To Donald Trump, it’s “people who love our country”. To the FBI, it’s a potential domestic terror threat. And to you or anyone else who has logged on to Facebook in recent months, it may just be a friend or family member who has started to show an alarming interest in child trafficking, the “cabal”, or conspiracy theories about Bill Gates and the coronavirus.
This is QAnon, a wide-ranging and baseless internet conspiracy theory that reached the American mainstream in August. The movement has been festering on the fringes of rightwing internet communities for years, but its visibility has exploded in recent months amid the social unrest and uncertainty of the coronavirus pandemic.
Now, a QAnon supporter is probably heading to the US Congress, the president (who plays a crucial role in QAnon’s false narrative) has refused to debunk and disavow it, and the successful hijacking of the #SaveTheChildren hashtag has provided the movement a more palatable banner under which to stage real-life recruiting events and manipulate local news coverage.
Here’s our guide to what you need to know about QAnon.
So what is QAnon?
“QAnon” is a baseless internet conspiracy theory whose followers believe that a cabal of Satan-worshipping Democrats, Hollywood celebrities and billionaires runs the world while engaging in pedophilia, human trafficking and the harvesting of a supposedly life-extending chemical from the blood of abused children. QAnon followers believe that Donald Trump is waging a secret battle against this cabal and its “deep state” collaborators to expose the malefactors and send them all to Guantánamo Bay.

There are many, many threads of the QAnon narrative, all as far-fetched and evidence-free as the rest, including subplots that focus on John F Kennedy Jr being alive (he isn’t), the Rothschild family controlling all the banks (they don’t) and children being sold through the website of the furniture retailer Wayfair (they aren’t). Hillary Clinton, Barack Obama, George Soros, Bill Gates, Tom Hanks, Oprah Winfrey, Chrissy Teigen and Pope Francis are just some of the people whom QAnon followers have cast as villains in their alternative reality.
This all sounds familiar. Haven’t we seen this before?
Yes. QAnon has its roots in previously established conspiracy theories, some relatively new and some a millennium old.
The contemporary antecedent is Pizzagate, the conspiracy theory that went viral during the 2016 presidential campaign when rightwing news outlets and influencers promoted the baseless idea that references to food and a popular Washington DC pizza restaurant in the stolen emails of Clinton campaign manager John Podesta were actually a secret code for a child trafficking ring. The theory touched off serious harassment of the restaurant and its employees, culminating in a December 2016 shooting by a man who had travelled to the restaurant believing there were children there in need of rescue.
QAnon evolved out of Pizzagate and includes many of the same basic characters and plotlines without the easily disprovable specifics. But QAnon also has its roots in much older antisemitic conspiracy theories. The idea of the all-powerful, world-ruling cabal comes straight out of the Protocols of the Elders of Zion, a fake document purporting to expose a Jewish plot to control the world that was used throughout the 20th century to justify antisemitism. Another QAnon canard – the idea that members of the cabal extract the chemical adrenochrome from the blood of their child victims and ingest it to extend their lives – is a modern remix of the age-old antisemitic blood libel.
How did QAnon start?
On 28 October 2017, “Q” emerged from the primordial swamp of the internet on the message board 4chan with a post in which he confidently asserted that Hillary Clinton’s “extradition” was “already in motion” and her arrest imminent. In subsequent posts – there have been more than 4,000 so far – Q established his legend as a government insider with top security clearance who knew the truth about the secret struggle for power between Trump and the “deep state”.
Though posting anonymously, Q uses a “trip code” that allows followers to distinguish his posts from those of other anonymous users (known as “anons”). Q switched from posting on 4chan to posting on 8chan in November 2017, went silent for several months after 8chan shut down in August 2019, and eventually re-emerged on a new website established by 8chan’s owner, 8kun.
Q’s posts are cryptic and elliptical. They often consist of a long string of leading questions designed to guide readers toward discovering the “truth” for themselves through “research”. As with Clinton’s supposed “extradition”, Q has consistently made predictions that failed to come to pass, but true believers tend to simply adapt their narratives to account for inconsistencies.
For close followers of QAnon, the posts (or “drops”) contain “crumbs” of intelligence that they “bake” into “proofs”. For “bakers”, QAnon is both a fun hobby and a deadly serious calling. It’s a kind of participatory internet scavenger hunt with incredibly high stakes and a ready-made community of fellow adherents.
How do you go from anonymous posts on 4chan to a full-fledged conspiracy movement?
Not by accident, that’s for sure. Anonymous internet posters who claim to have access to secret information are fairly common, and they usually disappear once people lose interest or realize they are being fooled. (Liberal versions of this phenomenon were rampant during the early months of the Trump administration when dozens of Twitter accounts claiming to be controlled by “rogue” employees of federal agencies went viral.)

QAnon might have faded away as well, were it not for the dedicated work of three conspiracy theorists who latched on to it at the very beginning and translated it into a digestible narrative for mainstream social media networks. A 2018 investigation by NBC News uncovered how this trio worked together to promote and profit off QAnon, turning it into the broad, multi-platform internet phenomenon that it is today. There now exists an entire QAnon media ecosystem, with enormous amounts of video content, memes, e-books, chatrooms, and more, all designed to snare the interest of potential recruits, then draw them “down the rabbit hole” and into QAnon’s alternate reality.
How many people believe in QAnon? And who are they?
Nobody knows, but we think it’s fair to say at least 100,000 people.
Experts in conspiracy theories point out that belief in QAnon is far from common. While at one point, 80% of Americans believed a conspiracy theory about the Kennedy assassination, a poll by Pew Research in March found that 76% of Americans had never heard of QAnon and just 3% knew “a lot” about it.
The largest Facebook groups dedicated to QAnon had approximately 200,000 members in them before Facebook banned them in mid-August. When Twitter took similar action against QAnon accounts in July, it limited features for approximately 150,000 accounts. In June, a Q drop that contained a link to a year-old Guardian article resulted in approximately 150,000 page views over the next 24 hours.
These are rough figures to draw a conclusion from, but in the absence of better data, they hint at the scale of the online movement.
In general, QAnon appears to be most popular among older Republicans and evangelical Christians. There are subcultures within QAnon for people who approach studying Q drops in a manner similar to Bible study. Other followers appear to have come to QAnon from New Age spiritual movements, from more traditional conspiracy theory communities, or from the far right. Since adulation for Trump is a prerequisite, it is almost exclusively a conservative movement, though the #SaveTheChildren campaign is helping it make inroads among non-Trump supporters (see below).
QAnon has spread to Latin America and Europe, where it appears to be catching on among certain far-right movements.
Why does QAnon matter?
First, there’s the threat of violence. For those who truly believe that powerful figures are holding children hostage in order to exploit them sexually or for their blood, taking action to stop the abuse can seem like a moral imperative. While most QAnon followers will not engage in violence, many already have, or have attempted to, which is why the FBI has identified the movement as a potential domestic terror threat. Participation in QAnon also often involves vicious online harassment campaigns against perceived enemies, which can have serious consequences for the targets.
QAnon is also gaining traction as a political force in the Republican party, which could have real and damaging effects on American democracy. Media Matters has compiled a list of 77 candidates for congressional seats who have indicated support for QAnon and at least one of them, Georgia’s Marjorie Taylor Greene, will in all likelihood be elected in November.
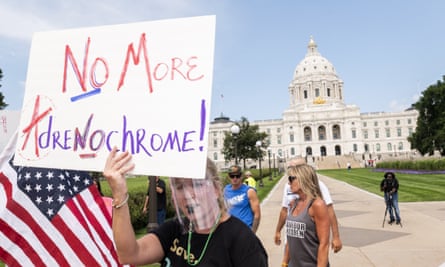
As the hero of the overall narrative, Trump has the unique ability to influence QAnon believers. On 19 August, at a White House press briefing, he was given the opportunity to debunk the theory once and for all. Instead, he praised QAnon followers as patriots and appeared to affirm the central premise of the belief, saying: “If I can help save the world from problems, I’m willing to do it; I’m willing to put myself out there, and we are, actually. We’re saving the world from a radical left philosophy that will destroy this country and, when this country is gone, the rest of the world will follow.”
QAnon believers were jubilant.
Didn’t you mention #SaveTheChildren? What’s that all about?
Participating in QAnon is largely made up of “research” – ie learning more about the byzantine theories or decoding Q drops – and evangelism. Most of the proselytization relies on media manipulation tactics designed to catch users’ attention and send them into a controlled online media environment where they will become “redpilled” through consuming pro-QAnon content.
QAnon followers have for years used a wide range of online tactics to achieve virality and garner mainstream media coverage, including making “documentaries” full of misinformation, hijacking trending hashtags with QAnon messaging, showing up at Trump rallies with Q signs, or running for elected office.
A very potent iteration of this tactic emerged this summer with the #SaveTheChildren or #SaveOurChildren campaign. The innocuous sounding hashtag, which had previously been used by anti-child-trafficking NGOs, has been flooded with emotive content by QAnon adherents hinting at the broader QAnon narrative. (It doesn’t help that the debate around human trafficking is already full of bogus statistics.)
On Facebook, anxiety over children due to the coronavirus pandemic, a resurgent anti-vaxx movement, and QAnon-fueled scaremongering about child trafficking have all combined to inspire a modern-day moral panic, somewhat akin to the “Satanic Panic” of the 1980s.
Hundreds of real-life “Save Our Children” protests have been organized on Facebook in communities across the US (and around the world). These small rallies are in turn driving local news coverage by outlets who don’t realize that by publishing news designed to “raise awareness” about child trafficking, they are encouraging their readers or viewers to head to the internet, where a search for “save our children” could send them straight down the QAnon rabbit hole.