Let us consider, that you are sitting on your sofa watching TV, think about whether you are in motion or at rest. You are at rest. But let us re-evaluate a situation where the earth is in motion and we are sitting still. Finding the answer to such perplexing questions can be confusing. Before you gear up to find the answer to such complex questions, you must gather thorough knowledge about various types of motion. Here is a blog that aims to elucidate the same with examples that can help you in various competitive and entrance exams 410.
This Blog Includes:
What is Motion?
The free movement of a body concerning time is known as motion. For example fan, the dust falling from the carpet, the water that flows from the tap, a ball rolling around, a moving car etc. Even the universe is in continual motion. Are all these motions the same? Is the motion of a pendulum the same as that of a moving car or train? Various types of motions are happening around us and they can be distinguished based on:
- Time
- Speed
- Distance
- Path
Also Read: Basic Physics Formulas & Notes for Competitive Exams!
Types of Motion
As per physics and mechanics, there are mainly 4 types of motion, i.e.
- Rotary Motion: A special type of motion in which the object is on rotation around a fixed axis like, a figure skater rotating on an ice rink.
- Oscillatory Motion: A repeating motion in which an object continuously repeats in the same motion again and again like a swing.
- Linear Motion: A one-dimensional motion on a straight line, like an athlete running on a straight track.
- Reciprocating Motions: A repetitive and continuous up and down or back and forth motion like a needle in a sewing machine.
Also Read: Essay on Albert Einstein
There are also different other types of motion as per directions or as per state of motion.
Types of motion as per state
- Uniform Motion
- Non-Uniform Motion
Types of motion as per direction
- One Dimensional Motion
- Two Dimensional Motion
- Three Dimensional Motion
Other types of motion
- Translational Motion
- Periodic Motion
- Circular Motion
Here is a chart on types of motion:

Other Types of Motion
Below we have explained the major 7 types of motion as per Physics:
Oscillatory Motion
Oscillatory motion is simply the motion that an object does by repeating the same movement again and again. Oscillatory motion would keep on moving forever when there is an absence of friction but in our real world, the motion eventually stops and comes to an equilibrium. Some of the best examples of Oscillatory Motion are:
- A swinging swing
- The motion of a pendulum
- A boat tossing up and down a river
- The tuning fork
Rotational Motion
Rotational motion can be defined as when an object moves along its axis and all the parts of it move for a different distance in a given period. Thus, if an object is under rotational motion all of its parts will move different distances in the same interval of time. As an example, merry-go-round, blades of a fan, blades of a windmill etc.
Also Read: Physics Project for Class 12
Translational Motion
When all the parts of an object move the same distance in a given time is known as transitional motion. For example, a cycle moving on a track, a man walking on the road, birds flying in the sky.

Mainly, there are two types of translation motion which are explained below:
| Curvilinear Motion | Rectilinear Motion |
| When an object moving in translational motion follows a curved path it is known as Curvilinear motion. | An object moving in translation motion opts a straight-line path, then it is known as Rectilinear motion. |
| Example: A stone thrown up in the air | Example: A train moving on a straight track or a car moving on a straight road |
Also Read: Experiment With Diverse Career in Physics
Periodic Motion

A motion that repeats itself after equal intervals of time is known as periodic motion. Commonly, the objects under this motion are mostly in the to and fro motion. Here are a few examples of periodic motion.
- A moving pendulum
- Hands of a working clock
- the earth rotating on its axis, etc.
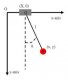
Also Read: List of Competitive Exams after 12th
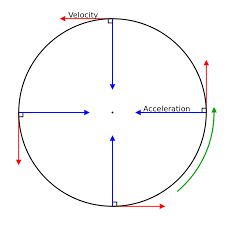
Circular Motion
When an object is constantly moving in circular a path it is called circular motion. It circular motion, the speed of the object should be constant. A few examples of circular motion are:
- Movement of the earth on its axis
- a bicycle or a car moving on a circular track of the park
- the motion of the moon around the earth etc.
Also Read: BSc Physics
Linear Motion
Linear motion can be defined as the movement of a body in a straight line without any deviation. Important examples of linear motion are:
- An athlete running on a straight track in a park
- a bullet shot from a pistol
Uniform Motion
A body is said to be in a state of uniform motion when it covers an equal amount of distance in equal intervals of time. In such cases, if we represent the motion on the graph, it would be a straight line. Examples of uniform motion are:
- A car moving on a straight road at a steady speed
- a flying aeroplane at a set height at a constant speed, etc

Non-Uniform Motion
Non-uniform motion can be defined as when a given body is covering unequal distances in a set and given intervals of time. If you represent the path of a body moving in non-uniform motion on a graph, it will be a curved line. Examples of non-uniform motion are:
- a man walking on the road
- a freely falling body
- a train moving at various speed limits, etc.
FAQs
General motion is the most common type of motion in sport and physical exercise.
All motions are relative to a reference frame. Saying that a body is at rest, or that it is not in motion, simply means that it is being described a frame of reference that is moving along with it.
Related Articles
We hope now you can differentiate between different types of motion! If you have any queries regarding careers, courses and universities abroad, let Leverage Edu be at your service. Book a free 30-minute session with us and get your doubts resolved!
-
It very very good
-
Nice

 One app for all your study abroad needs
One app for all your study abroad needs


















 25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.


12 comments
It very very good
Nice
I love this, thanks
Yea i understand a bit,little.im from Zimbabwe and currently doing physics.indeed this is helpful.
Thanks for reading.
Also, check: Motion in a Plane
Laws of Motion Class 11
Thanks for learning about motion.
Hi Moe!
Thank you for the comment! Check out these blogs-
https://leverageedu.com/blog/types-of-motion/
https://leverageedu.com/blog/physics-project-for-class-12/
loved the way it was explained. Thanks for the information.
Hi Rashmi, we are glad that you enjoyed our explanation and found the blog informative.
Alhamdulillah ! It’s very educative and helpful . Thanks a million.
I have been help alot using this website
thanks for your valuable feedback