Matt Talbot
Matt Talbot | |
|---|---|
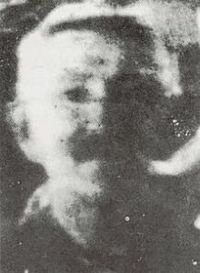 Portrait of Matt Talbot, from the only known photograph. | |
| Born | 2 May 1856 Dublin, Ireland |
| Died | 7 June 1925 (aged 69) Dublin, Ireland |
| Resting place | Our Lady of Lourdes Church, Seán McDermott Street, Dublin |
| Patronage |
|
| Major works | Piety, charity and mortification of the flesh |
Matthew Talbot (2 May 1856 – 7 June 1925) was an Irish ascetic revered by many Catholics for his piety, charity and mortification of the flesh.
Talbot was a manual labourer. Though he lived alone for most of his life, Talbot did live with his mother for a time.[2] His life would have gone unnoticed were it not for the cords and chains discovered on his body when he died suddenly on a Dublin street in 1925.
Though he has not yet been formally recognized as a saint, he has been declared Venerable and is considered a patron of those struggling with alcoholism.[1][3] He is commemorated on 19 June.[4]
Early life – alcoholism[edit]
Talbot was born on 2 May 1856 at 13 Aldborough Court, Dublin, Ireland,[5] the second eldest of twelve children of Charles and Elizabeth Talbot, a poor family in the North Strand area. He was baptized in St. Mary's Pro-Cathedral on 5 May.[6] His father and all but the oldest of his brothers were heavy drinkers. In 1868 Matt left school at the age of twelve and went to work in a wine merchant's store. He very soon began "sampling their wares", and was considered a hopeless alcoholic by age thirteen.[7] He then went to the Port & Docks Board where he worked in the whiskey stores. He frequented pubs in the city with his brothers and friends, spending most or all of his wages and running up debts.[8] When his wages were spent, he borrowed and scrounged for money. He pawned his clothes and boots to get money for alcohol. On one occasion, he stole a fiddle from a street entertainer and sold it to buy drink.[7]
"Taking the pledge"[edit]
One evening in 1884 28-year old Talbot, who was penniless and out of credit, waited outside a pub in the hope that somebody would invite him in for a drink. After several friends had passed him without offering to treat him, he went home in disgust and announced to his mother that he was going to "take the pledge" (renounce drink). He went to Holy Cross College, Clonliffe where he took the pledge for three months. At the end of the three months, he took the pledge for six months, then for life.[9]
Having drunk excessively for 16 years, Talbot maintained sobriety for the following forty years of his life. There is evidence that Talbot's first seven years after taking the pledge were especially difficult.[1] He found strength in prayer, began to attend daily Mass, and read religious books and pamphlets. He repaid all his debts scrupulously. Having searched for the fiddler whose instrument he had stolen, and having failed to find him, he gave the money to the church to have Mass said for him.
Working life[edit]
Even when his drinking was at its worst, Talbot was a hard worker. When he joined Pembertons, the building contractors, as a hod-carrier, his work-rate was such that he was put first on the line of hodmen to set the pace. Later, in Martin's timber yard, he took on the meanest and hardest jobs. He was respectful to his bosses but not obsequious, and on occasion stood up for a fellow-worker. On 22 September 1911 Talbot joined the builder's labourers branch of the Irish Transport and General Workers Union. When the Dublin Lockout of 1913 led to sympathy strikes throughout the city, the men of Martin's, including Talbot, came out.[8] At first Talbot refused his strike pay, saying that he had not earned it. Later he accepted it but asked that it be shared out among the other strikers. After his death a rumour was put about that he was a strike-breaker in 1913, but all the evidence contradicts this.[citation needed]
Spirituality[edit]

From being an indifferent Catholic in his drinking days, Talbot became increasingly devout. He lived a life of prayer, fasting, and service, trying to model himself on the sixth century Irish monks.[7] He was guided for most of his life by Michael Hickey, Professor of Philosophy in Clonliffe College. Under Hickey's guidance Talbot's reading became wider. He laboriously read scripture, the lives of saints, the Confessions of Saint Augustine, and the writings of Francis de Sales and others. When he found a part difficult to understand, he asked a priest to clarify it.[7]
Hickey also gave him a light chain, much like a clock chain, to wear as a form of penance.[7] He became a Third Order Franciscan in 1890 and was a member of several other associations and sodalities.[8] Talbot was a generous man. Although poor himself, he gave unstintingly to neighbours and fellow workers, to charitable institutions and the Church. He ate very little. After his mother's death in 1915 he lived in a small flat with very little furniture. He slept on a plank bed with a piece of timber for a pillow. He rose at 5 a.m. every day so as to attend Mass before work. At work, whenever he had spare time, he found a quiet place to pray. He spent most of every evening on his knees. On Sundays he attended several Masses. He walked quickly, with his head down, so that he appeared to be hurrying from one Mass to another.
Death[edit]
Talbot was on his way to Mass on Trinity Sunday, 7 June 1925, when he collapsed and died of heart failure on Granby Lane in Dublin. Nobody at the scene was able to identify him. His body was taken to Jervis Street Hospital, where he was undressed, revealing the extent of his austerities. A chain had been wound around his waist, with more chains around an arm and a leg, and cords around the other arm and leg.[8] The chains found on his body at death were not some extreme penitential regime but a symbol of his devotion to Mary, Mother of God that he wished to give himself to her totally as a slave.[10] Talbot's story quickly filtered through the community, and there were many spectators when his funeral took place at Glasnevin Cemetery on 11 June 1925. In 1972 his remains were removed to a tomb in Our Lady of Lourdes Church in Seán McDermott Street, Dublin, in the area where Tabot spent his life.[10]
Legacy and veneration[edit]
On 6 November 1931, Edward Joseph Byrne, Archbishop of Dublin, opened a sworn inquiry into the alleged claims of holiness of the former dock worker. Theologians approved his spiritual writings on 27 November 1937.[11] The Apostolic Process, the official sworn inquiry at the Vatican, began on 28 November 1947, granting Talbot the title of Servant of God.[11] On 3 October 1975 Pope Paul VI declared him to be Venerable Matt Talbot, which is a step on the road to his canonisation, a process which needs evidence of a physical miracle in order to be successful.[8] There is a particular devotion to Matt Talbot among some North American Roman Catholics[10] and in Australia among those involved in a ministry to achieve or maintain sobriety. An American Carmelite priest, Rev. Albert H. Dolan, founded the Matt Talbot Legion, "to aid alcoholics through prayer and the inspiration of Matt Talbott's example."[12] Dolan wrote two books about Matt Talbot: We Knew Matt Talbot: Visits with His Relatives and Friends (1948)[1] and Matt Talbot, Alcoholic: The Story of a Slave to Alcohol who Became a Comrade of Christ (1947).
Matt Talbot features in Brendan Behan’s autobiography Confessions of an Irish Rebel. Behan remembers that Talbot’s piety was widely mocked by ordinary working class Dubliners. Behan states that it was only after a concerted campaign by the Catholic Church and middle class business owners (concerned about work absenteeism due to alcoholism) that his legacy as a credible figure within the temperance movement was secured.[13]

Never be too hard on the man who can’t give up drink. It’s as hard to give up the drink as it is to raise the dead to life again. But both are possible and even easy for Our Lord. We have only to depend on him. — Matt Talbot[4]
As word of Matt Talbot spread, he rapidly became an icon for Ireland's Catholic temperance movement; the Pioneer Total Abstinence Association. His story soon became known to the large Irish diaspora communities. Many addiction clinics, youth hostels and statues have been named after him throughout the world. One of Dublin's main bridges is also named after him. A statue of Talbot was erected at Sir John Rogerson's Quay in 1988. Pope John Paul II, as a young man, wrote a paper on him.
The Matthew Talbot Hostel for homeless men in Sydney, Australia is named after him.
Graham Linehan has stated that the character of Matty Hislop in his comedy series Father Ted was intended to be a satire of Matt Talbot.[14] Derek Warfield of The Wolfe Tones recorded a song "Matt Talbot" about Talbot.[15]
Talbot's remains were removed from Glasnevin Cemetery to Our Lady of Lourdes Roman Catholic Church on Seán McDermott Street, Dublin in 1972. The tomb has a glass panel through which the coffin may be seen.
There is a small plaque in Granby Lane at the site of Matt Talbot's death. Prior to the current plaque on the Eastern side of the lane, a small brass cross was inlaid in a stone wall on the Western side of the lane.
In August 1971 Archbishop John Charles McQuaid unveiled a plaque to Talbot at a block of flats known as 'Matt Talbot Court' due to it being on the same site as one of Talbot's residences. President Éamon de Valera and Fine Gael leader Liam Cosgrave attended the ceremony.[16]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Leonard Foley OFM, "Venerable Matt Talbot", in Saint of the Day, Lives, Lessons, and Feast, (revised by Pat McCloskey OFM), Franciscan Media, ISBN 978-0-86716-887-7
- ^ 1911 Census of Dublin
- ^ Don Miller OFM, "Venerable Matt Talbot", Franciscan Media
- ^ a b LaPointe, Fr. Larry, "Matt Talbot", Connecticut College Archived 1 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ ""Matt Talbot", Diocese of Dublin". Archived from the original on 27 June 2013. Retrieved 15 March 2013.
- ^ "Venerable Matt Talbot, 1856 – 1925", St. Mary's Pro-Cathedral, Dublin
- ^ a b c d e "Venerable Matt Talbot (Patron of Struggling and Recovering Addicts and Alcoholics)", Archdiocese of Atlanta Archived 2 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c d e Boylan, Henry (1998). A Dictionary of Irish Biography, 3rd Edition. Dublin: Gill and MacMillan. p. 419. ISBN 0-7171-2945-4.
- ^ Talbot's pledge certificate from the "Total Abstinence League of Sacred Heart", 4 May 1890
- ^ a b c "Matt Talbot", Irish Bishop's Conference
- ^ a b Index ac status causarum beatificationis servorum dei et canonizationis beatorum (in Latin). Typis polyglottis vaticanis. January 1953. p. 172.
- ^ "Fr. Dolan, Founder of U.S. Little Flower Shrine, Dies". Catholic News Service - Newsfeeds. 29 January 1951. p. 8.
- ^ Confessions of an Irish Rebel (1965)
- ^ Writer's commentary to 'Cigarettes and Alcohol and Rollerblading', Father Ted – The Definitive Collection, 2 Entertain Video, 2002
- ^ "Matt Talbot Lyrics By Derek Warfield".
- ^ "Matt Talbot Court 1971". RTE Archives.
Bibliography[edit]
- Doherty, Eddie. Matt Talbot. Madonna House, 2nd edition 2001. ISBN 0-921440-67-7
- Glynn, Sir Joseph A. Matt Talbot. Dublin: Catholic Truth Society, 1924. Print.
- Marynard, Philip. Slake a Thirst: The Matt Talbot Way to Sobriety, Alba House 2000 ISBN 0-8189-0843-2
- Purcell, Mary. Matt Talbot and His Times. Franciscan Pr; Revised edition, 1977 ISBN 1-85390-185-7
- Wallace, Susan Helen. Matt Talbot: His Struggle, His Victory over Alcoholism, Pauline Books & Media 1992, ISBN 0-8198-4766-6
External links[edit]
- Matt Talbot, a biography by journalist Eddie Doherty
- Matt Talbot – the workers' saint at Catholic Ireland
- Irish Presidential Acknowledgement of the Matt Talbot Community at Clare County Library
- Venerable Matthew Talbot at Savior.org
- Patron Saints Index: Venerable Matt Talbot at Catholic Community Forum
- Venerable Matt Talbot at Catholic Online
