参考:
- cocodataset/cocoapi
- philferriere/cocoapi- support Windows build and python3
- COCO 标注详解
- COCO数据集annotation内容
- Dataset - COCO Dataset 数据特点
完整代码点击此处
JSON文件
json文件主要包含以下几个字段:
详细描述参考 COCO 标注详解
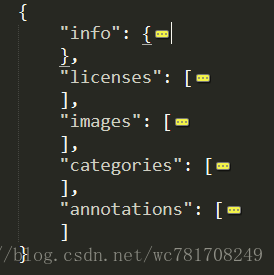
{
"info": info, # dict
"licenses": [license], # list ,内部是dict
"images": [image], # list ,内部是dict
"annotations": [annotation], # list ,内部是dict
"categories": # list ,内部是dict
}打开JSON文件查看数据特点
由于JSON文件太大,很多都是重复定义的,所以只提取一张图片,存储成新的JSON文件,便于观察。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
import os, sys, zipfile
import urllib.request
import shutil
import numpy as np
import skimage.io as io
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab
import json
json_file='./annotations/instances_val2017.json' # # Object Instance 类型的标注
# person_keypoints_val2017.json # Object Keypoint 类型的标注格式
# captions_val2017.json # Image Caption的标注格式
data=json.load(open(json_file,'r'))
data_2={}
data_2['info']=data['info']
data_2['licenses']=data['licenses']
data_2['images']=[data['images'][0]] # 只提取第一张图片
data_2['categories']=data['categories']
annotation=[]
# 通过imgID 找到其所有对象
imgID=data_2['images'][0]['id']
for ann in data['annotations']:
if ann['image_id']==imgID:
annotation.append(ann)
data_2['annotations']=annotation
# 保存到新的JSON文件,便于查看数据特点
json.dump(data_2,open('./new_instances_val2017.json','w'),indent=4) # indent=4 更加美观显示Object Instance 类型的标注格式
主要有以下几个字段:
info
"info": { # 数据集信息描述
"description": "COCO 2017 Dataset", # 数据集描述
"url": "http://cocodataset.org", # 下载地址
"version": "1.0", # 版本
"year": 2017, # 年份
"contributor": "COCO Consortium", # 提供者
"date_created": "2017/09/01" # 数据创建日期
},licenses
"licenses": [
{
"url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/",
"id": 1,
"name": "Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License"
},
……
……
],images
"images": [
{
"license": 4,
"file_name": "000000397133.jpg", # 图片名
"coco_url": "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000397133.jpg",# 网路地址路径
"height": 427, # 高
"width": 640, # 宽
"date_captured": "2013-11-14 17:02:52", # 数据获取日期
"flickr_url": "http://farm7.staticflickr.com/6116/6255196340_da26cf2c9e_z.jpg",# flickr网路地址
"id": 397133 # 图片的ID编号(每张图片ID是唯一的)
},
……
……
],categories
"categories": [ # 类别描述
{
"supercategory": "person", # 主类别
"id": 1, # 类对应的id (0 默认为背景)
"name": "person" # 子类别
},
{
"supercategory": "vehicle",
"id": 2,
"name": "bicycle"
},
{
"supercategory": "vehicle",
"id": 3,
"name": "car"
},
……
……
],注: bicycle 与car都属于vehicle,但两者又属于不同的类别。例如:羊(主类别)分为山羊、绵羊、藏羚羊(子类别)等
annotations
"annotation": [
{
"segmentation": [ # 对象的边界点(边界多边形)
[
224.24,297.18,# 第一个点 x,y坐标
228.29,297.18, # 第二个点 x,y坐标
234.91,298.29,
……
……
225.34,297.55
]
],
"area": 1481.3806499999994, # 区域面积
"iscrowd": 0, #
"image_id": 397133, # 对应的图片ID(与images中的ID对应)
"bbox": [217.62,240.54,38.99,57.75], # 定位边框 [x,y,w,h]
"category_id": 44, # 类别ID(与categories中的ID对应)
"id": 82445 # 对象ID,因为每一个图像有不止一个对象,所以要对每一个对象编号(每个对象的ID是唯一的)
},
……
……
]注意,单个的对象(iscrowd=0)可能需要多个polygon来表示,比如这个对象在图像中被挡住了。而iscrowd=1时(将标注一组对象,比如一群人)的segmentation使用的就是RLE格式。
可视化
现在调用cocoapi显示刚生成的JSON文件,并检查是否有问题。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
import os, sys, zipfile
import urllib.request
import shutil
import numpy as np
import skimage.io as io
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab
pylab.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8.0, 10.0)
annFile='./new_instances_val2017.json'
coco=COCO(annFile)
# display COCO categories and supercategories
cats = coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds())
nms=[cat['name'] for cat in cats]
print('COCO categories: \n{}\n'.format(' '.join(nms)))
nms = set([cat['supercategory'] for cat in cats])
print('COCO supercategories: \n{}'.format(' '.join(nms)))
# imgIds = coco.getImgIds(imgIds = [324158])
imgIds = coco.getImgIds()
img = coco.loadImgs(imgIds[0])[0]
dataDir = '.'
dataType = 'val2017'
I = io.imread('%s/%s/%s'%(dataDir,dataType,img['file_name']))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(I)
plt.show()
# load and display instance annotations
# 加载实例掩膜
# catIds = coco.getCatIds(catNms=['person','dog','skateboard']);
# catIds=coco.getCatIds()
catIds=[]
for ann in coco.dataset['annotations']:
if ann['image_id']==imgIds[0]:
catIds.append(ann['category_id'])
plt.imshow(I); plt.axis('off')
annIds = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id'], catIds=catIds, iscrowd=None)
anns = coco.loadAnns(annIds)
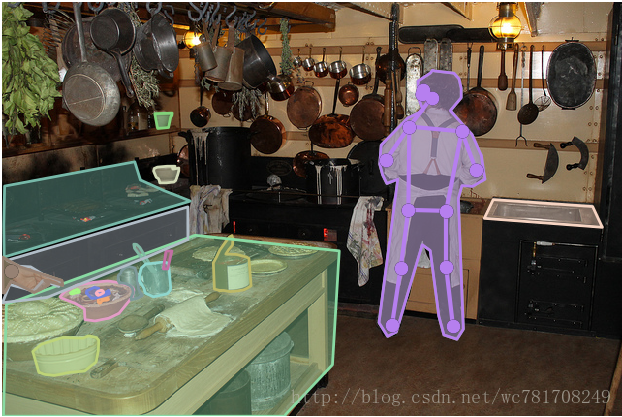
coco.showAnns(anns)
# initialize COCO api for person keypoints annotations
annFile = '{}/annotations/person_keypoints_{}.json'.format(dataDir,dataType)
coco_kps=COCO(annFile)
# load and display keypoints annotations
# 加载肢体关键点
plt.imshow(I); plt.axis('off')
ax = plt.gca()
annIds = coco_kps.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id'], catIds=catIds, iscrowd=None)
anns = coco_kps.loadAnns(annIds)
coco_kps.showAnns(anns)
# initialize COCO api for caption annotations
annFile = '{}/annotations/captions_{}.json'.format(dataDir,dataType)
coco_caps=COCO(annFile)
# load and display caption annotations
# 加载文本描述
annIds = coco_caps.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id']);
anns = coco_caps.loadAnns(annIds)
coco_caps.showAnns(anns)
plt.imshow(I); plt.axis('off'); plt.show()
A man is in a kitchen making pizzas.
Man in apron standing on front of oven with pans and bakeware
A baker is working in the kitchen rolling dough.
A person standing by a stove in a kitchen.
A table with pies being made and a person standing near a wall with pots and pans hanging on the wall.仿照COCO JSON文件
仿照COCO的数据格式,将labelme的JSON改造成COCO的JSON
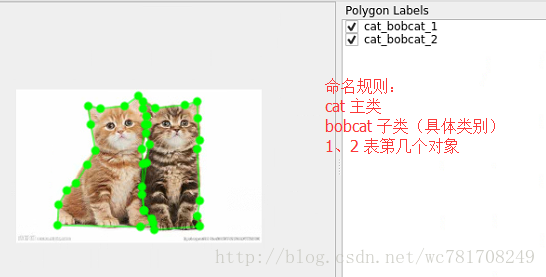
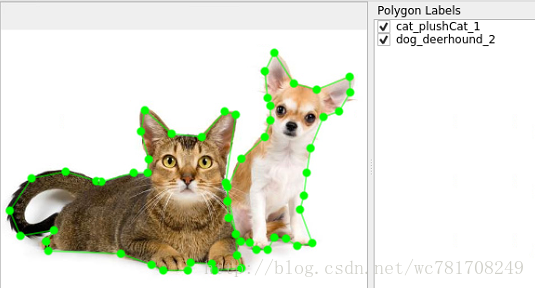
首先是要labelme做好图片标注
说明:(类别不一定对,只是为了说明问题)
bobcat-美国短耳猫
plushcat-布偶猫
deerhound-小鹿犬
mainecat-缅因猫
golden-金毛
将labelme的JSON转成COCO格式JSON
这里写一个class实现以下功能,labelme2COCO.py中 的部分代码如下:
def image(self,data,num):
image={}
img = utils.img_b64_to_array(data['imageData']) # 解析原图片数据
# img=io.imread(data['imagePath']) # 通过图片路径打开图片
# img = cv2.imread(data['imagePath'], 0)
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img = None
image['height']=height
image['width'] = width
image['id']=num+1
image['file_name'] = data['imagePath'].split('/')[-1]
self.height=height
self.width=width
return image
def categorie(self,label):
categorie={}
categorie['supercategory'] = label[0]
categorie['id']=len(self.label)+1 # 0 默认为背景
categorie['name'] = label[1]
return categorie
def annotation(self,points,label,num):
annotation={}
annotation['segmentation']=[list(np.asarray(points).flatten())]
annotation['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation['image_id'] = num+1
# annotation['bbox'] = str(self.getbbox(points)) # 使用list保存json文件时报错(不知道为什么)
# list(map(int,a[1:-1].split(','))) a=annotation['bbox'] 使用该方式转成list
annotation['bbox'] = list(map(float,self.getbbox(points)))
annotation['category_id'] = self.getcatid(label)
annotation['id'] = self.annID
return annotation注:这里只实现images、categories、annotations三个字段内容,因为只用到这几个字段
可视化数据
这部分是使用COCO的API接口打开刚才自己生成的JSON文件,以验证是否存在问题。
visualization.py
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
import os, sys, zipfile
import urllib.request
import shutil
import numpy as np
import skimage.io as io
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab
pylab.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8.0, 10.0)
annFile='./new.json'
coco=COCO(annFile)
# display COCO categories and supercategories
cats = coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds())
nms=[cat['name'] for cat in cats]
print('COCO categories: \n{}\n'.format(' '.join(nms)))
nms = set([cat['supercategory'] for cat in cats])
print('COCO supercategories: \n{}'.format(' '.join(nms)))
# imgIds = coco.getImgIds(imgIds = [324158])
imgIds = coco.getImgIds()
imgId=np.random.randint(0,len(imgIds))
img = coco.loadImgs(imgIds[imgId])[0]
dataDir = '.'
# dataType = 'val2017'
# I = io.imread('%s/%s/%s'%(dataDir,dataType,img['file_name']))
I = io.imread('%s/%s'%(dataDir,img['file_name']))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(I)
plt.show()
# load and display instance annotations
# 加载实例掩膜
# catIds = coco.getCatIds(catNms=['person','dog','skateboard']);
# catIds=coco.getCatIds()
catIds=[]
for ann in coco.dataset['annotations']:
if ann['image_id']==imgIds[imgId]:
catIds.append(ann['category_id'])
plt.imshow(I); plt.axis('off')
annIds = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id'], catIds=catIds, iscrowd=None)
anns = coco.loadAnns(annIds)
coco.showAnns(anns)
plt.show()显示结果:
Object Keypoint 类型的标注格式
运行脚本one_image_json.py 得到单张图片的JSON信息。
基本上内容与Object Instance的标注格式一样,不同的地方在于categories、annotations字段内容不一样。
主要内容有:
{
"info": {
"description": "COCO 2017 Dataset",
"url": "http://cocodataset.org",
"version": "1.0",
"year": 2017,
"contributor": "COCO Consortium",
"date_created": "2017/09/01"
},
"licenses": [
{
"url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/",
"id": 1,
"name": "Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License"
},
……
……
],
"images": [
{
"license": 4,
"file_name": "000000397133.jpg", # 图片名
"coco_url": "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000397133.jpg", # coco 链接地址
"height": 427, # 高
"width": 640, # 宽
"date_captured": "2013-11-14 17:02:52", # 获取日期
"flickr_url": "http://farm7.staticflickr.com/6116/6255196340_da26cf2c9e_z.jpg", # flickr 链接地址
"id": 397133 # 图片ID(每张图片ID唯一)
}
],
"categories": [
{
"supercategory": "person", # 主类
"id": 1, # class id
"name": "person", # 子类(具体类别)
"keypoints": [ # 相比Object Instance多了这个字段
"nose",
"left_eye",
"right_eye",
"left_ear",
"right_ear",
"left_shoulder",
"right_shoulder",
"left_elbow",
"right_elbow",
"left_wrist",
"right_wrist",
"left_hip",
"right_hip",
"left_knee",
"right_knee",
"left_ankle",
"right_ankle"
],
"skeleton": [ # 骨架
[
16,14
],
[
14,12
],
……
……
[
5,7
]
]
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"segmentation": [
[
446.71,70.66, # 多边形(对象mask)第一个点 x,y
466.07,72.89,
471.28,78.85,
473.51,88.52,
473.51,98.2,
……
……
443.74,69.92
]
],
"num_keypoints": 13, # 关键点数
"area": 17376.91885,
"iscrowd": 0,
"keypoints": [
# v=0 表示这个关键点没有标注(这种情况下x=y=v=0)
# v=1 表示这个关键点标注了但是不可见(被遮挡了)
# v=2 表示这个关键点标注了同时也可见
433,94,2, # x,y,v
434,90,2,
0,0,0,
443,98,2,
0,0,0,
……
……
],
"image_id": 397133, # 对应的图片ID
"bbox": [
388.66,69.92,109.41,277.62 # [x,y,w,h] 对象定位框
],
"category_id": 1, # 类别id
"id": 200887 # 对象id(每个对象id都是唯一的,即不能出现重复)
},
……
……
]
}Image Caption的标注格式
运行脚本one_image_json.py 得到单张图片的JSON信息。
基本上内容与Object Instance的标注格式一样,不同的地方在于annotations字段内容不一样以及没有categories字段
{
"info": {
"description": "COCO 2017 Dataset",
"url": "http://cocodataset.org",
"version": "1.0",
"year": 2017,
"contributor": "COCO Consortium",
"date_created": "2017/09/01"
},
"licenses": [
{
"url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/",
"id": 1,
"name": "Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License"
},
……
……
],
"images": [
{
"license": 4,
"file_name": "000000397133.jpg",
"coco_url": "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000397133.jpg",
"height": 427,
"width": 640,
"date_captured": "2013-11-14 17:02:52",
"flickr_url": "http://farm7.staticflickr.com/6116/6255196340_da26cf2c9e_z.jpg",
"id": 397133
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"image_id": 397133, # 图片ID(唯一)
"id": 370509, # 对象ID(唯一) (没有类别ID)
"caption": "A man is in a kitchen making pizzas." # 图片描述
},
……
……
{
"image_id": 397133,
"id": 375891,
"caption": "A table with pies being made and a person standing near a wall with pots and pans hanging on the wall."
}
]
}这三种标注的info,licenses,images的内容是一样的。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wc781708249/article/details/79603522?utm_source=copy

























 2078
2078











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








