-and-roll at the same volume. Both animals stay in the room.5. Make an observation
Assess your scientific process and ensure the conditions remain the same throughout all testing measures. If you change any factors in your experiment, keep all others the same to maintain fairness. After completing the experiment, repeat it a few more times to ensure the results are accurate.Example: In reviewing the cause and effect of your experiment, you observe that despite what you had thought would happen, it did not. More specifically, the type of music being played did not impact the reaction of the animals.Therefore, you adjust your hypothesis to state that the animals will react based on the volume of the music. You conduct another experiment, playing classical music at a low volume and then at a high volume. The animals remain in the room when the music is quiet and leave the room when the music is loud.6. Analyze the results and draw a conclusion
You can now take your experiment findings and analyze them to determine if they support your hypothesis.Drawing a conclusion means determining whether what you believed would happen did happen. If it did not happen, you can create a new hypothesis, return to step four, and conduct a new experiment to prove your new theory. If what you hypothesized happened during the experimentation phase, the final step is putting together your findings and presenting them to others.Example: You determine the behavior of animals is more affected by the volume of music being played rather than the type of music played.7. Present the findings
The method for presenting your findings depends on your scientific position and level. If you are entering a project into the science fair, you will likely communicate your findings in a written report, on a display board or during a presentation at the event. If you are a scientist by profession, you may present your findings in a scientific publication or to your supervisors.Example: You write a formal report and prepare an oral presentation to share your findings.Frequently asked questions
What questions can the scientific method answer?
The scientific method can help researchers, scientists and students answer questions that they can prove or disprove through testing.What questions can the scientific method not answer?
The scientific method can't answer questions that are difficult or impossible to test, like what the nature of dark matter is or whether we're alone in the universe.How can you increase the validity of the scientific method?
You can improve the scientific method and increase its accuracy by improving the testing technique, controlling a greater number of variables and reducing sample bias by increasing randomization.Ever wondered how scientists uncover the mysteries of the universe? In this brief video, we’ll explore the scientific method, a systematic approach to conducting research and making discoveries.
Explore more articles
- How To Become a Project Manager in 7 Steps (Plus Salary)
- How To Separate Numbers From Text in Excel (3 Methods)
- How To Lock Formulas in Excel in 5 Steps
- 12 Effective Teaching Practices and Their Benefits
- Turning Down a Promotion: How and When to Do So
- What To Do When You Feel Excluded by Colleagues (With Steps)
- How To Deal With Dishonesty in the Workplace
- The Key To Successful Speech Writing
- 56 Inspiring Team Communication Quotes To Motivate Your Team
- What To Do if You Feel Threatened at Work (With Tips)
- 36 Ideas for Fun Morning Huddles
- 41 Important Engineering KPIs (With Definitions)


