The Countries In Asia
Need some geography help? Here's a list of all countries in Asia, with their capitals. List of Asian nations, which consists of Asian countries and capitals, can be found here. The list of Asian countries and list of Asian capitals is alphabetical. Countries that are Asian can also be sorted according to column. Whether you have a geography test to study for or you're simply curious about how many countries are in Asia, you can find them all right here.
- KabulAfghanistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located within South Asia and Central Asia. It has a population of approximately 31 million people, making it the 42nd most populous country in the world. It is bordered by Pakistan in the south and east; Iran in the west; Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan in the north; and China in the far northeast. Its territory covers 652,000 km², making it the 41st largest country in the world. Human habitation in Afghanistan dates back to the Middle Paleolithic Era, and the country's strategic location along the Silk Road connected it to the cultures of the Middle East and other parts of Asia. Through the ages the land has been home to various peoples and witnessed numerous military campaigns, notably by Alexander the Great, Muslim Arabs, Mongols, British, Soviet Russians, and in the modern-era by Western powers. The land also served as the source from which the Kushans, Hephthalites, Samanids, Saffarids, Ghaznavids, Ghorids, Khiljis, Mughals, Hotaks, Durranis, and others have risen to form major empires.More Afghanistan
- Dig Deeper...The Best Books About Afghanistan
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #157 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- YerevanArmenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a mountainous country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located in the north of Western Asia, it is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, the de facto independent Nagorno-Karabakh Republic and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south. Armenia is a unitary, multi-party, democratic nation-state with an ancient cultural heritage. The Satrapy of Armenia was established in the 6th century BC, after the fall of Urartu. In the first century BC the Kingdom of Armenia reached its height under Tigranes the Great. Armenia became the first state in the world to adopt Christianity as its official religion, in between late 3rd to early years of the 4th century, becoming the first Christian nation." An Armenian principality and later a kingdom, known as Cilician Armenia, existed on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea between the 11th and 14th centuries. Between the 16th and early 19th century, the traditional Armenian homeland composed of Eastern Armenia and Western Armenia came under rule of the rivaling Ottoman and Persian Empires, passing between the two over the centuries.More Armenia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Nations That Are 'Against' Death Penalty
- #110 of 232 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BakuAzerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a contiguous transcontinental presidential republic in the Caucasus region, situated at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west and Iran to the south. The exclave of Nakhchivan is bounded by Armenia to the north and east, Iran to the south and west, while having a short border with Turkey in the northwest. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence in 1918 and became the first Muslim-majority democratic and secular republic. It was also the first Muslim-majority country to have operas, theaters and modern universities. The country was incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1920 as the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic. Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence in October 1991, before the official dissolution of the USSR. Earlier, in September 1991, the disputed Armenian-majority Nagorno-Karabakh region re-affirmed its willingness to create a separate state as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic.More Azerbaijan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #78 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ManamaBahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is a small island country situated near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago with Bahrain Island, the largest land mass, at 55 km long by 18 km wide. Saudi Arabia lies to the west and is connected to Bahrain by the King Fahd Causeway while Iran lies 200 km to the north across the Persian Gulf. The peninsula of Qatar is to the southeast across the Gulf of Bahrain. The population in 2010 stood at 1,234,571, including 666,172 non-nationals. Bahrain is the site of the ancient land of the Dilmun civilisation. Bahrain was one of the earliest areas to convert to Islam in 628 AD. Following a period of Arab rule, Bahrain was occupied by the Portuguese in 1521, who in turn were expelled in 1602 by Shah Abbas I of the Safavid dynasty under the Persian Empire. In 1783, the Bani Utbah clan captured Bahrain from Nasr Al-Madhkur and has since been ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family, with Ahmed al Fateh as Bahrain's first hakim. In the late 1800s, following successive treaties with the British, Bahrain became a protectorate of the United Kingdom. In 1971, Bahrain declared independence.More Bahrain
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #186 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- DhakaBangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia; and is bordered by India to its west, north and east; Burma to its southeast and separated from Nepal and Bhutan by the Chicken’s Neck corridor. To its south, it faces the Bay of Bengal. Bangladesh is the world's eighth-most populous country, with over 160 million people, and among the most densely populated countries. It forms part of the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal, along with the neighbouring Indian states of West Bengal and Tripura. The present-day borders of Bangladesh took shape during the Partition of Bengal and British India in 1947, when the region came to be known as East Pakistan, as a part of the newly formed state of Pakistan. It was separated from West Pakistan by 1,400 km of Indian territory. Due to political exclusion, ethnic and linguistic discrimination and economic neglect by the politically dominant western wing, nationalism, popular agitation and civil disobedience led to the Bangladesh Liberation War and independence in 1971. After independence, the new state endured poverty, famine, political turmoil and military coups.More Bangladesh
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #203 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ThimphuBhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia at the eastern end of the Himalayas. It is bordered to the north by China and to the south, east and west by India. To the west, it is separated from Nepal by the Indian state of Sikkim, while farther south it is separated from Bangladesh by the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal. Bhutan's capital and largest city is Thimphu. At that time the lama and military leader Ngawang Namgyal, the first Zhabdrung Rinpoche, who was fleeing religious persecution in Tibet, unified the area and cultivated a distinct Bhutanese .More Bhutan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #19 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
British Indian Ocean Territory
The British Indian Ocean Territory is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 individual islands – many tiny – amounting to a total land area of 60 square kilometres. The largest and most southerly island is Diego Garcia, 44 km², the site of a joint military facility of the United Kingdom and the United States. Following the eviction of the native population, the Chagossians, in the 1960s and 70s, the only inhabitants are US and British military personnel and associated contractors, who collectively number around 4,000. The islands are off-limits to casual tourists, the media, and their former inhabitants. Mauritius sought to resume control over the Chagos Archipelago which was split from its territory by the UK in 1965 to form the British Indian Ocean Territory. Between 1968 and 1973, the Chagossians, then numbering about 2,000 people, were expelled by the British government to Mauritius and Seychelles to allow the United States to establish a military base on the island.- Bandar Seri BegawanBrunei officially the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace, is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its coastline with the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the state of Sarawak, Malaysia; and it is separated into two parts by the Sarawak district of Limbang. It is the only sovereign state completely on the island of Borneo; the remainder of the island's territory is divided between the nations of Malaysia and Indonesia. Brunei's population was 408,786 in July 2012. At the peak of Bruneian Empire, Sultan Bolkiah is alleged to have had control over most regions of Borneo, including modern-day Sarawak and Sabah, as well as the Sulu archipelago off the northeast tip of Borneo, Seludong, and the islands off the northwest tip of Borneo. The maritime state was visited by Spain's Magellan Expedition in 1521 and fought against Spain in 1578's Castille War. During the 19th century, the Bruneian Empire began to decline. The Sultanate ceded Sarawak to James Brooke and installed him as the White Rajah, and it ceded Sabah to the British North Borneo Chartered Company.More Brunei
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #112 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Phnom PenhCambodia, officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia and once known as the Khmer Empire, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Its total landmass is 181,035 square kilometres, bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, and the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. With a population of over 15 million, Cambodia is the 69th most populous country in the world. The official religion is Theravada Buddhism, practiced by approximately 95 percent of the population. The country's minority groups include Vietnamese, Chinese, Chams, and 30 hill tribes. The capital and largest city is Phnom Penh, the political, economic, and cultural center of Cambodia. The kingdom is a constitutional monarchy with Norodom Sihamoni, a monarch chosen by the Royal Throne Council, as head of state. The head of government is Hun Sen, who is currently the longest serving non-royal leader in South East Asia and has ruled Cambodia for over 25 years. Cambodia's ancient name is "Kambuja".More Cambodia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #76 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BeijingChina, officially the People's Republic of China, is a sovereign state located in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population of over 1.35 billion. The PRC is a single-party state governed by the Chinese Communist Party, with its seat of government in the capital city of Beijing. It exercises jurisdiction over 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four direct-controlled municipalities, and two mostly self-governing special administrative regions. The PRC also claims the territories governed by the Republic of China, a separate political entity commonly known as Taiwan, as a part of its territory, which includes the island of Taiwan as Taiwan Province, Kinmen and Matsu as a part of Fujian Province and islands the ROC controls in the South China Sea as a part of Hainan Province. These claims are controversial due to the complex political status of Taiwan. Covering approximately 9.6 million square kilometers, China is the world's second-largest country by land area, and either the third or fourth-largest by total area, depending on the method of measurement.More China
- Dig Deeper...Frightening Facts About the Chinese Military
- And Deeper...The 40+ Best Documentaries On China, Ranked
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- Flying Fish CoveThe Territory of Christmas Island is a territory of Australia in the Indian Ocean, composed solely of that island. It has a population of 2,072 residents who live in a number of "settlement areas" on the northern tip of the island: Flying Fish Cove, Silver City, Poon Saan, and Drumsite. The majority of the population are Chinese Australian. It is called "Christmas Island" because it was discovered on Christmas Day. The island's geographic isolation and history of minimal human disturbance has led to a high level of endemism among its flora and fauna, which is of interest to scientists and naturalists. 63% of its 135 square kilometres is an Australian national park. There exist large areas of primary monsoonal forest. Phosphate, deposited originally as guano, has been mined on the island for many years.More Christmas Island
- #42 of 57 onThe Best Asian Countries to Visit
- #149 of 217 onThe Best Countries to Travel To
- #50 of 56 onThe Best Island Honeymoon Destinations
- West Island, Cocos (Keeling) IslandsThe Territory of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, also called Cocos Islands and Keeling Islands, is a territory of Australia, located in the Indian Ocean, southwest of Christmas Island and approximately midway between Australia and Sri Lanka. The territory consists of two atolls and 27 coral islands, of which two, West Island and Home Island, are inhabited with a total population of approximately 600.
- NicosiaCyprus, officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Cyprus is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, and a member state of the European Union. It is located south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel, north of Egypt and east of Greece. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains from this period include the well-preserved Neolithic village of Khirokitia, and Cyprus is home to some of the oldest water wells in the world. Cyprus was settled by Mycenaean Greeks in two waves in the 2nd millennium BC. At a strategic location in the Middle East, it was subsequently occupied by several major powers, including the empires of the Assyrians, Egyptians and Persians, from whom the island was seized in 333 BC by Alexander the Great. Subsequent rule by Ptolemaic Egypt, the Classical and Eastern Roman Empire, Arab caliphates for a short period, the French Lusignan dynasty and the Venetians, was followed by over three centuries of Ottoman rule between 1571 and 1878.More Cyprus
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...36 Countries with Universal Healthcare
- #52 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- TbilisiGeorgia is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres, and its population is almost 5 million. Georgia is a unitary, semi-presidential republic, with the government elected through a representative democracy. During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia. The kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia adopted Christianity in the early 4th century. A unified Kingdom of Georgia reached the peak of its political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 11th–12th centuries. Thereafter the area was dominated by various large empires, including the Safavids, Afsharids, and Qajar Persians. In the late 18th century, the kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti forged an alliance with the Russian Empire, and the area was annexed by Russia in 1801.More Georgia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Nations That Are 'Against' Death Penalty
- #26 of 232 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Hong Kong, officially known as Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China, is a city on the southern coast of China at the Pearl River Estuary and the South China Sea. Hong Kong is well known for its expansive skyline, deep natural harbour and extreme population density. The current population of Hong Kong comprises 93.6% ethnic Chinese. A major part of Hong Kong's Cantonese-speaking majority originated from the neighbouring Canton province, from where skilled labour fled after the communist government took over China in 1949 and subsequently purged its population during the 1960s. After China's defeat in the First Opium War against the British Empire, Hong Kong became a British colony with the perpetual cession of Hong Kong Island, followed by Kowloon Peninsula in 1860 and a 99-year lease of the New Territories in 1898. After it was occupied by Japan during the Second World War, the British resumed control until 30 June 1997. As a result of the negotiations between China and Britain, Hong Kong was transferred to the People's Republic of China under the 1984 Sino-British Joint Declaration.More Hong Kong
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #65 of 130 onThe Most Beautiful Cities In The World
- New DelhiIndia, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the south-west, and the Bay of Bengal on the south-east, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north-east; and Burma and Bangladesh to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia. Home to the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation and a region of historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian subcontinent was identified with its commercial and cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism—originated here, whereas Zoroastrianism and the abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam arrived in the 1st millennium CE and also helped shape the region's diverse culture.More India
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Computers In Use: World's Top 15 Countries In PC Usage
- #30 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- JakartaIndonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a sovereign state in Southeast Asia. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising thousands of islands. With an estimated total population of over 252 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most-populous country. Indonesia's republican form of government comprises an elected legislature and president. It encompasses 34 provinces, of which five have Special Administrative status. The nation's capital city is Jakarta. The country shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and Malaysia. Other neighbouring countries include Singapore, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and the Indian territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Indonesia is a founding member of ASEAN and a member of the G-20 major economies. The Indonesian economy is the world's 17th largest by nominal GDP. The Indonesian archipelago has been an important trade region since at least the 7th century, when Srivijaya and then later Majapahit traded with China and India. Local rulers gradually absorbed foreign cultural, religious and political models from the early centuries CE, and Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms flourished.More Indonesia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #208 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- TehranIran, also known as Persia, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered to the northwest by Armenia, the de facto independent Nagorno-Karabakh Republic, and Azerbaijan; with Kazakhstan and Russia across the Caspian Sea; to the northeast by Turkmenistan; to the east by Afghanistan and Pakistan; to the south by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman; and to the west by Turkey and Iraq. Comprising a land area of 1,648,195 km², it is the second-largest nation in the Middle East and the 18th-largest in the world; with 78.4 million inhabitants, Iran is the world's 17th most populous nation. It is the only country that has both a Caspian Sea and Indian Ocean coastline. Iran has been of geostrategic importance because of its central location in Eurasia and Western Asia and the Strait of Hormuz. Iran is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Proto-Elamite and Elamite kingdom in 3200–2800 BC. The Iranian Medes unified the country into the first of many empires in 625 BC, after which it became the dominant cultural and political power in the region.More Iran
- Dig Deeper...31 Celebrities Who Are Persian
- And Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From Iran
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
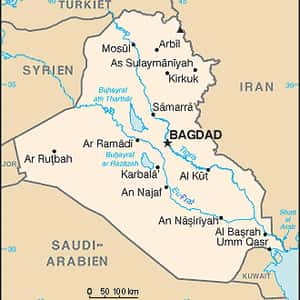
- BaghdadIraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in Western Asia. The country borders Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to the southwest, and Syria to the west. The southern part of Iraq is within the Arabian Peninsula. The capital, Baghdad, is in the center of the country and its largest city. The largest ethnic groups in Iraq are Arabs and Kurds. Other ethnic groups include Assyrians, Turkmen, Shabakis, Armenians, Mandeans, Circassians and Kawliya. Around 95% of the country's 36 million citizens are Shia or Sunni Muslims, with Christianity, Yarsan, Yezidism and Mandeanism also present. Iraq has a narrow section of coastline measuring 58 km on the northern Persian Gulf and its territory encompasses the Mesopotamian Alluvial Plain, the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, and the eastern part of the Syrian Desert. Two major rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, run south through the center of Iraq and flow into the Shatt al-Arab near the Persian Gulf. These rivers provide Iraq with significant amounts of fertile land.More Iraq
- Dig Deeper...The 40+ Best Iraq War Movies
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #200 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- JerusalemIsrael or, officially the State of Israel, is a country in Western Asia, situated at the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea. It shares land borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria in the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories comprising the West Bank and Gaza Strip on the east and southwest, respectively, and Egypt and the Gulf of Aqaba in the Red Sea to the south. It contains geographically diverse features within its relatively small area. Israel's financial center is Tel Aviv, while Jerusalem is both its designated capital and the most populous individual city under the country's governmental administration. Israeli sovereignty over Jerusalem is internationally disputed. On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly recommended the adoption and implementation of the Partition Plan for Mandatory Palestine. Borders for a new Jewish state were specified by the UN but ultimately not recognized by either Israel or neighboring countries. The end of the British Mandate for Palestine was set for midnight on 14 May 1948.More Israel
- TokyoJapan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. The Kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and Japan is often called "Land of the Rising Sun". Japan is a stratovolcanic archipelago of 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku, which make up about ninety-seven percent of Japan's land area. Japan's population of 126 million is the world's tenth largest. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes the de facto capital of Tokyo and several surrounding prefectures, is the world's largest metropolitan area, with over 30 million residents. Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period. The first written mention of Japan is in Chinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly Imperial China, followed by periods of isolation, later from Western European influence, has characterized Japan's history.More Japan
- AmmanJordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is an Arab kingdom in the Middle East, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north, and Israel and Palestine to the west. After the post-World War I division of West Asia by Britain and France, the Emirate of Transjordan was officially recognized by the Council of the League of Nations in 1922. In 1946, Jordan became an independent sovereign state officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Transjordan. After capturing the West Bank during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Abdullah I took the title King of Jordan. The name of the state was changed to The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan on 1 December 1948. Although Jordan is a constitutional monarchy, the king holds wide executive and legislative powers. Jordan is classified as a country of "high human development" by the 2014 Human Development Report. Jordan has an "upper middle income" economy. Jordan enjoys "advanced status" with the European Union since December 2010, and it is a member of the Euro-Mediterranean free trade area.More Jordan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #202 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
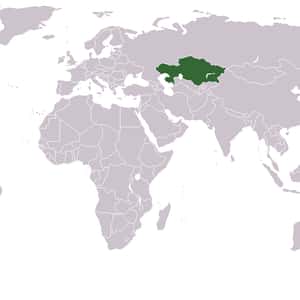
- AstanaKazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a country in Central Asia, with its smaller part west of the Ural River in Europe. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country by land area and the ninth largest country in the world; its territory of 2,724,900 square kilometres is larger than Western Europe. It has borders with Russia, China, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, and also adjoins a large part of the Caspian Sea. The terrain of Kazakhstan includes flatlands, steppe, taiga, rock canyons, hills, deltas, snow-capped mountains, and deserts. With an estimated 17 million people as of 2013 Kazakhstan is the 61st most populous country in the world, though its population density is among the lowest, at less than 6 people per square kilometre. The capital is Astana, where it was moved from Almaty in 1997. The territory of Kazakhstan has historically been inhabited by nomadic tribes. This changed in the 13th century, when Genghis Khan occupied the country. Following internal struggles among the conquerors, power eventually reverted to the nomads. By the 16th century, the Kazakhs emerged as a distinct group, divided into three jüz.More Kazakhstan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Nations That Are 'Against' Death Penalty
- #33 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- SeoulSouth Korea, officially the Republic of Korea, and commonly referred to as Korea, is a sovereign state in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula. The name Korea is derived from the Kingdom of Goryeo, also spelled as Koryŏ. It shares land borders with North Korea to the north, and oversea borders with Japan to the east and China to the west. Roughly half of the country's 50 million people reside in the metropolitan area surrounding its capital, the Seoul Capital Area, which is the second largest in the world with over 25 million residents. Korea was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period and its civilization began with the founding of Gojoseon. After the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea in 668, Korea enjoyed over a millennium of relative tranquility under dynasties lasting for centuries in which its trade, culture, literature, science and technology flourished. In 1910 it was annexed by the Japanese Empire, after whose surrender in 1945, Korea was divided into Soviet and U.S. zones of occupation, with the latter becoming the Republic of Korea in August 1948.More South Korea
- Dig Deeper...The Best K-pop Boy Groups Of All Time
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #12 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
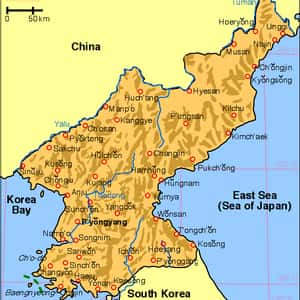
- PyongyangNorth Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, is a country in East Asia, in the northern part of the Korean Peninsula. The capital and largest city is Pyongyang. North Korea shares a land border with China to the north and north-west, along the Amnok and Tumen rivers. A small section of the Tumen River also forms North Korea's border with Russia to the northeast. The Korean Demilitarized Zone marks the boundary between North Korea and South Korea. The legitimacy of this border is not accepted by either side, as both states claim to be the legitimate government of the entire peninsula.More North Korea
- Dig Deeper...Here's Why Korea Became Two Different Countries
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #101 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Kuwait CityKuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is an Arab country in Western Asia. Situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, it shares borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia. As of 2014, Kuwait has a population of 4.1 million people; 1.2 million are Kuwaitis and 2.8 million are expatriates. During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Kuwait was a prosperous trade hub. Starting in the early 20th century, its regional economic importance declined, and by 1934 Kuwait had lost its prominence in long-distance trade. Kuwait's economy was devastated by several trade blockades. During World War I, the British Empire imposed a blockade against Kuwait because its ruler supported the Ottoman Empire. Following the Kuwait–Najd War of 1919–1920, Saudi Arabia maintained a trade blockade against the country from 1923 until 1937. In 1990, Kuwait was invaded by Iraq. The Iraqi occupation came to an end in 1991 after military intervention by United States-led forces. Kuwait is a constitutional emirate with an elected parliamentary system. Kuwait has a petroleum-based economy.
- BishkekKyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, formerly known as Kirghizia, is a country located in Central Asia. Landlocked and mountainous, Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the southwest and China to the east. Its capital and largest city is Bishkek. Kyrgyzstan's history spans over 2,000 years, encompassing a variety of cultures and empires. Although geographically isolated by its highly mountainous terrain – which has helped preserve its ancient culture – Kyrgyzstan has historically been at the crossroads of several great civilizations, namely as part of the Silk Road and other commercial and cultural routes. Though long inhabited by a succession of independent tribes and clans, Kyrgyzstan has periodically come under foreign domination due to its strategic location, attaining sovereignty as a nation-state only after the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991. Since independence, Kyrgyzstan has officially been a unitary parliamentary republic, although it continues to endure ethnic conflicts, revolts, economic troubles, transitional governments, and political party conflicts.More Kyrgyzstan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #102 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- VientianeLaos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south, and Thailand to the west. Since 1975, it has been ruled by a Marxist and communist government. Its population was estimated to be around 6.8 million in July 2014.More Laos
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #201 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BeirutLebanon, officially the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south. Lebanon's location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has dictated its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious and ethnic diversity. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back more than seven thousand years, predating recorded history. Lebanon was the home of the Phoenicians and their kingdom, a maritime culture that flourished for over a thousand years. In 64 BC, the region came under the rule of the Roman Empire, and eventually became one of the Empire's leading centers of Christianity. In the Mount Lebanon range a monastic tradition known as the Maronite Church was established. As the Arab Muslims conquered the region, the Maronites held onto their religion and identity. However, a new religious group, the Druze, established themselves in Mount Lebanon as well, a religious divide that would last for centuries. During the Crusades, the Maronites re-established contact with the Roman Catholic Church and asserted their communion with Rome.More Lebanon
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #57 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Macau, also spelled Macao, is one of the two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China, the other being Hong Kong. Macau lies on the western side of the Pearl River Delta across from Hong Kong, which is about 64 kilometers to the east, and it is also bordered by Guangdong Province to the north and the South China Sea to the east and south. With an estimated population of around 636,200 living in an area of 30.3 km², it is the most densely populated region in the world. A former Portuguese colony, Macau was administered by Portugal from the mid-16th century until late 1999, when it was the last remaining European colony in Asia. Portuguese traders first settled in Macau in the 1550s. In 1557, Macau was rented to Portugal by the Ming Dynasty as a trading port. The Portuguese administered the city under Chinese authority and sovereignty until 1887, when Macau became a colony of the Portuguese Empire. Sovereignty over Macau was transferred back to China on 20 December 1999. The Sino-Portuguese Joint Declaration and the Basic Law of Macau stipulate that Macau operate with a high degree of autonomy until at least 2049, fifty years after the transfer.