1649 in England
Last updated
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | Other events of 1649 | ||||
Events from the year 1649 in England . The Second English Civil War ends and the Third English Civil War begins.
Contents
Incumbents
Events
- 3 January – An explosion of several barrels of gunpowder in Tower Street, London kills 67 people and destroys 60 houses. [1] [2]
- 4 January – The Rump Parliament passes an ordinance to set up a High Court of Justice for the trial of Charles I for high treason in the name of the people of England.
- 20 to 27 January – Trial and conviction of King Charles I by the High Court of Justice convened in Westminster Hall. [3]
- 30 January
- King Charles is beheaded outside the Banqueting House, Whitehall. [4]
- Prince Charles Stuart declares himself King Charles II of England, Scotland and Ireland. At this time none of the three Kingdoms have recognised him as ruler. Parliament this day has passed an "Act prohibiting the proclaiming any person to be King of England or Ireland, or the Dominions thereof".
- HMS Garland (of Topsham), carrying some of the royal possessions into exile, is wrecked in St Ives Bay (Cornwall) with only 2 survivors of about sixty passengers and crew. [5]
- 9 February – Eikon Basilike: the Pourtrature of His Sacred Majestie in His Solitudes and Sufferings, purporting to be the spiritual autobiography of Charles I, is published.
- 23 February – Ships of the Parliamentary navy are to fly the flag of England. [6]
- 17 March – The Rump Parliament formally abolishes the English monarchy by passing an act abolishing the kingship [3] creating the Commonwealth of England, a republican form of government later extended to Scotland and Ireland.
- 19 March – The House of Commons passes an act abolishing the House of Lords, declaring that it is "useless and dangerous to the people of England". [3]
- March – Robert Blake is promoted to become a General at Sea of the English fleet. [7]
- April – Bishopsgate mutiny: Soldiers of the New Model Army refuse to leave London – some are court martialled and one executed.
- 2 May – Lawyer and regicide Sir Isaac Dorislaus, while in The Hague to negotiate an alliance with the Dutch Republic, is murdered by royalist exiles. [8]
- 17 May – Banbury mutiny ends – leaders of the Leveller mutineers in the New Model Army are hanged at Burford.
- 19 May – An act declaring England to be a Commonwealth is passed by the Rump Parliament.
- 22 May–October – Robert Blake blockades Prince Rupert's fleet in Kinsale, Ireland.
- August – The Diggers abandon their last major colony, at St. George's Hill, Weybridge.
- 15 August – Oliver Cromwell lands in Dublin to begin the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland.
- 3–11 September – Siege of Drogheda in Ireland: Cromwell's New Model Army massacres the Irish Catholic Confederation garrison. [4]
- 2–11 October – Sack of Wexford in Ireland: New Model Army massacres the Irish Catholic Confederation garrison.
- October – John Milton's Eikonoklastes: in Answer to a Book Intitl'd Eikon Basilike, a defence of the execution of Charles I, is published.
Births
- 23 February (bapt.) – John Blow, composer and organist (died 1708)
- 9 April – James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth, claimant to the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland (died 1685)
- 15 September – Titus Oates, minister and plotter (died 1705)
Deaths
- 30 January – King Charles I of England, Scotland, and Ireland (executed) (born 1600 in Scotland) [9]
- 9 March
- James Hamilton, 1st Duke of Hamilton (executed) (born 1606)
- Henry Rich, 1st Earl of Holland, soldier (executed) (born 1590)
- 26 March – John Winthrop First Governor of Massachusetts Bay Colony (born c. 1587)
- 11 July – Susanna Hall, daughter and heir of William Shakespeare (born 1583)
- 6 September – Robert Dudley, styled Earl of Warwick, explorer and geographer (born 1574)
- 15 September – John Floyd, Jesuit preacher (born 1572)
Related Research Articles

The Commonwealth was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when England and Wales, later along with Ireland and Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the trial and execution of Charles I. The republic's existence was declared through "An Act declaring England to be a Commonwealth", adopted by the Rump Parliament on 19 May 1649. Power in the early Commonwealth was vested primarily in the Parliament and a Council of State. During the period, fighting continued, particularly in Ireland and Scotland, between the parliamentary forces and those opposed to them, in the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland and the Anglo-Scottish war of 1650–1652.

The Long Parliament was an English Parliament which lasted from 1640 until 1660. It followed the fiasco of the Short Parliament, which had convened for only three weeks during the spring of 1640 after an 11-year parliamentary absence. In September 1640, King Charles I issued writs summoning a parliament to convene on 3 November 1640. He intended it to pass financial bills, a step made necessary by the costs of the Bishops' Wars against Scotland. The Long Parliament received its name from the fact that, by Act of Parliament, it stipulated it could be dissolved only with agreement of the members; and those members did not agree to its dissolution until 16 March 1660, after the English Civil War and near the close of the Interregnum.

Oliver Cromwell was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in the history of the British Isles. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially as a senior commander in the Parliamentarian army and latterly as a politician. A leading advocate of the execution of Charles I in January 1649, which led to the establishment of The Protectorate, he ruled as Lord Protector from December 1653 until his death in September 1658. Cromwell remains a controversial figure due to his use of the army to acquire political power, and the brutality of his 1649 campaign in Ireland.

.

The Protectorate, officially the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, was the English form of government lasting from 16 December 1653 to 25 May 1659, under which the kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland, with their associated territories were joined together in the Commonwealth of England, governed by a Lord Protector. It began when Barebone's Parliament was dissolved, and the Instrument of Government appointed Oliver Cromwell as Lord Protector of the Commonwealth. Cromwell died in September 1658 and was succeeded by his son Richard Cromwell.

Major-General William Goffe, probably born between 1613 and 1618, died c. 1679/1680, was an English Parliamentarian soldier who served with the New Model Army during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A religious radical nicknamed “Praying William” by contemporaries, he approved the Execution of Charles I in January 1649, and later escaped prosecution as a regicide by fleeing to New England.

Pride's Purge is the name commonly given to an event that took place on 6 December 1648, when soldiers prevented members of Parliament considered hostile to the New Model Army from entering the House of Commons of England.

The Rump Parliament was the English Parliament after Colonel Thomas Pride commanded soldiers to purge the Long Parliament, on 6 December 1648, of those members hostile to the Grandees' intention to try King Charles I for high treason.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1649.

The Wars of the Three Kingdoms, sometimes known as the British Civil Wars, were a series of intertwined conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 Bishops' Wars, the First and Second English Civil Wars, the Irish Confederate Wars, the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland and the Anglo-Scottish War of 1650–1652. They resulted in victory for the Parliamentarian army, the execution of Charles I, the abolition of monarchy, and founding of the Commonwealth of England, a unitary state which controlled the British Isles until the Stuart Restoration in 1660.
This is a timeline of events leading up to, culminating in, and resulting from the English Civil Wars.

The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland or Cromwellian war in Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the forces of the English Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Cromwell invaded Ireland with the New Model Army on behalf of England's Rump Parliament in August 1649.

The English Council of State, later also known as the Protector's Privy Council, was first appointed by the Rump Parliament on 14 February 1649 after the execution of King Charles I.
The Interregnum was the period between the execution of Charles I on 30 January 1649 and the arrival of his son Charles II in London on 29 May 1660 which marked the start of the Restoration. During the Interregnum, England was under various forms of republican government.
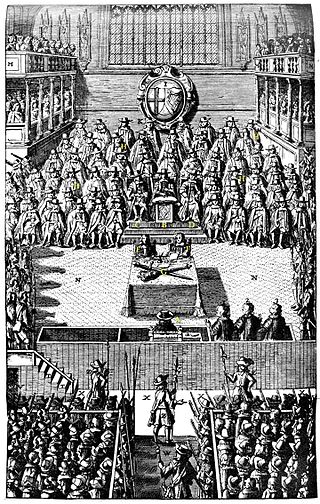
The High Court of Justice was the court established by the Rump Parliament to try Charles I, King of England, Scotland and Ireland. Even though this was an ad hoc tribunal that was specifically created for the purpose of trying the king, its name was eventually used by the government as a designation for subsequent courts.

William Levett, Esq., was a long serving courtier to King Charles I of England. Levett accompanied the King during his flight from Parliamentary forces, including his escape from Hampton Court palace, and eventually to his imprisonment in Carisbrooke Castle on the Isle of Wight, and finally to the scaffold on which he was executed. Following the King's death, Levett wrote a letter claiming that he had witnessed the King writing the so-called Eikon Basilike during his imprisonment, an allegation that produced a flurry of new claims about the disputed manuscript and flamed a growing movement to rehabilitate the image of the executed monarch.

The Instrument of Government was a constitution of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland. Drafted by Major-General John Lambert in 1653, it was the first sovereign codified and written constitution in England.

Charles Fleetwood, c. 1618 to 4 October 1692, was an English lawyer from Northamptonshire, who served with the Parliamentarian army during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A close associate of Oliver Cromwell, to whom he was related by marriage, Fleetwood held a number of senior political and administrative posts under the Commonwealth, including Lord Deputy of Ireland from 1652 to 1655.
The Treasons Act 1649 or Act declaring what offences shall be adjudged Treason was passed on 17 July 1649 by the Rump Parliament during the Commonwealth of England. It superseded the Act declaring what offences shall be adjudged Treason passed about two months earlier on 14 May 1649.

The Reliquiae Sacrae Carolinae, or The Works of That Great Monarch and Glorious Martyr King Charls the I, is a book that deals with the events leading to the execution of Charles I of England. Originally published in 1650, it is a collective work of the civil and sacred writings on the King. It incorporates the Eikon Basilike as well as speeches and letters by the King during the rise of Oliver Cromwell and the Parliamentarians. It is sometimes referred to as "The King's Works".
References
- ↑ Munsell, Joel (1858). The Every Day Book of History and Chronology. D. Appleton & Co.
- ↑ "BBC London, Features, Tower Street". Archived from the original on 25 February 2006. Retrieved 5 December 2007.
- 1 2 3 Palmer, Alan; Palmer, Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 185–186. ISBN 978-0-7126-5616-0.
- 1 2 Penguin Pocket On This Day. Penguin Reference Library. 2006. ISBN 978-0-14-102715-9.
- ↑ "HMS Garland (+1649)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- ↑ Groom, Nick (2007). The Union Jack: the story of the British flag (Paperback ed.). London: Atlantic Books. p. 145. ISBN 978-1-84354-337-4.
- ↑ Baumber, Michael (2004). "Blake, Robert (bap. 1598, d. 1657)" . Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/2582 . Retrieved 24 August 2010.(Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ Todd, Margo (2004). "Dorislaus, Isaac (1595–1649)" . Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/7832.(Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ "Charles I | Accomplishments, Execution, Successor, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.