Countries Ruled by Monarchies
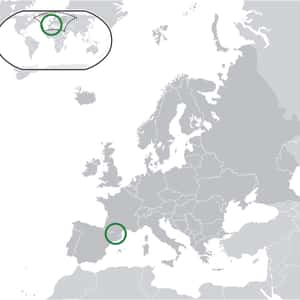
- Andorra la VellaAndorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, is a sovereign landlocked microstate in Southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe, having an area of 468 km² and a population of ca. 85,000. Its capital, Andorra la Vella, is the highest capital city in Europe, at an elevation of 1,023 metres above sea level. The official language is Catalan, although Spanish, Portuguese, and French are also commonly spoken. Created under a charter in A.D. 988, the present Principality was formed in A.D. 1278. It is known as a principality as it is a monarchy headed by two Co-Princes – the Spanish/Roman Catholic Bishop of Urgell and the President of France. Andorra's tourism services an estimated 10.2 million visitors annually. It is not a member of the European Union, but the euro is the de facto currency. It has been a member of the United Nations since 1993. The people of Andorra have one of the highest life expectancies in the world and as of December 2014, according to The Lancet, has the highest in the world - 81 years in 2013.More Andorra
- Dig Deeper...Nations That Are 'Against' Death Penalty
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #139 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
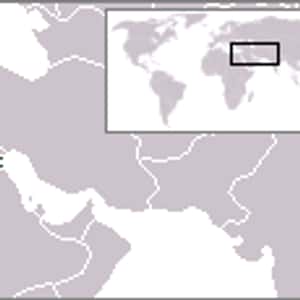
- ManamaBahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is a small island country situated near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago with Bahrain Island, the largest land mass, at 55 km long by 18 km wide. Saudi Arabia lies to the west and is connected to Bahrain by the King Fahd Causeway while Iran lies 200 km to the north across the Persian Gulf. The peninsula of Qatar is to the southeast across the Gulf of Bahrain. The population in 2010 stood at 1,234,571, including 666,172 non-nationals. Bahrain is the site of the ancient land of the Dilmun civilisation. Bahrain was one of the earliest areas to convert to Islam in 628 AD. Following a period of Arab rule, Bahrain was occupied by the Portuguese in 1521, who in turn were expelled in 1602 by Shah Abbas I of the Safavid dynasty under the Persian Empire. In 1783, the Bani Utbah clan captured Bahrain from Nasr Al-Madhkur and has since been ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family, with Ahmed al Fateh as Bahrain's first hakim. In the late 1800s, following successive treaties with the British, Bahrain became a protectorate of the United Kingdom. In 1971, Bahrain declared independence.More Bahrain
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #186 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ThimphuBhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia at the eastern end of the Himalayas. It is bordered to the north by China and to the south, east and west by India. To the west, it is separated from Nepal by the Indian state of Sikkim, while farther south it is separated from Bangladesh by the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal. Bhutan's capital and largest city is Thimphu. At that time the lama and military leader Ngawang Namgyal, the first Zhabdrung Rinpoche, who was fleeing religious persecution in Tibet, unified the area and cultivated a distinct Bhutanese .More Bhutan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #19 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Bandar Seri BegawanBrunei officially the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace, is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its coastline with the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the state of Sarawak, Malaysia; and it is separated into two parts by the Sarawak district of Limbang. It is the only sovereign state completely on the island of Borneo; the remainder of the island's territory is divided between the nations of Malaysia and Indonesia. Brunei's population was 408,786 in July 2012. At the peak of Bruneian Empire, Sultan Bolkiah is alleged to have had control over most regions of Borneo, including modern-day Sarawak and Sabah, as well as the Sulu archipelago off the northeast tip of Borneo, Seludong, and the islands off the northwest tip of Borneo. The maritime state was visited by Spain's Magellan Expedition in 1521 and fought against Spain in 1578's Castille War. During the 19th century, the Bruneian Empire began to decline. The Sultanate ceded Sarawak to James Brooke and installed him as the White Rajah, and it ceded Sabah to the British North Borneo Chartered Company.More Brunei
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #112 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Phnom PenhCambodia, officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia and once known as the Khmer Empire, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Its total landmass is 181,035 square kilometres, bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, and the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. With a population of over 15 million, Cambodia is the 69th most populous country in the world. The official religion is Theravada Buddhism, practiced by approximately 95 percent of the population. The country's minority groups include Vietnamese, Chinese, Chams, and 30 hill tribes. The capital and largest city is Phnom Penh, the political, economic, and cultural center of Cambodia. The kingdom is a constitutional monarchy with Norodom Sihamoni, a monarch chosen by the Royal Throne Council, as head of state. The head of government is Hun Sen, who is currently the longest serving non-royal leader in South East Asia and has ruled Cambodia for over 25 years. Cambodia's ancient name is "Kambuja".More Cambodia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #77 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
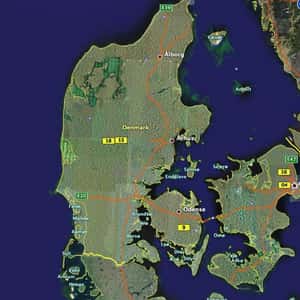
- CopenhagenDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The southernmost of the Nordic countries, it is located southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark is a sovereign state that comprises Denmark and two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark proper has an area of 43,094 square kilometres, and a population of 5,659,715. The country consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and the Danish archipelago of 443 named islands, of which around 70 are inhabited. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate. The unified kingdom of Denmark emerged in the 10th century as a proficient seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea. Danish rule over the personal Kalmar Union, established in 1397, ended with Swedish secession in 1523. However, Denmark still kept a union over Norway which lasted until its dissolution in 1814. Denmark inherited an expansive colonial empire from this union, of which the Faroe Islands and Greenland are remnants.
Holy Roman Empire
Frankfurt, RegensburgThe Holy Roman Empire was a multi-ethnic complex of territories in central Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806. The largest territory of the empire after 962 was the Kingdom of Germany, though it included the Kingdom of Bohemia, the Kingdom of Burgundy, the Kingdom of Italy, and numerous other territories. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as Emperor, reviving the title in Western Europe after more than three centuries. The title continued in the Carolingian family until 888, after which it was contested by the rulers of Italy in a series of civil wars until the death of the last Italian claimant, Berengar, in 924. The title was revived in 962 when Otto I was crowned emperor, fashioning himself as the successor of Charlemagne and beginning a continuous existence of the empire for over eight centuries. Some historians refer to the coronation of Charlemagne as the origin of the empire, while others prefer the coronation of Otto I as its beginning.- The Holy See is the ecclesiastical jurisdiction of the Catholic Church in Rome, the episcopal see of the Bishop of Rome—the Pope. It is the central point of reference for the church everywhere and the focal point of communion due to its prominence. It traces its origin to the apostolic era, when Saint Peter arrived in Rome to evangelize, thus forming a community of believers there which maintained a significant Christian presence. Today, it is responsible for the governance of the faithful, organized in their local Christian communities. The Holy See is viewed as analogous to a sovereign state, having a centralized government called the Roman Curia with the Secretary of State as its chief administrator and various departments essential to administration comparable to ministries and executive departments. It enters diplomatic relations with states, and has Vatican City as its sovereign territory. Diplomatically, the Holy See acts and speaks for the whole church. It is also recognized by other subjects of international law as a sovereign entity, headed by the Pope, with which diplomatic relations can be maintained.
- TokyoJapan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. The Kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and Japan is often called "Land of the Rising Sun". Japan is a stratovolcanic archipelago of 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku, which make up about ninety-seven percent of Japan's land area. Japan's population of 126 million is the world's tenth largest. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes the de facto capital of Tokyo and several surrounding prefectures, is the world's largest metropolitan area, with over 30 million residents. Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period. The first written mention of Japan is in Chinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly Imperial China, followed by periods of isolation, later from Western European influence, has characterized Japan's history.More Japan
- AmmanJordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is an Arab kingdom in the Middle East, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north, and Israel and Palestine to the west. After the post-World War I division of West Asia by Britain and France, the Emirate of Transjordan was officially recognized by the Council of the League of Nations in 1922. In 1946, Jordan became an independent sovereign state officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Transjordan. After capturing the West Bank during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Abdullah I took the title King of Jordan. The name of the state was changed to The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan on 1 December 1948. Although Jordan is a constitutional monarchy, the king holds wide executive and legislative powers. Jordan is classified as a country of "high human development" by the 2014 Human Development Report. Jordan has an "upper middle income" economy. Jordan enjoys "advanced status" with the European Union since December 2010, and it is a member of the Euro-Mediterranean free trade area.More Jordan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #201 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
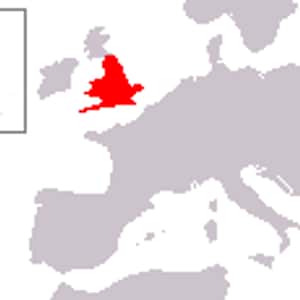
- Winchester, WestminsterThe Kingdom of England was a state on the island of Great Britain from the 10th century, when it emerged following the unification of various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1707, when it united with Scotland to form a unified Kingdom of Great Britain. The Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were unified under Æthelstan during the 10th century. In the early 11th century, England became part of the "North Sea Empire" of Cnut the Great. With the Norman conquest, the kingdom became one of the territories ruled by the House of Anjou. The English capital and chief royal residence in the Anglo-Saxon period was Winchester, but Westminster and Gloucester were accorded almost equal status, with Westminster gradually gaining preference and becoming the administrative capital by the beginning of the 12th century. During the 10th century, the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest town and principal commercial centre. The history of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 is conventionally divided into periods named after the ruling dynasty as follows: Norman 1066–1154, Plantagenet 1216–1485, Tudor 1485–1603 and Stuart 1603–1714.
- Kuwait CityKuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is an Arab country in Western Asia. Situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, it shares borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia. As of 2014, Kuwait has a population of 4.1 million people; 1.2 million are Kuwaitis and 2.8 million are expatriates. During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Kuwait was a prosperous trade hub. Starting in the early 20th century, its regional economic importance declined, and by 1934 Kuwait had lost its prominence in long-distance trade. Kuwait's economy was devastated by several trade blockades. During World War I, the British Empire imposed a blockade against Kuwait because its ruler supported the Ottoman Empire. Following the Kuwait–Najd War of 1919–1920, Saudi Arabia maintained a trade blockade against the country from 1923 until 1937. In 1990, Kuwait was invaded by Iraq. The Iraqi occupation came to an end in 1991 after military intervention by United States-led forces. Kuwait is a constitutional emirate with an elected parliamentary system. Kuwait has a petroleum-based economy.
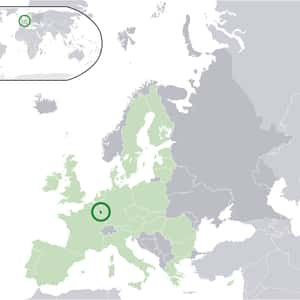
- VaduzLiechtenstein, officially the Principality of Liechtenstein, is a doubly landlocked German-speaking microstate in Central Europe. It is a constitutional principality headed by the Prince of Liechtenstein. Liechtenstein is bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and Austria to the east and north. It has an area of just over 160 square kilometres and an estimated population of 35,000. Divided into 11 municipalities, its capital is Vaduz and largest town Schaan. Economically, Liechtenstein has the highest gross domestic product per person in the world when adjusted by purchasing power parity. It is also the 2nd richest country in the world, after Qatar, and has one of the lowest unemployment rates at 1.5%. An alpine country, Liechtenstein is mainly mountainous, making it a winter sports destination. Many cultivated fields and small farms are found both in the south and north. The country has a strong financial sector centered in Vaduz, and has been identified as a tax haven. It is a member of the European Free Trade Association and part of the European Economic Area and the Schengen Area, but not of the European Union.
- LuxembourgLuxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. It comprises two principal regions: the Oesling in the north as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south. Luxembourg had a population of 524,853 in October 2012 and has an area of 2,586 square kilometres, making it one of the smallest sovereign nations in Europe. As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by a grand duke, Henri, Grand Duke of Luxembourg, and is the world's only remaining grand duchy. Luxembourg is a developed country, with an advanced economy and the world's second highest GDP per capita, according to the World Bank. Its central location has historically made it of great strategic importance to numerous powers, dating back to its founding as a Roman fortress, its hosting of a vital Frankish castle during the Early Middle Ages, and its role as a bastion for the Spanish Road between 16th and 17th centuries.More Luxembourg
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #155 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- PellaMacedonia or Macedon was an ancient kingdom on the northern periphery of Classical Greece and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. It was ruled during most of its existence initially by the legendary founding dynasty of the Argeads, the intermittent Antipatrids and finally the Antigonids. Home to the Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, the region of Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. The rise of Macedon, from a small kingdom at the fringe of typical Greek city states affairs, to one which came to control the fate of the entire Hellenic world, occurred under the reign of Philip II. With the innovative Macedonian army, he defeated the old powers of Athens and Thebes in the decisive Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC and subdued them, while keeping Sparta in check. His son Alexander the Great pursued his father's effort to command the whole of Greece through the federation of Greek states, a feat he finally accomplished after destroying a revolting Thebes.
- Kuala LumpurMalaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy located in Southeast Asia. It consists of thirteen states and three federal territories and has a total landmass of 329,847 square kilometres separated by the South China Sea into two similarly sized regions, Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime border with Thailand and maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia and a maritime border with the Philippines. The capital city is Kuala Lumpur, while Putrajaya is the seat of the federal government. By 2015, with a population of over 30 million, Malaysia became the 43rd most populous country in the world. The southernmost point of continental Eurasia, Tanjung Piai, is in Malaysia, located in the tropics. It is one of 17 megadiverse countries on earth, with large numbers of endemic species. Malaysia has its origins in the Malay kingdoms present in the area which, from the 18th century, became subject to the British Empire.More Malaysia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #95 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a sovereign city-state and microstate, located on the French Riviera in Western Europe. It is bordered by France on three sides; one side borders the Mediterranean Sea. Monaco has an area of 2.02 km² and a population of 36,371; it is the second smallest and the most densely populated country in the world. Monaco has a land border of 4.4 km, a coastline of 4.1 km, and a width that varies between 1,700 and 349 m. The highest point in the country is a narrow pathway named Chemin des Révoires on the slopes of Mont Agel, in the Les Révoires Ward, which is 161 metres above sea level. Monaco's most populous Quartier is Monte Carlo and the most populous Ward is Larvotto/Bas Moulins. Through land reclamation, Monaco's land mass has expanded by twenty percent. Monaco is a principality governed under a form of constitutional monarchy, with Prince Albert II as head of state. Although Prince Albert II is a constitutional monarch, he wields immense political power. The House of Grimaldi have ruled Monaco, with brief interruptions, since 1297. The official language is French, but Monégasque, Italian, and English are widely spoken and understood.More Monaco
- Dig Deeper...All About Charlene, Princess Of Monaco, The Championship Swimmer Who Became A Royal
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #194 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
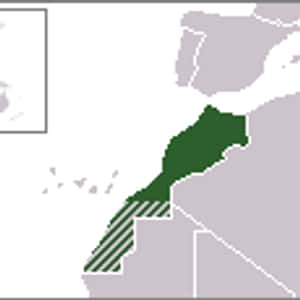
- RabatMorocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. Geographically, Morocco is characterized by a rugged mountainous interior and large portions of desert. It is one of only three countries to have both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines. The Arabic name al-Mamlakah al-Maghribiyah and Al-Maghrib are commonly used as alternate names. Morocco has a population of over 33 million and an area of 446,550 km².More Morocco
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #82 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
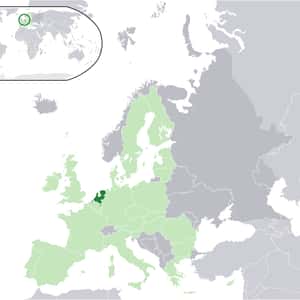
- AmsterdamThe Netherlands is the main constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It is a small, densely populated country, lying mainly in Western Europe, but also including three islands in the Caribbean. The European part of the Netherlands borders Germany to the east, Belgium to the south, and the North Sea to the northwest, sharing maritime borders with Belgium, the United Kingdom and Germany. The largest and most important cities in the Netherlands are Amsterdam, The Hague and Rotterdam. Amsterdam is the country's capital, while The Hague holds the Dutch seat of government and parliament. The port of Rotterdam is the largest port in Europe – as large as the next three largest combined. The Netherlands' name literally means "Low Country", inspired by its low and flat geography, with only about 50% of its land exceeding one metre above sea level. Most of the areas below sea level are man-made. Since the late 16th century, large areas have been reclaimed from the sea and from lakes, amounting to nearly 17% of the country's current land mass.More Netherlands
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From The Netherlands
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #78 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- OsloNorway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a sovereign and unitary monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula plus Jan Mayen and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard. The Antarctic Peter I Island and the sub-Antarctic Bouvet Island are dependent territories and thus not considered part of the Kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land. Until 1814, the Kingdom included the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. Norway has a total area of 385,252 square kilometres and a population of 5,109,059 people. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden. Norway is bordered by Finland and Russia to the north-east, and the Skagerrak Strait to the south, with Denmark on the other side. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. King Harald V of the House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg is the current monarch of Norway. Erna Solberg became Prime Minister in 2013, replacing Jens Stoltenberg. A constitutional monarchy since 1814, state power is divided between the Parliament, the King and his Council, and the Supreme Court.More Norway
- Dig Deeper...The Top Beers from Norway
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #18 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- MuscatOman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is an Arab country in the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Holding a strategically important position at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, the nation is bordered by the United Arab Emirates to the northwest, Saudi Arabia to the west, and Yemen to the southwest, and shares marine borders with Iran and Pakistan. The coast is formed by the Arabian Sea on the southeast and the Gulf of Oman on the northeast. The Madha and Musandam exclaves are surrounded by the UAE on their land borders, with the Strait of Hormuz and Gulf of Oman forming Musandam's coastal boundaries. From the late 17th century, the Omani Sultanate was a powerful empire, vying with Portugal and Britain for influence in the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. At its peak in the 19th century, Omani influence or control extended across the Strait of Hormuz to Iran and modern-day Pakistan, and as far south as Zanzibar. As its power declined in the 20th century, the sultanate came under the influence of the United Kingdom. Historically, Muscat was the principal trading port of the Persian Gulf region. Muscat was also among the most important trading ports of the Indian Ocean.More Oman
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #188 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Söğüt, Bursa, İnegölThe Ottoman Empire, also historically referred to as the Turkish Empire or Turkey, was a Sunni Islamic state founded in 1299 by Oghuz Turks under Osman I in northwestern Anatolia. With conquests in the Balkans by Murad I between 1362 and 1389, the Ottoman sultanate was transformed into a transcontinental empire and claimant to caliphate. The Ottomans overthrew the Byzantine Empire with the 1453 conquest of Constantinople by Mehmed II. During the 16th and 17th centuries, in particular at the height of its power under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was a powerful multinational, multilingual empire controlling much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, the Caucasus, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa. At the beginning of the 17th century the empire contained 32 provinces and numerous vassal states. Some of these were later absorbed into the empire, while others were granted various types of autonomy during the course of centuries. With Constantinople as its capital and control of lands around the Mediterranean basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds for six centuries.
- DohaQatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a sovereign Arab country located in Southwest Asia, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the rest of its territory surrounded by the Persian Gulf. A strait in the Persian Gulf separates Qatar from the nearby island kingdom of Bahrain. In 2013, Qatar's total population was 1.8 million: 278,000 Qatari citizens and 1.5 million expatriates. Following Ottoman rule, Qatar became a British protectorate in the early 20th century until gaining independence in 1971. Qatar has been ruled by the Al Thani family since the mid-19th century. Qatar is an absolute monarchy and its head of state is Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani. After Saudi Arabia, Qatar is the most conservative society in the GCC as most Qataris adhere to the strict Wahhabi interpretation of Islam. Sharia law is the main source of Qatari legislation according to Qatar's Constitution.More Qatar
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #109 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ApiaSamoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa, formerly known as Western Samoa, is an Oceanian country encompassing the western part of the Samoan Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. It became independent from New Zealand in 1962. The two main islands of Samoa are Upolu and Savai'i, one of the biggest islands in Polynesia. The capital city, Apia, and Faleolo International Airport are situated on the island of Upolu. Samoa was admitted to the United Nations on 15 December 1976. The entire island group, which includes American Samoa, was called "Navigator Islands" by European explorers before the 20th century because of the Samoans' seafaring skills. The language spoken is Samoan language or Gagana Fa'asāmoa. This is the same language spoken in American Samoa.More Samoa
- Dig Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #67 of 217 onThe Best Countries to Travel To
- MadridSpain, officially the Kingdom of Spain, is a sovereign state located on the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe. Its mainland is bordered to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea except for a small land boundary with Gibraltar; to the north and northeast by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west and northwest by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Along with France and Morocco, it is one of only three countries to have both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines. Spain's 1,214 km border with Portugal is the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. Spanish territory also includes two archipelagos; the Balearic Islands, in the Mediterranean Sea, and the Canary Islands, in the Atlantic Ocean off the African coast; two major exclaves, Ceuta and Melilla, in continental North Africa; and the islands and peñones of Alborán, Alhucemas, Chafarinas and Vélez de la Gomera. With an area of 505,990 km², Spain is the second largest country in Western Europe and the European Union, and the fourth largest country in Europe. By population, Spain is the sixth largest in Europe and the fifth in the European Union.More Spain
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From Spain
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #24 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Mbabane, LobambaEswatini, officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named in English as Swaziland is a sovereign state in Southern Africa. It is neighbored by Mozambique to its east and by South Africa to its north, west and south. The country and its people take their names from Mswati II. At no more than 200 kilometres north to south and 130 kilometres east to west, Swaziland is one of the smallest countries in Africa. Despite its size, however, its climate and topography is diverse, ranging from a cool and mountainous highveld to a hot and dry lowveld. The population is primarily ethnic Swazis whose language is siSwati. The kingdom was established in the mid-18th century under the leadership of Ngwane III; the present boundaries were drawn up in 1881. After the Anglo-Boer War, Swaziland was a British protectorate from 1903 until 1967. It regained its independence on 6 September 1968. The country is an absolute monarchy, currently ruled by Ngwenyama Mswati III.More Eswatini
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #108 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- StockholmSweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. Sweden borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres, Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of about 9.7 million. Sweden has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre, with the population mostly concentrated in the southern half of the country. About 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the collective geographical group of nations Fennoscandia. Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats/Götar and Swedes/Svear and contributing to the sea peoples known as the Vikings. Sweden emerged as an independent and unified country during the Middle Ages. In the 17th century, the country expanded its territories to form the Swedish Empire. The empire grew to be one of the great powers of Europe in the 17th and early 18th centuries.More Sweden
- Dig Deeper...The Most Stunning Swedish Fashion Models
- And Deeper...The Top Beers from Sweden
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- BangkokThailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand, formerly known as Siam, is a country at the centre of the Indochina peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the southern extremity of Burma. Its maritime boundaries include Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast, and Indonesia and India on the Andaman Sea to the southwest. Thailand is a monarchy headed by King Bhumibol Adulyadej, Rama IX, and governed by a military junta that took power in May 2014. The king is the ninth of the House of Chakri, and has reigned since 1946 as the world's longest-serving current head of state and the country's longest-reigning monarch. The King of Thailand's titles include Head of State, Head of the Armed Forces, Adherent of Buddhism, and Upholder of religions. Although a constitutional system was established in 1932, the monarchy and military have continued to intervene periodically in politics.More Thailand
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Thailand
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #141 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- NukuʻalofaTonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is a Polynesian sovereign state and archipelago comprising 177 islands with a total surface area of about 750 square kilometres scattered over 700,000 square kilometres of the southern Pacific Ocean, of which 52 islands are inhabited by its 103,000 people. Seventy percent of Tongans reside on the main island of Tongatapu. Tonga stretches over about 800 kilometres in a north-south line – about a third of the distance from New Zealand to Hawaii. It is surrounded by Fiji and Wallis and Futuna to the northwest, Samoa to the northeast, Niue to the east, Kermadec to the southwest, and New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the farther west. Tonga became known as the Friendly Islands because of the congenial reception accorded to Captain James Cook on his first visit in 1773. He arrived at the time of the ʻinasi festival, the yearly donation of the First Fruits to the Tuʻi Tonga and so received an invitation to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, the chiefs wanted to kill Cook during the gathering but could not agree on a plan.More Tonga
- Dig Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #54 of 161 onThe Most Beautiful Countries In The World
- Abu DhabiThe United Arab Emirates, sometimes simply called the Emirates or the UAE, is a country located in the southeast end of the Arabian Peninsula on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman to the east and Saudi Arabia to the south, as well as sharing sea borders with Qatar and Iran. In 2013, the UAE's total population was 9.2 million, of which 1.4 million are Emirati citizens and 7.8 million are expatriates. Established in December 1971, the country is a federation of seven emirates. The constituent emirates are Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras al-Khaimah, Sharjah, and Umm al-Quwain. Each emirate is governed by an absolute monarch who jointly form the Federal Supreme Council. One of the monarchs is selected as the President of the United Arab Emirates. Islam is the official religion of the UAE, and Arabic is the official language, although English is widely used. The UAE's oil reserves are the fourth-largest in the world, while its natural gas reserves are the world's seventeenth-largest. The late Sheikh Zayed, ruler of Abu Dhabi and the first President of the UAE, oversaw the development of the Emirates and steered oil revenues into healthcare, education and infrastructure.More United Arab Emirates
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #99 of 161 onThe Most Beautiful Countries In The World