Ethiopia Languages and Useful Tips Before a Visit
Language is the basic tradition of every nation that serves as a communicative tool or skill and it all starts from a word. Ethiopia becoming one of the ancient nations has developed a great deal on the subject field and the linguistics structure. With all the difficulty to limit the insight of the topic it is essential to fall under the most important characteristics and features of the language, in order to maintain the theme of the topic. What language do they speak in ethiopia
Ethiopia languages are the pioneer to the linguistics area due to the interest of relating to multiple features when bounded together; in other words, in the sense of geographical aspect, they distinguish them from any other naturally placed definitive group of languages in the world.
Even though this is one of the main features, some will not fall under this and some don’t even follow any of the patterns at all. These languages will have shared features due to genetic relations and those that are shared from the process of reciprocal diffusion among languages.
Some don’t match with any of the described features again, but generally, most of the languages relate to Ethiopia’s boundaries and have the features of pronunciation, grammar, vocabularies, and patterns of expression.
Ethiopia constitutes a language that is rich with features of pronunciation; that have retroflex consonants, nasal vowel, and aspired slops, they have few spirants and lack word accent. Currently, it is quite difficult to assure the number of Ethiopia Languages; but based on some adequate information it is possible to say that there are 75 – 80 types of languages.
The two main reasons for us not to say the numbers of spoken Ethiopia Languages are due to – Writings and researches that elaborate the kinds of languages claim by giving them one group name while instead, they have many specific names within their grouped names.
The most important reason; a research couldn’t explain if the languages are highly similar but are having different language names or they are just of the same language but have different dialect. Some classify similar languages as specific languages giving each one of them their own name and others will put them under on definitive term.
According to linguistic science it is possible to say if two people communicate using their own language it means these are of the same language but different dialect; but if they couldn’t communicate then they are two different languages.
For example a man from Gojam( northern Ethiopia, speaking Amharic) and a man from Addis Ababa can communicate using their own language, of course it is possible to find few words that one couldn’t understand but these are negotiable terms; but in other context its quite impossible to have conversation with that of a man who speaks Argoba.
It is important to notice that when you listen to the language at first it looks so much similar to Amharic but in order to understand to necessarily, you need to know the language. Therefore, Argoba is considered as one language by itself.
Languages are different means of communication among people. Most countries of the world are known to have a national language and other languages spoken by the minority as well. Ethiopia languages are a lot in number and are unique. To understand the Ethiopia languages, we need a better way of classification, other than in region or location.
Here we see Ethiopia language at different periods and locations in the history of Ethiopia and also the endangered Ethiopia Languages or the extinction that this may have resulted in. These languages are diversified both culturally and by the means of the language classifications.
With Ethiopia being an ethnically diverse country, there are more than 80 Ethiopia languages used by the different cultural and religious groups of each language from the different linguistic families.

What Are Ethiopia Languages Categories?
Language classification is based on the origin from which language descends.
It is possible to classify languages in respective of their family. Ethiopia Languages are basically under Afro-Asian and Nilo-Saharan families. This means the languages are created with either of the two.
Afro-Asian has six sub-divisions within it.
The mainly known linguistic groups in Ethiopia are Semitic, Kushitic, Nilo Saharan and Omotic.
From this we can understand that once upon a time these six languages were just one but through time, they fall into six groups. According to linguistic researchers, such languages are called proto-languages. It is quite difficult to say Afro-Asian was the name of that language because the language was spoken 15,000 years ago; therefore, we have no clue what they called it back then.
As described on the above paragraph we have mentioned that Afro-Asian is classified into six; from that Semitic, Cushitic and Omotic are spoken in Ethiopia. Omotic is only found in Ethiopia and Cushitic is spoken in Ethiopia and neighbouring countries. Most of the Semitic languages are spoken in Ethiopia and few of them in Middle East and some parts of Africa.
Semitic Ethiopia Languages
Semitic language group is internationally used by the largest world’s Semitic languages. Thsese groups are found in Ethiopia as well and are located in the northern and central parts of Ethiopia and are classified as north Semitic and South Semitic. Some of the known North Semitic languages include Tigrinya and Ge’ez, and in the south Semitic group Amharic, Harari, Argoba, East and West Gurage language group clusters, Silte are a few examples.
Semitic Languages that are spoken in Ethiopia are classified into North Ethio-Semetic and South Ethio-Semetic. North Ethio-Semetic consists of three languages and those are Geez, Tigrigna and Tigr’e which is spoken in Eritrea. South Ethio-Semetic are classified into two groups and each have many under them.
And within those are Harari, Amharic, Argobic, Selte, Zayi, sodo, Gogot, Cheha, Endegagn, Mes’qan etc. Since the relation of these languages is different, they can be placed in different categories.
For example, Amharic and Argob under one; Seltte, Harari, and Zayi in other categories and Gogot, sodo, and Mesqan under Gurage and the rest guragina languages are under western gurage. And those that are in Western Gurage can again be classified into two sub-groups; West Central gurage and West edged gurage.

Cushitic Ethiopia Languages
The Cushitic group are located on the southwestern and eastern parts of the country and are grouped into several classifications. They are known as Agew languages, East Cushitic, Lowland East Cushitic, Southern lowland East Cushitic, and transversal southern East Cushitic.
These Ethiopia languages are spoken by people of Oromo, Somali, Agew, Hadiyya, Kambata, Konso and many other southern nations and nationalities in Ethiopia. Other than Ethiopia, the Cushitic family languages are known to be spoken in the horn of Africa.
This language is classified as Northern Cushitic, Central Cushitic, Eastern Cushitic and Southern Cushitic. From these four sub-groups Central and Eastern Cushitic are spoken in Ethiopia. The central Cushitic language is represented by Agaw and within it consists of Hemttegna, Qemantigna and Awngegra languages. The Eastern Cushitic is also classified as Qolla and Dega (which means according to the climatic nature Qolla hot and Degga being cold).
Then Dega is classified into Burjigna, Gedeo, Sidamo, Kambata and Hadiya. And the Qolla is classified inthree families; one is Afar-Saho include Afar and Saho the secone one includes Oromic, Busa, Barareit, Gidol, Konso, Erborie, Dasenech, Gewad, Gobezegna, Tsamay and Worzigna. The third one includes Somali and Bargo.
Ethiopia Languages like Oromo, Somali, and Arabic are also spoken in neighboring countries. For example, in Kenya, Djibouti, Eritrea, Somali.
Afro Asiatic Ethiopia Languages
Another large linguistic group which is the combination of the Cushitic and Semitic families is known as the Afro-Asiatic family. It is also known as “Hamito Semitic” or “Semito Hamitic” which originated from the book of Genesis in the bible.
These families have over 300 languages located in West Asia, North Africa, Horn of Africa, and Sahil. It is the 4th largest linguistic family group.
Omotic Ethiopia Languages
The other language family we can see is the Omotic group which is spoken widely in the southwest regions of the country. It is named after the Omo River so the location of the users is around that region. It has unclear classification so some of the languages are uncertain.
It’s mostly used by Wolayta people and another minimum of 30 Ethiopia languages are identified as members of this group.
This language consists of Anfilo, Welayita, Gamo, Hamer, Dime, Male, Kore Zeyise, Ganjule, Dizzi, sheko, Keficho, Nay, Baskelo, Oyida etc…
Welayita, Kulo, Konta and Gamo are highly similar but in order to give a conclusion it’s important to do additional researches. Anfilo has less than 100 speakers so it’s a language about to be extinct.
Nilo Saharan Ethiopia Languages
The Nilo Saharan language group is part of the larger Nilo Saharan group which consists of the African countries located along the Nile River and the Sahara Desert. It is located mostly around the southwestern and western margins of the country.
The term in Ethiopia is referred to as Nilotic. Anuak, Berta, Gumuz, Mursi, Nuwer, and Suri are a few examples of these Nilotic family languages.
This proto-language has many sub-groupes; some are Komo, Abay, Surm etc… under this proto-language Kunama, Agniwak, Nuwer, Komo, Mesengo, Opa, Gumuz, Shabo, Berta etc are included.
In Ethiopia compared to those Cushitic and Semetic speakers; Omotic is smaller and is placed third in rank.
Actually, in Ethiopia there is a language that won’t be under any of the languages we mentioned and has no class and it’s called Berayle or Onogota. It is spoken around Southern area and has less than 10 speakers. Therefore, it’s a language that will be extinct within few years.
The other one is Symbol Language. This one has its own structure meaning grammar. But it is not studied well so it’s difficult to relate with language or even understand if there is any relation.
Phonetic Writing in Ethiopia Languages
It is important to mention this while speaking of language. There is a difference between the Phonetic writing and typical way writing. Phonetic writing is when the consonant letters are written in their solid six letter form ( ሳድስ) and the vowels make up to being the intended word.
The Vowels are አ- አ-ኢ-አ-ኢ-እ-ኦ and the rest of the letters are consonant. Therefore in order to say for example GOBEZ (ጐበዝ) ጐ is made when ግ and ኦ are combined and በ is made when ብ and ኧ and ዝ since it’s in the six letter we do not touch that.
What Language Do They Speak in Ethiopia?
Amharic and English are used throughout Ethiopia.
Ethiopia is amazing country with more than 80 local language. This means each ethnic group has its own language. Since the country has never been under colonialism, the European influence is low to none.
However, English has been used as a learning language, especially for the high school and university level. It is expected students to learn the language since the kinder garden level. Due to the low-quality teachers or medium, the use of the language is still very low, although many understand and respond with English.
Amharic is a working language in Ethiopia, and many people know the language. This means you either need to communicate using Amharic or English for fast response. Oromigna is also famous in the Oromo regions.
What Is Ethiopia Official Language?
Amharic is one of the official language of Ethiopia.
Amharic gain its influence in the 10th century -12 century where power structure shifted from the north (Axum) to Amhara. Since then the use of the language grew rapidly.
Amharic is a working language in Ethiopia. Amharic is spoken clearly by many throughout the country. Other languages like English are used for office and education sectors. English is used to communicate with the rest of the world. Oromigna or Oromiffa and Somali have many speakers as well. Foreign languages such as Italian, French and Arabic have many speakers in the country.
In other regions of Ethiopia, several Ethiopia languages of the different families mentioned earlier were used widely. Following the unification of Ethiopia, Amharic was being imposed as a national language in many parts of the country. The only language used as a medium of instruction is Amharic and it kept spreading throughout all of the regions.
With request of some Ethiopian regions with large number of populations, other Ethiopia languages are also considered to be a working language as well. As a result, a new government system allowed regions to use their Ethiopia languages as working language in addition to the Amharic. Amharic proceeded to be the official language of the country and the medium of instruction but all the other regions still enjoyed their rights to use their languages.
Is Swahili Spoken in Ethiopia?
No. Swahili is rather much known in the countries south of Ethiopia, including Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania. Amharic is much known language in Ethiopia. It is a decedent of Geez language that was created before 3000 BC, before both Amharic and Arabic.
Ethiopia Languages and Literature in Ethiopia
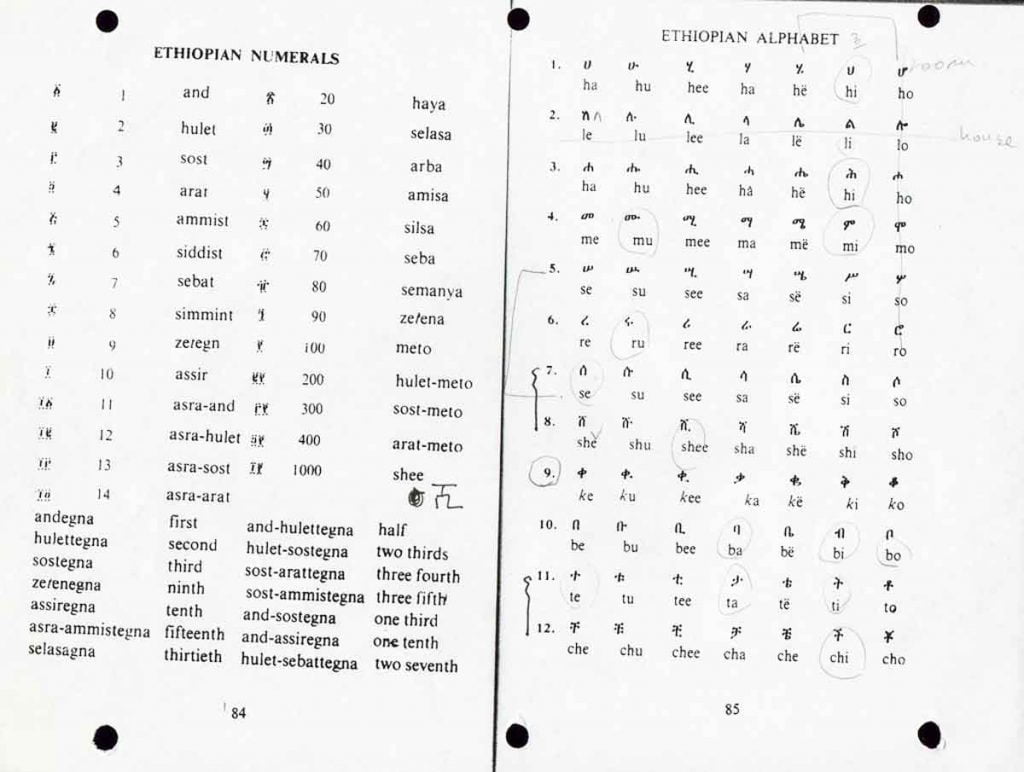
As mentioned earlier, Ethiopia has so many languages but most of them are known to be oral. Ethiopian history has been studied by the different manuscripts which are written documents. A language not written not only prevents the language from sustaining, but also prevents us from understanding the history of the country. Documentation in many Ethiopia Languages is very low. The fact that Ethiopia is known as the only black African country with its own alphabet, most of the other Ethiopia languages did not employ the alphabet.
The only Ethiopia Languages that made use of Ge’ez in their written documents starting from old times are Ge’ez, Amharic, and Tigrigna. However, other region populations of Ethiopia particularly the Muslim population made use of the Arabic alphabets to write their languages.
With the coming of Islam and the conversion of different Ethiopian communities, Arabic literacy was introduced. This population made use of Arabic literature to understand their religion and later on wrote their local languages using the Arabic alphabet. These literatures are called “Ajami”. We can find Harari, Oromo, Afar, Somali, Silte, Amharic, Alaba, Argoba, Hadiyya and Gurage Ethiopia languages written in the Ajami form of writing. It has more than 30 other languages spoken in black Africa.
What Was the First Ethiopia Language?
The first language known as Ge’ez used during the Axumite period in the central highlands of the country till the 14th century. This ancient language served both as an official, means of communication and liturgic purposes used by the state royals and the rest of the population.
Several pieces of kinds of literature were believed to be produced during the 4th century in the reign of Ezana as he introduced the religion of Christianity. The nine saints who fled from the religious prosecution in the Middle East were believed to have translated the bible from Greek to Ge’ez. Thus, we find manuscripts with these religious contents in the ancient Ge’ez language.
These manuscripts were spread to monasteries in different parts of the country. The alphabet used to write Ge’ez which has become the Ethiopic alphabet is known to have Sabaec origins. However, from the 14th century, it was replaced by Amharic as an official and communication language. Ge’ez remained for church and religious purposes until the present day.
What are Endangered Ethiopia languages?
Languages can live or die depending on the number of users it has and the population of its people. The less the number of speakers of a particular language is, the closer it is to the risk of extinction. These Ethiopia languages are called endangered languages.
Some Ethiopia languages have been extinct which also took place as a result of a lack of population of users. The second factor that results in the extinction of languages is socio-economic factors as a group of people are influenced and dominated by another group of people. The other reason would be the languages existing as oral and not having a written document for the language. Not having institutions that record or study the languages also contributes to the extinction of the language. Preserving diversity in languages is a responsibility to the people of a country as well as government officials.
One of the most used ancient Ethiopia languages is Ge’ez as it has lost its role as a national communicative language. But since it’s still serving for liturgy purposes, we cannot call it fully extinct. Qimant is also an Ethiopia language that has already been extinct. To prevent this risk of extinction that we are fearing it is very important that speaking the different Ethiopia Languages are encouraged and used as a medium of instruction in their regions.
What Language Is Spoken in Ethiopia Today?
Today, the Oromo language speakers have the highest population. Amharic has the second-highest number of speakers and Somali follows as the third most spoken language in Ethiopia. There were many debates going on still since the language usage does not consider the population.
The recent news on the number of national languages is to engage five Ethiopia languages with large number of speakers as national languages in Ethiopia. These Ethiopia languages are Oromigna, Amharic, Tigrigna, Somali and Afar.
When these proposals of language usage have been announced, a lot of effort needed to uplift the languages like Somali, Afar, Tigrigna, and Oromigna up to the standards of education, official languages and medium of instruction.
Conclusion
Ethiopia has a widely diversified culture and thus, diversified languages and populations. When trying to understand Ethiopia languages and their structures it is very crucial that we study their classifications and that can help us identify the similarities and differences of the various types of languages.
A language is a national heritage of a country so it has to be preserved and studied and documented. It is a cliché that a country or a nation has a single language as a medium of communication and that can prevent the cultural and linguistic diversity.
So, the solution might be to engage in practicing as many languages as possible which will not only preserve the languages from being extinct but also will promote a strong relationship between people of different cultural groups. Seeing the timeline and location of the languages is a major source of history so we must study the sources and the time they were spoken at.
Ethiopia Tribes: 10 Most Dazzling Culture
Cover: “alphabet_textbook” by newflower is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0

