Bronchitis: Is It Contagious, Causes, Symptoms, and Transmission
Bronchitis is a respiratory illness that can be contagious and it causes coughing, breathing difficulties, and possible wheezing. The answer to the question if bronchitis is contagious depends on the type of bronchitis a person has. Bacterial or viral respiratory infections that cause acute bronchitis means that this type of bronchitis is contagious. However, chronic bronchitis usually isn’t infectious because the deep cough usually results from long-term inhalation of irritants, for example, smoking.
Bronchitis that is transmittable can also be a complication of the cold or flu virus, and if left untreated can lead to pneumonia. Contagious bronchitis is usually spread by touching something that an infected person has sneezed or coughed on. The infection then enters your body when you touch your nose, eyes, or mouth.
Many people who suffer from acute infectious bronchitis find that various natural remedies help to relieve the symptoms within a week to 3 weeks. Because you can easily spread bronchitis to another person, it’s important to always sneeze or cough into a clean tissue and wash your hands frequently to prevent others catching bronchitis from you.
In this article, you will find out about the types of bronchitis that are contagious and how to prevent the infection spreading. You will also find out how to treat the symptoms of both acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis.
Is Bronchitis Contagious?
If you develop bronchitis as a symptom of the cold or flu, then your bronchitis is probably contagious.
According to Dr. James M. Steckelberg, a consultant in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Mayo Medical School, acute (short-term) bronchitis is spreadable via infected droplets that are coughed up. A person can become infected with bronchitis if the infected droplets are transmitted to their mouth, nose, or eyes.1
This means that you can get bronchitis by talking with an infected people if drops of respiratory fluid from them land near your mouth or eye. Bronchitis is also spreadable by kissing an infected person.
Not all types of bronchitis are transmittable. Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD says that bronchitis from smoking, breathing in dust, or other irritants causes a non-infectious cough. This may last for a few months or even longer.2
What is Bronchitis?
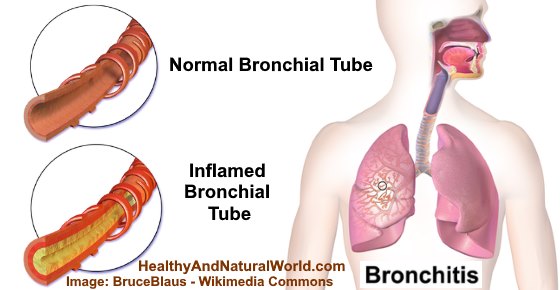
So, what exactly is bronchitis? Doctors from the Mayo Clinic explain that bronchitis is inflammation of the mucous membranes in your bronchial tubes. The inflamed bronchial lining produces a thick phlegm which may be yellowish or green. This often comes up when muscle spasms in the bronchia result in a cough.3
There are two types of bronchitis.
- Acute bronchitis. Generally caused by a viral or bacterial infection in the respiratory system that results in coughing up mucus for at least 5 days. Acute bronchitis is usually contagious.
- Chronic bronchitis. This non-contagious form of bronchitis is caused by breathing in irritants that results in chronic inflammation in the bronchial tubes. The cough from chronic bronchitis can last for years.
A persistent hacky cough that brings up sputum (mucus) is the main symptom of contagious and non-infectious bronchitis.
Symptoms of bronchitis
Clinical Professor, Dr. Charles Patrick Davis says that other symptoms of acute and chronic bronchitis can include:4
- A sore throat either from the flu virus or frequent coughing that irritates the back of your throat.
- A headache
- Blocked up nose and sinuses (from a cold or flu infection)
- Mild fever and chills because of a respiratory infection
- Chest discomfort from frequently coughing up phlegm
- Shortness of breath
- Night sweats
The severity of your bronchitis cough depends on the type of bronchitis you have and how severe the infection is.
Is Acute Bronchitis Contagious?
Yes, acute bronchitis is generally infectious which means that it is spreadable from person to person.
Doctors from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute say that the cold and flu viruses are usually to blame for acute bronchitis. The infections that cause bronchitis are transmitted the same way as the flu and cold viruses.5
The book Informed Health Online says, that if you have acute bronchitis, you should stay at home until you are no longer contagious to prevent spreading the infection.6
Is Chronic Bronchitis Contagious?
No, chronic bronchitis is not contagious because it is generally not caused by infectious germs in the respiratory system.
According to Dr. John M. Heath from the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, chronic bronchitis means that you have a chronic cough with mucus for over 3 months. The symptoms of chronic bronchitis may flare up occasionally, or they can affect you regularly, depending on the damage and inflammation in your bronchial tubes.7
The journal Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine says that chronic bronchitis is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Smoking is one of the biggest causes of long-term inflammation of the bronchia, and stopping smoking is required to address the symptoms of chronic bronchitis.8 Lung disease is just one of the ways that smoking damages your respiratory system.
Dr. John M. Heath (quoted earlier) says that other ways to manage the symptoms of long-term bronchitis include keeping well-hydrated, eating a balanced nutritious diet, and strengthening your respiratory muscles.7
What is Viral Bronchitis?
Viruses are one of the main reasons for bronchitis that lasts between 5 days and a few weeks. When discussing infections of the respiratory system, the book Medical Microbiology says that the common cold and influenza viruses usually result in lower respiratory or upper respiratory tract infections.9
One complication of viral bronchitis caused by the flu virus is pneumonia which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Enjoying a healthy diet with plenty of green leafy vegetables is one of the ways to strengthen your immune system and keep your lungs fit and healthy.
Is viral bronchitis contagious?
Yes. Respiratory tract inflammation caused by viruses causes contagious bronchitis that can be easily spread by close contact.
What is Bacterial Bronchitis?
Bronchitis caused by bacterial pathogens results in a persistent chesty cough that brings up discolored mucus or sputum.
According to the journal Canadian Family Physician, bronchitis caused by bacterial infections account for between 5% and 15% of all bronchial infections. Usually, you can get relief from an irritating cough by remedies that treat the symptoms of bacterial bronchitis.10
Is bacterial bronchitis contagious?
Just like with viral bronchitis, bacterial bronchitis is also infectious and contagious. The journal Canadian Family Physician says that it’s not possible to tell the difference between viral and bacterial bronchitis just from the color of sputum.10
Is Asthmatic Bronchitis Contagious?
No. Asthmatic bronchitis is not contagious because it is not caused by a bacterial or viral infection. According to the Journal of Family Practice, respiratory infections aren’t the only cause of acute bronchitis. The bronchial-like cough is caused by muscle spasms because of irritants that exacerbate the symptoms of asthma.11
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that can cause a bronchial-like cough with wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. The journal Deutsches Ärzteblatt International says that the term “bronchial asthma” refers to attacks of coughing and wheezing that asthma suffers have. Bronchial asthma can also cause a productive cough that brings up mucus from the airways.12
There are many natural remedies that can help relieve symptoms of asthma and other respiratory diseases. For example, many essential oils have properties that open up airways and make breathing easier.
How Long is Bronchitis Contagious?
Your infectious bronchitis may be contagious for up to a week. However, it can be difficult to tell exactly how long bronchitis is contagious because it can be symptomatic of hundreds of different viruses.
According to Dr. Charles Patrick Davis on MedicineNet, you are usually contagious for as long as you have cold or flu symptoms. Usually, as the severity of your symptoms diminishes, your bronchitis will be less contagious. Therefore, to prevent spreading bronchitis, you should assume that your cough is infectious as long as you have symptoms.4
Is Bronchitis Contagious After Taking Antibiotics
In some cases of bacterial bronchitis, doctors prescribe antibiotics to kill off the infection and prevent other pulmonary complications. Therefore, many people ask how long they will be infectious after starting antibiotics for bronchitis.
Doctors from the National Health Service explain that you will no longer be contagious around 24 hours after starting a course of antibiotics. However, the exact time bronchitis infections are infectious varies from person to person.
If you have taken a course of antibiotics, it’s important to take probiotics to help restore “healthy” bacteria to your gut. This can help to prevent gastrointestinal problems after antibiotics and lower your chances of a candida yeast infection.
How Long Does Bronchitis Last?
The symptoms of acute bronchitis can last as long as 20 days or so until the hacky cough goes completely. You may find that your cough lasts longer than the symptoms of your cold or flu that caused bronchitis in the first place.
Dr. Charles Patrick Davis on MedicineNet says that doctors class bronchitis as a cough that lasts at least 5 days. Usually, the average time that acute bronchitis lasts is anywhere between 10 and 20 days.4
How is Bronchitis Spread?
Bronchitis spreads via infectious sputum or mucus that enters the body of another person. Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD, explains that bronchitis is spread by the following ways:2
- Breathing in air that has droplets of infected respiratory fluid. For example, when in close contact with an infected person and talking with them.
- Touching surfaces that are infected and then touching your nose, eyes, or mouth.
- Somebody sneezes, coughs, or blows their nose near you.
Bronchitis vs. Cold
Bronchitis is a common complication of the common cold and is sometimes called a chest cold.
According to Dr. Jennifer Robinson on WebMD, if the cold virus affects your airways, mucus can build up due to inflammation. This irritation causes a “chesty cough” as your body tries to rid itself of the phlegm buildup.13
Bronchitis vs. Flu
The flu can cause infectious bronchitis that is easily transmissible to other people in close contact with the infected person.
Doctors from Cedars-Sinai say that bronchitis is often a symptom of the influenza virus. The acute hoarse cough can last longer than your other flu symptoms. In some cases, frequent upper respiratory infections can cause acute bronchitis to develop into chronic bronchitis.14
The difference between flu and cold symptoms are that the flu in general is worse than cold, and symptoms are more intense. Flu causes aches, chills, a fever, muscle or body aches, and general fatigue. Cold symptoms are milder and cause runny or stuffy nose. Bronchitis is more common if you have the flu rather than the common cold.15
Bronchitis vs. Pneumonia
It can be difficult to tell the difference between severe bronchitis and the symptoms of pneumonia. Viruses, bacterial infections, and fungi can also cause severe lung infections that lead to pneumonia.
According to an expert in primary care and internal medicine, Dr. Neha Pathak, pneumonia can cause a severe cough that may bring up yellowish or greenish mucus. Usually, the symptoms of pneumonia clear up within 3 weeks. However, for the elderly or very young, pneumonia can cause serious complications.16
Pneumonia causes many symptoms similar to bronchitis, however, pneumonia usually makes a person feel very fatigued and causes a high fever as well as a deep chesty cough.
According to doctors from the National Health Service, the germs, viruses, and bacteria that cause pneumonia are often highly contagious. They recommend not sharing cups or eating utensils, washing your hands regularly, and coughing or sneezing into a tissue can help prevent spreading respiratory infections.17
What Are the Best Home Remedies to Treat the Symptoms of Bronchitis?
Usually, the only way to treat bronchitis is to use remedies to ease its symptoms. According to the journal American Family Physician, many people use natural remedies to relieve symptoms of bronchitis.18
Eucalyptus oil is an effective way to treat the symptoms of contagious bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. Eucalyptus oil contains a compound called cineole. According to the journal Cough, cineole has proven results in treating bronchitis symptoms. Scientists found that symptoms of coughing, wheezing, and mucus were noticeably less after 4 days of treatment that included cineole.19
How to use eucalyptus oil for bronchitis:
- Mix 6 drops of eucalyptus oil, 3 drops of peppermint oil, and 3 drops of tea tree oil with 1 oz. sweet almond oil or other carrier oil.
- Put some of the home remedy on your chest and massage well until it’s absorbed into your skin.
- Cover your chest with a blanket to increase heat and allow the eucalyptus home remedy thin mucus buildup in your chest.
For information on other essential oils you can use, please see my article about the best essential oils for bronchitis. You can also try my great home recipe using pineapple as a cough syrup to help get rid of mucus from your throat naturally.
If your cold or flu has blocked up your sinuses, you can also use eucalyptus oil as a natural decongestant.
Natural Ways to relieve the symptoms of contagious bronchitis
Apart from using essential oils as a home remedy to ease your bronchial infection symptoms, there are some practical ways to make yourself feel better. Some ways to get symptomatic relief from bronchitis include:
- Rest at home. Getting plenty of rest will help your body fight the respiratory infection and speed up the healing time.20
- Stay hydrated. You also need to drink plenty of fluids to help thin mucus and make it easier to cough up. Dr. William Blahd on WebMD recommends drinking up to 12 glasses of water a day.21
- Take a hot shower. The steam from a hot shower can help to loosen mucus in your bronchial tubes and make it easier to cough it up.
- Avoid smoky environments. To help reduce the time bronchitis takes to heal, it’s important to avoid being in smoky or dusty environments. Continuing to breathe in irritants can cause acute contagious bronchitis to turn into chronic bronchitis.
Do You Need Antibiotics for Bronchitis?
You don’t need antibiotics to treat most cases of bronchitis because most causes of infectious bronchitis are the result of viral infections.
According to information published by PubMed Health, studies into using antibiotics to treat bronchitis have found that they are of limited, if any, help. It’s impossible to tell the difference clinically between viral bronchitis and bacterial bronchitis. Even though antibiotics could help slightly reduce the bronchial infection symptoms in some people, they cause gastrointestinal upset.22
The American Academy of Family Physicians reports that antibiotics for acute bronchitis are ineffective for viral infections and rarely relieve the symptoms of bacterial bronchitis.23
When to See a Doctor
The symptoms of acute bronchitis usually clear up on their own within a few weeks. You can also use effective home remedies to ease chest congestion quickly. However, if you still have a chesty cough after a few weeks, you should visit your doctor for a checkup.
There are a number of other symptoms of a severe bronchitis infection that means you should see a doctor. These include:20
- A fever of more than 100.4 °F (38 °C) for more than 3 days.
- A severe cough that lasts longer than 3 weeks and shows no sign of getting better.
- Coughing up mucus that has streaks of blood in it.
- You also experience chest pain.
- You have extreme fatigue and lightheadedness.
- You get frequent bouts of acute bronchitis.
Read my other related articles:
- Top 10 Scientifically Proven Essential Oils to Relieve Bronchitis
- This Fruit is 500% More Effective Than Cough Syrup
- Coughing Up Brown or Black Mucus: What It Means According to Science
Article Sources
