Countries Ruled by A Parliamentary Republic
List of countries, nations and states governed or ruled by a parliamentary republic, sorted alphabetically. In some cases nations may have multiple ruling bodies or government types, meaning they're not exclusively countries that are governed by parliamentary republic. This list of countries that use parliamentary republic as their form of government contains various bits of information about each nation, such as the official language or currency of the country. If you're looking for the names of countries with parliamentary republic governments then you're in the right place.
Hungary and Austria are a great starting point for your to rank your favorites on this list
This list answers the questions, "Which countries are ruled by parliamentary republic?" and "Which countries are governed by parliamentary republic?"- TiranaAlbania, officially known as the Republic of Albania, is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east, and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the west and on the Ionian Sea to the southwest. It is less than 72 km from Italy, across the Strait of Otranto which links the Adriatic Sea to the Ionian Sea. Albania is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Council of Europe and the World Trade Organization. It is one of the founding members of the Energy Community and the Union for the Mediterranean. It is also an official candidate for membership in the European Union. The modern-day territory of Albania was at various points in history part of the Roman provinces of Dalmatia, Macedonia, and Moesia Superior. The modern Republic became independent after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in Europe following the Balkan Wars. Albania declared independence in 1912 and was recognized the following year.More Albania
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #13 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ViennaAustria, officially the Republic of Austria, is a federal republic and a landlocked country of over 8.5 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Hungary and Slovakia to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The territory of Austria covers 83,879 square kilometres and has an alpine climate. Austria's terrain is highly mountainous, lying within the Alps; only 32% of the country is below 500 metres, and its highest point is 3,798 metres. The majority of the population speak local Bavarian dialects of German as their native language, and Austrian German in its standard form is the country's official language. Other local official languages are Hungarian, Burgenland Croatian, and Slovene. The origins of modern-day Austria date back to the time of the Habsburg dynasty when the vast majority of the country was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. From the time of the Reformation, many Northern German princes, resenting the authority of the Emperor, used Protestantism as a flag of rebellion.More Austria
- Dig Deeper...The Most Stunning Austrian Actresses
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #72 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BakuAzerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a contiguous transcontinental presidential republic in the Caucasus region, situated at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia to the west and Iran to the south. The exclave of Nakhchivan is bounded by Armenia to the north and east, Iran to the south and west, while having a short border with Turkey in the northwest. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence in 1918 and became the first Muslim-majority democratic and secular republic. It was also the first Muslim-majority country to have operas, theaters and modern universities. The country was incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1920 as the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic. Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence in October 1991, before the official dissolution of the USSR. Earlier, in September 1991, the disputed Armenian-majority Nagorno-Karabakh region re-affirmed its willingness to create a separate state as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic.More Azerbaijan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #78 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- DhakaBangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia; and is bordered by India to its west, north and east; Burma to its southeast and separated from Nepal and Bhutan by the Chicken’s Neck corridor. To its south, it faces the Bay of Bengal. Bangladesh is the world's eighth-most populous country, with over 160 million people, and among the most densely populated countries. It forms part of the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal, along with the neighbouring Indian states of West Bengal and Tripura. The present-day borders of Bangladesh took shape during the Partition of Bengal and British India in 1947, when the region came to be known as East Pakistan, as a part of the newly formed state of Pakistan. It was separated from West Pakistan by 1,400 km of Indian territory. Due to political exclusion, ethnic and linguistic discrimination and economic neglect by the politically dominant western wing, nationalism, popular agitation and civil disobedience led to the Bangladesh Liberation War and independence in 1971. After independence, the new state endured poverty, famine, political turmoil and military coups.More Bangladesh
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #203 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- SarajevoBosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes called Bosnia-Herzegovina, abbreviated BiH, and in short often known informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeastern Europe located on the Balkan Peninsula. Sarajevo is the capital and largest city. Bordered by Croatia to the north, west and south, Serbia to the east, and Montenegro to the southeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for 20 kilometres of coastline on the Adriatic Sea surrounding the city of Neum. In the central and eastern interior of the country the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and the northeast is predominantly flatland. The inland is a geographically larger region and has a moderate continental climate, bookended by hot summers and cold and snowy winters. The southern tip of the country has a Mediterranean climate and plain topography. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a region that traces permanent human settlement back to the Neolithic age, during and after which it was populated by several Illyrian and Celtic civilizations.
- GaboroneBotswana, officially the Republic of Botswana, is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa. The citizens refer to themselves as Batswana. Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent within the Commonwealth on 30 September 1966. Since then, it has maintained a strong tradition as a stable representative democracy, with a consistent record of uninterrupted democratic elections. Geographically, Botswana is flat, with up to 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahari Desert. It is bordered by South Africa to the south and southeast, Namibia to the west and north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast. Its border with Zambia to the north near Kazungula is poorly defined but at most is a few hundred metres long. A mid-sized country of just over two million people, Botswana is one of the most sparsely populated nations in the world. Around 10 percent of the population lives in the capital and largest city, Gaborone.More Botswana
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #132 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- SofiaBulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. With a territory of 110,994 square kilometres, Bulgaria is Europe's 16th-largest country. Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period.More Bulgaria
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Population List
- #190 of 232 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
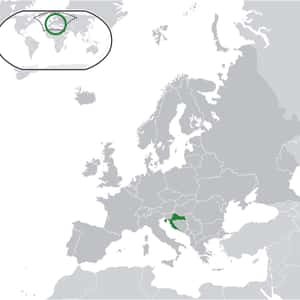
- ZagrebCroatia, officially the Republic of Croatia is a sovereign state at the crossroads of Central Europe, Southeast Europe, and the Mediterranean. Its capital city is Zagreb, which forms one of the country's primary subdivisions, along with its twenty counties. Croatia covers 56,594 square kilometres and has diverse, mostly continental and Mediterranean climates. Croatia's Adriatic Sea coast contains more than a thousand islands. The country's population is 4.28 million, most of whom are Croats, with the most common religious denomination being Roman Catholicism. The Croats arrived in the area of present-day Croatia during the early part of the 7th century AD. They organised the state into two duchies by the 9th century. Tomislav became the first king by 925, elevating Croatia to the status of a kingdom. The Kingdom of Croatia retained its sovereignty for nearly two centuries, reaching its peak during the rule of Kings Peter Krešimir IV and Dmitar Zvonimir. Croatia entered a personal union with Hungary in 1102. In 1527, faced with Ottoman conquest, the Croatian Parliament elected Ferdinand I of the House of Habsburg to the Croatian throne.
- PragueThe Czech Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the northwest and west, Austria to the south, Slovakia to the east and Poland to the northeast. Prague, the capital, is the largest city, with 1.3 million residents. The Czech Republic includes the historical territories of Bohemia and Moravia, and Czech Silesia. The Czech state was formed in the late 9th century as the Duchy of Bohemia under the Great Moravian Empire. After the fall of the Empire in 907, the centre of power transferred from Moravia to Bohemia under the Přemyslids. In 1004, the duchy was formally recognized as part of the Holy Roman Empire, becoming the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1212, and reaching its greatest territorial extent in the 14th century. The King of Bohemia ruled not only Bohemia itself, but also other lands, which together formed the so-called Crown of Bohemia, and he had a vote in the election of the Holy Roman Emperor.More Czech Republic
- Dig Deeper...Teen Titans Is The Greatest DC Superhero Cartoon Ever Made, Fight Me
- And Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Czech Republic
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- RoseauDominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island nation in the Lesser Antilles region of the Caribbean Sea, south-southeast of Guadeloupe and northwest of Martinique. Its size is 750 square kilometres and the highest point in the country is Morne Diablotins, which has an elevation of 1,447 metres. The Commonwealth of Dominica had a population of 72,301 at the 2014 Census. The capital is Roseau which is located on the leeward side of the island. Dominica was first discovered by the Spanish, then colonized by the French and British before finally obtaining independence in 1978. Dominica has been nicknamed the "Nature Isle of the Caribbean" for its unspoiled natural beauty. It is the youngest island in the Lesser Antilles, still being formed by geothermal-volcanic activity, as evidenced by the world's second-largest hot spring, Boiling Lake. The island features lush mountainous rainforests, home of many rare plant, animal, and bird species. There are xeric areas in some of the western coastal regions, but heavy rainfall occurs inland. The island has 365 rivers. The Sisserou parrot, is found only on Dominica and is the island's national bird.
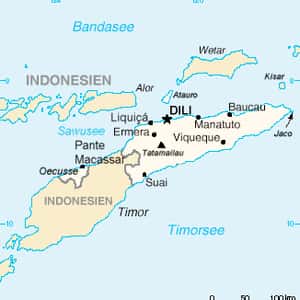
- DiliEast Timor or Timor-Leste, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a country in Maritime Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco, and Oecusse, an exclave on the northwestern side of the island, within Indonesian West Timor. The country's size is about 15,410 km. East Timor was colonised by Portugal in the 16th century, and was known as Portuguese Timor until Portugal's decolonisation of the country. In late 1975, East Timor declared its independence but later that year was invaded and occupied by Indonesia and was declared Indonesia's 27th province the following year. In 1999, following the United Nations-sponsored act of self-determination, Indonesia relinquished control of the territory, and East Timor became the first new sovereign state of the 21st century on May 20, 2002. After independence, East Timor became a member of the United Nations and the Community of Portuguese Language Countries. In 2011, East Timor announced its intention to gain membership status in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations by submitting a letter of application to become its eleventh member.
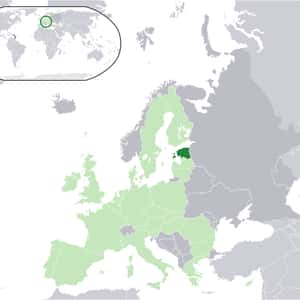
- TallinnEstonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. Across the Baltic Sea lies Sweden in the west and Finland in the north. The territory of Estonia covers 45,227 km², and is influenced by a humid continental climate. Estonia is a democratic parliamentary republic divided into fifteen counties, with its capital and largest city being Tallinn. With a population of 1.3 million, it is one of the least-populous member states of the European Union, Eurozone, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization and the Schengen Area. The Estonians are a Finnic people, and the official language, Estonian, is a Finno-Ugric language closely related to Finnish and the Sami languages, and distantly to Hungarian. A developed country with an advanced, high-income economy, Estonia is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. It ranks very high in the Human Development Index, and performs favourably in measurements of economic freedom, civil liberties, education, and press freedom.More Estonia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #51 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Addis AbabaEthiopia, officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea to the north and northeast, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Sudan and South Sudan to the west, and Kenya to the south. With over 90 million inhabitants, Ethiopia is the most populous landlocked country in the world, as well as the second-most populated nation on the African continent. It occupies a total area of 1,100,000 square kilometres, and its capital and largest city is Addis Ababa. Some of the oldest evidence for modern humans is found in Ethiopia, which is widely considered the region from which Homo sapiens first set out for the Middle East and points beyond. Tracing its roots to the 2nd millennium BC, Ethiopia was a monarchy for most of its history. During the first centuries of the Common Era the Kingdom of Aksum maintained a unified civilization in the region. Ethiopia derived prestige for its uniquely successful military resistance during the late 19th-century Scramble for Africa, and subsequently many African nations adopted the colors of Ethiopia's flag following their independence.More Ethiopia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #124 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- SuvaFiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about 1,100 nautical miles northeast of New Zealand's North Island. Its closest neighbours are Vanuatu to the west, New Caledonia to the southwest, New Zealand's Kermadec Islands to the southeast, Tonga to the east, the Samoas and France's Wallis and Futuna to the northeast, and Tuvalu to the north. Fiji is an archipelago of more than 332 islands, of which 110 are permanently inhabited, and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about 18,300 square kilometres. The farthest island is Onu-i-Lau. The two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu, account for 87% of the population of almost 860,000. The capital and largest city, Suva, is on Viti Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts, either in Suva or in smaller urban centres like Nadi or Lautoka. Viti Levu's interior is sparsely inhabited due to its terrain. Fiji has one of the most developed economies in the Pacific due to an abundance of forest, mineral, and fish resources. Today, the main sources of foreign exchange are its tourist industry and sugar exports.
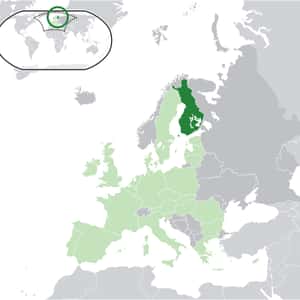
- HelsinkiFinland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe bordered by Sweden to the west, Norway to the north and Russia to the east; Estonia lies to the south across the Gulf of Finland. Finland is part of the collective geographical group of nations Fennoscandia. In 2013, Finland's population was around 5.5 million, with the majority living in its southern regions. In terms of area, it is the eighth largest country in Europe and the most sparsely populated country in the European Union. Finland is a parliamentary republic with a central government based in the capital Helsinki, local governments in 336 municipalities and an autonomous region, the Åland Islands. Over 1.4 million people live in the Greater Helsinki metropolitan area, which produces a third of the country's GDP. Other large cities include Tampere, Turku, Oulu, Jyväskylä, Lahti, and Kuopio. From the late 12th century until 1809, Finland was part of Sweden, a legacy reflected in the prevalence of the Swedish language and its official status.More Finland
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Finland
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #58 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
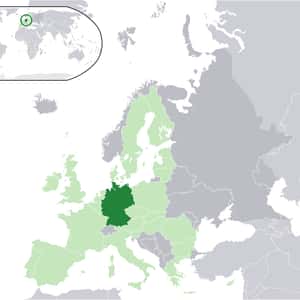
- BerlinGermany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It consists of 16 constituent states, which retain limited sovereignty, and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. The seat of government is Berlin and Bonn. Germany is a great power and traditionally a leader in many cultural, theoretical and technical fields. With 80.7 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is also the second most popular migration destination in the world. Germany has the world's fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world's third-largest exporter and third-largest importer of goods. It is a developed country with a very high standard of living, featuring comprehensive social security that includes the world's oldest universal health care system.More Germany
- Dig Deeper...How Two Families Escaped East Germany In A Homemade Hot Air Balloon
- And Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From Germany, Ranked
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
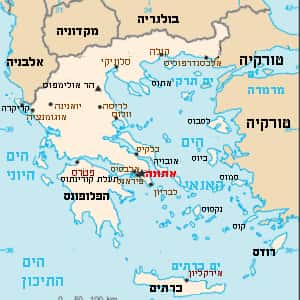
- AthensGreece, officially the Hellenic Republic and known since ancient times as Hellas, is a country located in southeastern Europe. According to the 2011 census, Greece's population is around 11 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, with Thessaloniki being the second largest and referred to as the co-capital. Greece is strategically located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia and Africa. Situated on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, the Republic of Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north and Turkey to the northeast. The country consists of nine geographic regions: Macedonia, Central Greece, the Peloponnese, Thessaly, Epirus, the Aegean Islands, Thrace, Crete, and the Ionian Islands. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin and the 11th longest coastline in the world at 13,676 km in length, featuring a vast number of islands. Eighty percent of Greece is mountainous, of which Mount Olympus is the highest peak at 2,917 m.More Greece
- Dig Deeper...The Best Greek Islands to Visit
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #8 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
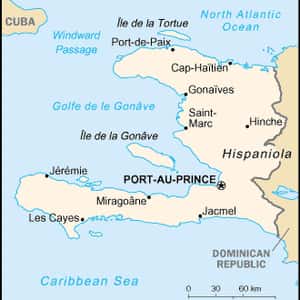
- Port-au-PrinceHaiti, officially the Republic of Haïti, is a Caribbean country. It occupies the western, smaller portion of the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. In addition, Haiti also occupies small satellite islands known for tourists, including; Île-à-Vache, which includes Port Morgan and Abaka Bay resorts. In French, the country's nickname is La Perle des Antilles, because of its natural beauty. It is the most mountainous nation in the Caribbean and the country's highest point is Pic la Selle, at 2,680 metres. By area and population, Haiti is the third largest Caribbean nation, with 27,750 square kilometres, and an estimated 9.9 million people; about a million of whom live in the capital city of Port-au-Prince. Haiti's regional, historical, and ethno-linguistic position is unique for several reasons. Originally inhabited by the indigenous Taíno people, the island was first discovered by Christopher Columbus during his first voyage across the Atlantic in 1492. When Columbus first landed in Haiti, he had thought he had found India or Asia.More Haiti
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #183 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BudapestHungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The country's capital and largest city is Budapest. Hungary is a member of the European Union, the OECD, the Visegrád Group, and the Schengen Area. The official language is Hungarian, which is the most widely spoken non-Indo-European language in Europe.More Hungary
- Dig Deeper...The Best Hungarian Soccer Players of All Time, Ranked
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #149 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ReykjavikIceland is a Nordic island country between the North Atlantic and the Arctic Ocean. It has a population of 329,100 and an area of 103,000 km², making it the most sparsely populated country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Reykjavík; the surrounding areas in the southwest of the country are home to two-thirds of the population. Iceland is volcanically and geologically active. The interior consists mainly of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, while many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. According to Landnámabók, the settlement of Iceland began in 874 CE when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first permanent settler on the island. In the following centuries, Scandinavians settled Iceland, bringing with them thralls of Gaelic origin. From 1262 to 1918, Iceland was ruled by Norway and later Denmark. The country became independent in 1918 and a republic in 1944. Until the 20th century, Iceland relied largely on fishing and agriculture.More Iceland
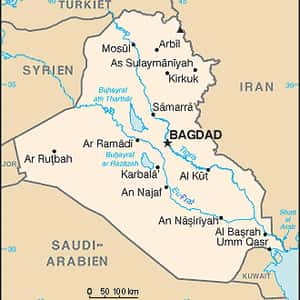
- BaghdadIraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in Western Asia. The country borders Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to the southwest, and Syria to the west. The southern part of Iraq is within the Arabian Peninsula. The capital, Baghdad, is in the center of the country and its largest city. The largest ethnic groups in Iraq are Arabs and Kurds. Other ethnic groups include Assyrians, Turkmen, Shabakis, Armenians, Mandeans, Circassians and Kawliya. Around 95% of the country's 36 million citizens are Shia or Sunni Muslims, with Christianity, Yarsan, Yezidism and Mandeanism also present. Iraq has a narrow section of coastline measuring 58 km on the northern Persian Gulf and its territory encompasses the Mesopotamian Alluvial Plain, the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, and the eastern part of the Syrian Desert. Two major rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, run south through the center of Iraq and flow into the Shatt al-Arab near the Persian Gulf. These rivers provide Iraq with significant amounts of fertile land.More Iraq
- Dig Deeper...The 40+ Best Iraq War Movies
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #200 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- RomeItaly, officially the Italian Republic, is a unitary parliamentary republic in Europe. Italy covers an area of 301,338 km² and has a largely temperate climate; due to its shape, it is often referred to in Italy as lo Stivale. With 61 million inhabitants, it is the 5th most populous country in Europe. Italy is a very highly developed country and has the third largest economy in the Eurozone and the eighth-largest in the world. Since ancient times, Etruscan, Magna Graecia and other cultures have flourished in the territory of present-day Italy, being eventually absorbed by Rome, that has for centuries remained the leading political and religious centre of Western civilisation, capital of the Roman Empire and Christianity. During the Dark Ages, the Italian Peninsula faced calamitous invasions by barbarian tribes, but beginning around the 11th century, numerous Italian city-states rose to great prosperity through shipping, commerce and banking. Especially during The Renaissance, Italian culture thrived, producing scholars, artists, and polymaths such as Leonardo da Vinci, Galileo, Michelangelo and Machiavelli.More Italy
- Dig Deeper...The Best Italian Foods
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #54 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BishkekKyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, formerly known as Kirghizia, is a country located in Central Asia. Landlocked and mountainous, Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the southwest and China to the east. Its capital and largest city is Bishkek. Kyrgyzstan's history spans over 2,000 years, encompassing a variety of cultures and empires. Although geographically isolated by its highly mountainous terrain – which has helped preserve its ancient culture – Kyrgyzstan has historically been at the crossroads of several great civilizations, namely as part of the Silk Road and other commercial and cultural routes. Though long inhabited by a succession of independent tribes and clans, Kyrgyzstan has periodically come under foreign domination due to its strategic location, attaining sovereignty as a nation-state only after the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991. Since independence, Kyrgyzstan has officially been a unitary parliamentary republic, although it continues to endure ethnic conflicts, revolts, economic troubles, transitional governments, and political party conflicts.More Kyrgyzstan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #102 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- RigaLatvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe, one of the three Baltic states. It is bordered by Estonia, Lithuania, Russia, and Belarus, as well as a maritime border to the west with Sweden. Latvia has 2,070,371 inhabitants and a territory of 64,589 km² (24,938 sq mi). The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Latvia is a democratic parliamentary republic established in 1918. The capital city is Riga, the European Capital of Culture 2014. Latvian is the official language. Latvia is a unitary state, divided into 118 administrative divisions, of which 109 are municipalities and 9 are cities. Latvians and Livs are the indigenous people of Latvia. Latvian is an Indo-European language; it and Lithuanian are the only two surviving Baltic languages. Despite foreign rule from the 13th to 20th centuries, the Latvian nation maintained its identity throughout the generations via the language and musical traditions. Latvia and Estonia share a long common history. As a consequence of the Soviet occupation, both countries are home to a large number of ethnic Russians (26.9% in Latvia and 25.5% in Estonia), some of whom are non-citizens.
- BeirutLebanon, officially the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south. Lebanon's location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has dictated its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious and ethnic diversity. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back more than seven thousand years, predating recorded history. Lebanon was the home of the Phoenicians and their kingdom, a maritime culture that flourished for over a thousand years. In 64 BC, the region came under the rule of the Roman Empire, and eventually became one of the Empire's leading centers of Christianity. In the Mount Lebanon range a monastic tradition known as the Maronite Church was established. As the Arab Muslims conquered the region, the Maronites held onto their religion and identity. However, a new religious group, the Druze, established themselves in Mount Lebanon as well, a religious divide that would last for centuries. During the Crusades, the Maronites re-established contact with the Roman Catholic Church and asserted their communion with Rome.More Lebanon
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #56 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- VallettaMalta, officially the Republic of Malta, is a Southern European island country comprising an archipelago of a few islands in the Mediterranean Sea. It lies 80 km south of Sicily, 284 km east of Tunisia, and 333 km north of Libya. The country covers just over 316 km², with a population of around 450,000, making it one of the world's smallest and most densely populated countries. The capital of Malta is Valletta, which at 0.8 km², is the smallest national capital in the European Union. Malta has two official languages: Maltese and English. Malta's location has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, and a succession of powers, including the Phoenicians, Romans, Moors, Normans, Sicilians, Habsburg Spain, Knights of St. John, French and British, have ruled the islands. Malta gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1964 and became a republic in 1974. Malta was admitted to the United Nations in 1964 and to the European Union in 2004; in 2008, it became part of the eurozone.More Malta
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...The Top 50 Healthcare Systems Around The World
- #167 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Port LouisMauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about 2,000 kilometres off the southeast coast of the African continent. The country includes the island of Mauritius, Rodrigues, the islands of Agalega, and the archipelago of Saint Brandon. The islands of Mauritius, Rodrigues, and Réunion form part of the Mascarene Islands. The area of the country is 2,040 km². The capital and largest city is Port Louis. Mauritius claims sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago and Tromelin Island. The United Kingdom excised the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritian territory prior to Mauritian independence in 1965. The UK gradually depopulated the archipelago's indigenous population and leased its biggest island, Diego Garcia, to the United States. The US soon thereafter established a military base on Diego Garcia. The island of Mauritius was visited during the medieval period by the Arabs and then by the Portuguese, who named it Dina Arobi and Cirne, respectively. The island was uninhabited until the Dutch Republic established a colony in 1638, with the Dutch naming the island after Prince Maurice van Nassau.More Mauritius
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #20 of 161 onThe Most Beautiful Countries In The World
- Ulan BatorMongolia is a landlocked country in east-central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and also the largest city, is home to about 45% of the population. Mongolia's political system is a parliamentary republic. The area of what is now Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the Turkic Khaganate, and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, and his grandson Kublai Khan conquered China to establish the Yuan Dynasty. After the collapse of the Yuan, the Mongols retreated to Mongolia and resumed their earlier pattern of factional conflict except during the era of Dayan Khan and Tumen Zasagt Khan. In the 16th centuries, Tibetan Buddhism began to spread in Mongolia and it was accelerated by the unwavering support of the Qing government after Mongolia was incorporated by the Qing dynasty. In the 1900s almost half of the adult male population were Buddhist monks. By the mid-18th century, all of Mongolia had been incorporated into the area ruled by the Manchus' Qing Dynasty.More Mongolia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #105 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
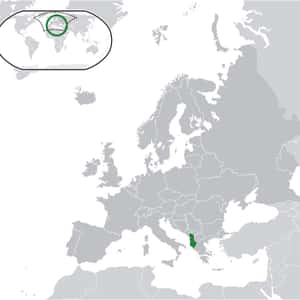
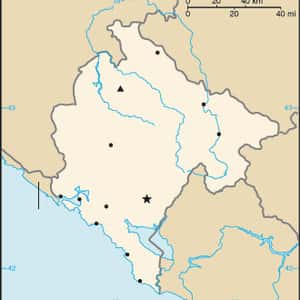
- PodgoricaMontenegro is a country in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast, and Albania to the south-east. Its capital and largest city is Podgorica, while Cetinje is designated as the Prijestonica, meaning the former Royal Capital City. In the 9th century, there existed three Serb principalities on the territory of Montenegro: Duklja, roughly corresponding to the southern half, Travunia, the west, and Rascia, the north. In 1042, archon Stefan Vojislav led a revolt that resulted in the independence of Duklja and the establishment of the Vojislavljević dynasty. Duklja reached its zenith under Vojislav's son, Mihailo, and his grandson Bodin. By the 13th century, Zeta had replaced Duklja when referring to the realm. In the late 14th century, southern Montenegro came under the rule of the Balšić noble family, then the Crnojević noble family, and by the 15th century, Zeta was more often referred to as Crna Gora. Large portions fell under the control of the Ottoman Empire from 1496 to 1878. Parts were controlled by Venice.
- IslamabadPakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a sovereign country in South Asia. With a population exceeding 180 million people, it is the sixth most populous country and with an area covering 796,095 km², it is the 36th largest country in the world in terms of area. Pakistan has a 1,046-kilometre coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by the nations of India to the east, Afghanistan to the west, Iran to the southwest and China in the far northeast respectively. It is separated from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's narrow Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a marine border with Oman. The territory that now constitutes Pakistan was previously home to several ancient cultures, including the Mehrgarh of the Neolithic and the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation, and was later home to kingdoms ruled by people of different faiths and cultures, including Hindus, Indo-Greeks, Muslims, Turco-Mongols, Afghans and Sikhs.More Pakistan
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Pakistan
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #71 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World