What is photosynthesis?
Animals need to eat food to get their energy. All animals, including humans, eat food that was, or is, a plant or an animal.
But green plants and algae can use light energy to make their own food! This process called photosynthesis.
Almost all life on Earth depends upon this process.
 Image source, BBC
Image source, BBCThese are the things that plants need for photosynthesis:
- carbon dioxide
- water
- light
These are the things that plants make by photosynthesis:
- glucose (sugar)
- oxygen
Here is the word equation for photosynthesis:

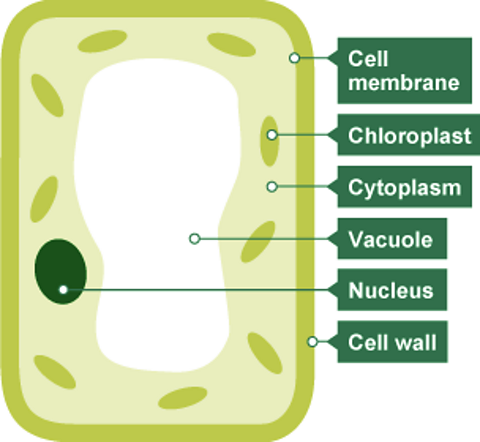
Photosynthesis takes place inside chloroplasts which are small objects inside plant cells.
Chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll. This traps the light energy needed to make photosynthesis happen. Plants and algae can only carry out photosynthesis in the light.

| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell wall | The outside of the cell which provides support and prevents the cell from bursting from the uptake of water. |
| Cell membrane | A selectively permeable membrane surrounding the cell that controls the entry and exit of materials. |
| Nucleus | The control centre of the cell. It controls what happens inside the cell and holds instructions needed to make new cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. |
| Cytoplasm | The living substance inside a cell. Cell reactions happen here. |
| Chloroplasts | Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps light energy to make food during photosynthesis |
| Vacuole | A space within the cytoplasm of plant cells that contains cell sap. |
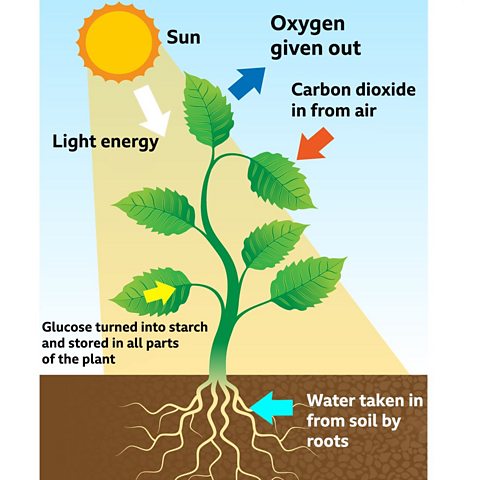
Plants get carbon dioxide from the air through their leaves, and water from the ground through their roots. Light energy comes from the Sun.
The oxygen produced is released into the air from the leaves. The glucose produced can be turned into other substances, such as starch and plant oils, which are used as an energy store. The glucose is also used to release energy through the process of respiration.

Why is photosynthesis so important?
Photosynthesis is really important for animals, including humans because
- without photosynthesis we wouldn’t have food because it converts energy from the sun into chemical energy for the food chains.
- photosynthesis keeps the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in balance – without it we would very quickly run out of oxygen.
Photosynthesis is really important for the plant because it provides the plant with food:
- some of the glucose is used immediately, to give the plant energy in the process of respiration.
- some of the glucose is changed into starch and stored in all parts of the plant. When it is needed, it is converted back into glucose.
Adaptations of the leaf
In most plants photosynthesis happens in the leaves. Leaves have adapted so that photosynthesis takes place efficiently. The table describes some of its adaptations:
| Adaptation | Function |
|---|---|
| Thin | Provides a short distance for carbon dioxide to move by diffusion into the leaf |
| Large surface area | It can absorb a lot of light |
| Contains chlorophyll | Traps light |
| Stomata | Small holes in the underside of the leaf that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to move in and out of the leaf by diffusion |
| Guard cells | To open and close the stomata depending on the conditions |
| Network of tubes | To transport water and food |
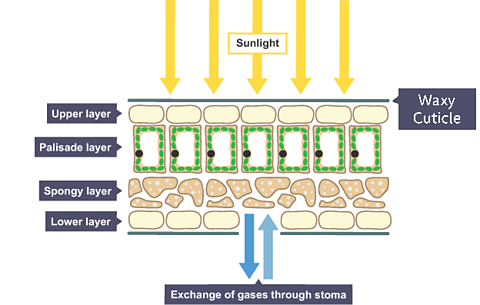
A leaf usually has a large surface area, so that it can absorb a lot of light. It's top surface is protected from water loss, disease and weather damage by a waxy cuticle, which does not stop light entering the leaf.
The upper part of the leaf is where the light falls, and it contains many cells called palisade cells. This has many chloroplasts, with lots of chlorophyll to trap as much light as possible. It is shaped like a tall box which helps pack them closely together.
Carbon dioxide
Plants get the carbon dioxide they need from the air through their leaves. It moves by diffusion through small holes in the underside of the leaf called stomata.Guard cells control the size of the stomata so that the leaf does not lose too much water in hot, windy or dry conditions.
The lower part of the leaf is a spongy layer with loose-fitting cells. Between the cells in this layer there are 'air spaces' - a bit like a sponge. These allow the gases to diffuse through the leaf.Stomata let carbon dioxide enter the leaf, and let the oxygen produced in photosynthesis leave the leaf easily. In many plants, stomata are open during the day and closed at night.
Water
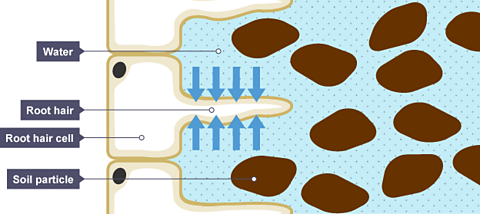
The water needed for photosynthesis is absorbed through the roots and transported through tubes to the leaf.The roots have a type of cell called a root hair cell. These project out from the root into the soil, and have a big surface area and thin walls. This lets water pass into them easily.Note that root cells do not contain chloroplasts, as they are normally in the dark and cannot carry out photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis and respiration in plants
Plant cells respire, just as animal cells do. If they stop respiring, they will die.
Remember that respiration happens in all living cells and is the way that energy is released from glucose - it is not the same as breathing, so take care - plants do not breathe!
Here is the word equation for aerobic respiration:glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
Here is the word equation for photosynthesis:

The word equations show that the reactants and products of aerobic respiration and photosynthesis are opposites:
- aerobic respiration uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide
- photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and produces oxygen
Plants respire all the time, whether it is dark or light. They photosynthesise only when they are in the light.
Hydrogencarbonate indicator
Hydrogencarbonate indicator can detect increases and decreases in carbon dioxide concentration.
- Hydrogencarbonate indicator is normally red.
- An increase in carbon dioxide changes the indicator to yellow
- A decrease in carbon dioxide changes it to purple
- If there are no change in the carbon dioxide levels then the indicator remains red.
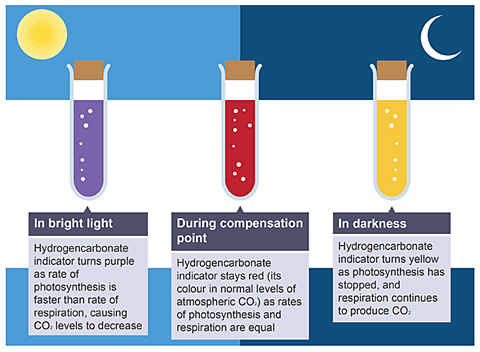
When photosynthesis and respiration happen.
Photosynthesis only happens in the light. Respiration happens all the time.
In bright light
Both photosynthesis and respiration are occurring but the rate of photosynthesis is higher than the rate of respiration, therefore there is more carbon dioxide into the leaf and oxygen out.
The removal of carbon dioxide from the hydrogencarbonate indicator into the leaf would change the indicator from red to purple.
At dusk/dawnWhen light intensity is low the rates of photosynthesis and respiration are equal. There is no net exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
No net gas exchange would cause the hydrogencarbonate to remain red because no change in carbon dioxide concentration will occur.
In the darkOnly respiration is occurring as there is no light for photosynthesis, therefore the only gas exchange happening is oxygen into and carbon dioxide out of the leaf.
The release of carbon dioxide from the leaf into the hydrogencarbonate indicator changes the indicator from red to yellow.
| Conditions | Photosynthesis v respiration | Overall result | Hydrogen carbonate indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dark | Respiration but no photosynthesis | Oxygen taken in, carbon dioxide given out | Yellow |
| Dim light (e.g. dawn or dusk) | Photosynthesis rate equals respiration rate | No overall exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen | Red |
| Bright light | Photosynthesis rate greater than respiration rate | Carbon dioxide taken in, oxygen given out | Purple |
When the rate of photosynthesis is greater than the rate of respiration, then there is a gain in glucose.
Plants that lose their leaves in winter store food produced during the summer by photosynthesis. They store enough food to last them over winter, and to provide energy reserves for new growth in the spring. They are called deciduous plants.
Investigating photosynthesis: Testing a leaf for starch
During photosynthesis carbon dioxide and water are converted to glucose. The glucose is normally quickly converted into starch, for storage in the leaves.
So, if a plant has photosynthesised its leaves will test positive for starch.
Destarching a plant:
- Before carrying out any photosynthesis practical it is necessary to destarch the plant by placing it in the dark for at least 48 hours. During this time any starch will be turned back into glucose and used by respiration.
- This step is important so you can be certain that any starch present at the end of the experiment has been produced during the experiment.
- You can check if a plant has been fully destarched by testing a leaf for starch. If the iodine remains yellow-brown, all the starch has successfully been removed.

The starch test:
- First destarch the plant – see above
- Stand a plant in bright light for at least two hours.
- After that time, remove a leaf from the plant.
- Place the leaf in boiling water for 30 seconds (diagram 1 above) – this kills it, stopping any further chemical reactions.
- Place the leaf in boiling ethanol (diagram 2 above) – this removes the chlorophyll, making the leaf paler in colour.
- Then dip the leaf in water (diagram 3 above) – this softens it.
- Spread the leaf onto a white tile and add iodine to test for the presence of starch.
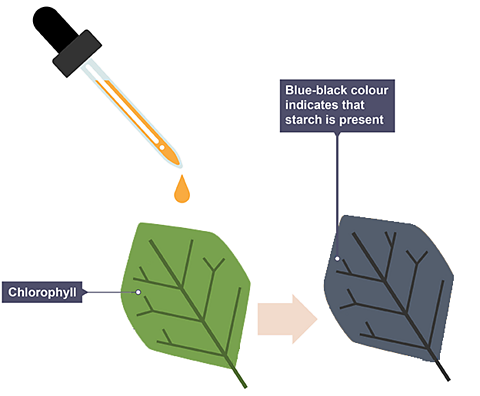
Results:
- If starch is present the iodine will change from yellow-brown to blue-black.
- If starch is absent the iodine will remain yellow-brown.

Safety:
- Wear goggles throughout the experiment,
- Ensure that the ethanol is not exposed to a naked flame during step 5, as it is highly flammable. It should be heated using a hot water bath instead of using a Bunsen burner
Showing that light and chlorophyll are required for photosynthesis
Two straightforward investigations can be carried out to show that light and chlorophyll are required for photosynthesis.
Showing the need for light in photosynthesis
Method
- Destarch a plant in the normal way (see above)
- Cover part of a leaf with lightproof paper or foil.
- Make a drawing of the leaf to show where the foil/paper is placed.
- Place the plant in bright light for several hours.
- Test the leaf for starch using the starch test (see above).
- Make another drawing of the leaf. In this drawing show the areas of the leaf that tested positive and those that tested negative for starch.
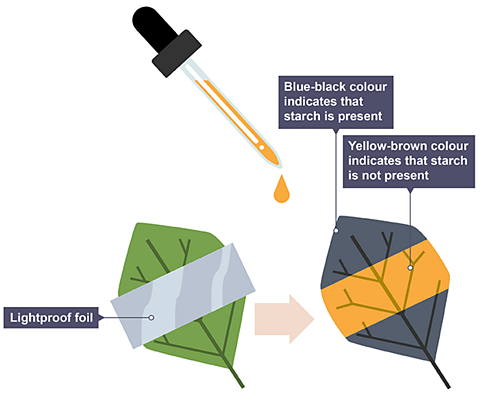
Results
Only the area that have been exposed to light tested positive for starch and hence showed that photosynthesis had occurred. This shows that light is necessary for photosynthesis.
Showing the need for chlorophyll in photosynthesis
Method
- Destarch a plant with variegated leaves. Variegated leaves are not completely green, as can be seen in the diagram. these discoloured areas do not contain chlorophyll.
- Make a drawing of the leaf to show the pattern of the variegated leaf.
- Place the plant in light for several hours.
- Test the leaf for starch using the starch test (see above).
- Make another drawing of the leaf. In this drawing show the areas of the leaf that tested positive and those that tested negative of starch.
ResultsOnly the areas of the leaf that were originally green tested positive for starch. The discoloured areas tested negative. As the green areas contained chlorophyll and the white did not, this proves that chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis.
Investigating the production of oxygen
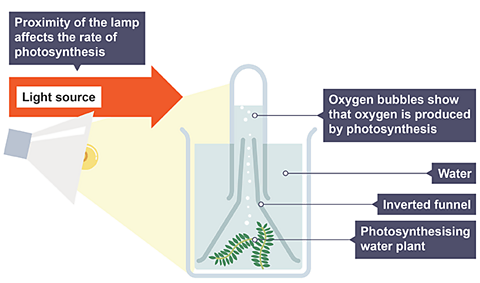
If the rate of photosynthesis increases (e.g. by increasing the brightness of the lamp) the number of oxygen bubbles or volume of oxygen produced will also increase.
Measuring the volume of oxygen produced is more accurate than counting the bubbles of oxygen produced.
An oxygen electrode connected to a data logger can be used to measure the change in oxygen concentration.
To test for oxygen remove the test tube and quickly inset a glowing wooden splint. This relights in a test tube of oxygen.
Summary: Comparing photosynthesis and respiration
| Photosynthesis | Respiration | |
|---|---|---|
| Gas taken in | Carbon dioxide | Oxygen |
| Gas given out | Oxygen | Carbon dioxide |
| What does the gas react with? | Water | Glucose |
| What else is produced? | Glucose | Water |
| Occurs in | Only plant cells containing chlorophyll | All living cells |
| When does it take place? | Only in light (day) only | In light (day) as well as in the dark (night) |
| Energy change | Light energy → Chemical energy | Chemical energy in food → Chemical energy that cells can use + heat energy + kinetic energy |
| Word equation | carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen | glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy |
Plant adaption for photosynthesis to occur
Different types of plants live in different conditions and different habitats. Plants develop features that help them survive and carry out photosynthesis.
How plants adapt to dry conditions
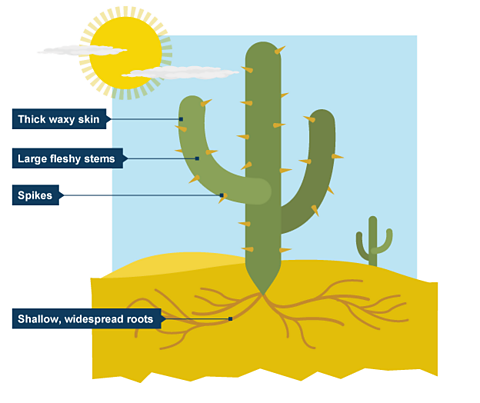
- thick, waxy cutile to reduce loss of water and to reflect heat
- large, fleshy stems to store water
- thorns and thin, spiky or glossy leaves to reduce water loss
- spikes protect cacti from animals wishing to use stored water
- deep roots to tap groundwater
- long shallow roots which spread over a wide area
- plants lie dormant for years until rain falls
How plants adapt in the rainforest

- Plants grow thick leaves with drip tips and waxy surfaces to allow water to drain away quickly to prevent rotting.
- Some plants called 'epiphytes' are flowering plants which grow on tree trunks and branches to get light. They get food from the air and water, and their roots hang in the air, eg orchids.

- Rainforest soils are poor and most nutrients are in the top layers, so roots are generally shallow. Wide buttress roots join the tree far up and help to support it. They also allow it to gather more nutrients

Some important terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Environment | All the conditions that surround a living organism |
| Habitat | The place where an organism lives |
| Population | All the members of a single species that live in a habitat |
| Community | All the populations of different organisms that live together in a habitat |
| Ecosystem | A community and the habitat in which organisms live |
More on Biology
Find out more by working through a topic
- count11 of 11

- count1 of 11
- count2 of 11

- count3 of 11
