Countries Ruled by A Constitutional Republic
List of countries, nations and states governed or ruled by a constitutional republic, sorted alphabetically. In some cases nations may have multiple ruling bodies or government types, meaning they're not exclusively countries that are governed by constitutional republic. This list of countries that use constitutional republic as their form of government contains various bits of information about each nation, such as the official language or currency of the country. If you're looking for the names of countries with constitutional republic governments then you're in the right place.
List includes Somaliland, Philippines and more.
This list answers the questions, "Which countries are ruled by constitutional republic?" and "Which countries are governed by constitutional republic?"- AccraGhana, officially called the Republic of Ghana, is a sovereign multinational state and unitary presidential constitutional democracy, located along the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean, in the subregion of West Africa. Spanning a land mass of 238,535 km, Ghana is bordered by the Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, Togo in the east and the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean in the south. The word Ghana means "Warrior King" in Mande. Ghana has a population of approximately 27 million, from a variety of ethnic and religious groups. Its varied geography includes savannas, forests, springs, cave systems, mountains, estuaries, and nature reserves. Ghana's 560 kilometres coast is dotted by culturally significant castles, forts, and harbours. Prior to colonisation by the British empire in the early-20th century, Ghana was the site of numerous kingdoms and empires, the most powerful being the Kingdom of Ashanti. In 1957, it became the first African nation to declare independence from European colonisation. This made the country a symbol of black achievement and an inspiration for African independence movements.
- TegucigalpaHonduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a republic in Central America. It was at times referred to as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize. The country is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, and to the north by the Gulf of Honduras, a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea. Honduras was home to several important Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya, prior to being conquered by Spain in the sixteenth century. The Spanish introduced Roman Catholicism and the now predominant Spanish language, along with numerous customs that have blended with the indigenous culture. The country became independent in 1821 and has since been a republic, although it has consistently endured much social strife and political instability, remaining one of the poorest countries in the Western Hemisphere. Honduras spans an area of about 112,492 km² and has a population exceeding 8 million. Its northern portions are part of the Western Caribbean Zone, as reflected in the area's demographics and culture.More Honduras
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #162 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- New DelhiIndia, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the south-west, and the Bay of Bengal on the south-east, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north-east; and Burma and Bangladesh to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia. Home to the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation and a region of historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian subcontinent was identified with its commercial and cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism—originated here, whereas Zoroastrianism and the abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam arrived in the 1st millennium CE and also helped shape the region's diverse culture.More India
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Computers In Use: World's Top 15 Countries In PC Usage
- #28 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Mexico CityMexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a federal republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Covering almost two million square kilometres, Mexico is the fifth largest country in the Americas by total area and the 13th largest independent nation in the world. With an estimated population of over 113 million, it is the eleventh most populous and the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world and the second most populous country in Latin America. Mexico is a federation comprising thirty-one states and a Federal District, its capital and largest city. In pre-Columbian Mexico many cultures matured into advanced civilizations such as the Olmec, the Toltec, the Teotihuacan, the Zapotec, the Maya and the Aztec before first contact with Europeans. In 1521, the Spanish Empire conquered and colonized the territory from its base in Mexico-Tenochtitlan, which was administered as the Viceroyalty of New Spain.More Mexico
- Dig Deeper...This Museum Has 111 Eerily Preserved 'Screaming Mummies'
- And Deeper...The 100+ Best Soccer Players From Mexico, Ranked
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- AsunciónParaguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in central South America, bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. Paraguay lies on both banks of the Paraguay River, which runs through the center of the country from north to south. Due to its central location in South America, it is sometimes referred to as Corazón de América. The indigenous Guaraní had been living in Paraguay for at least a millennium before the Spanish conquered the territory in the 16th century. Spanish settlers and Jesuit missions introduced Christianity and Spanish culture to the region. Paraguay was on the periphery of Spain's colonial empire, with few urban centers and a sparse population. Following independence from Spain in 1811, Paraguay was ruled by a series of dictators who implemented isolationist and protectionist policies. This development was truncated by the disastrous Paraguayan War, in which the country lost 60 to 70 percent of its population through war and disease, and about 140,000 square kilometers of territory to Argentina and Brazil.More Paraguay
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Nations That Are 'Against' Death Penalty
- #222 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ManilaThe Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines, is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of 7,107 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. Its capital city is Manila while its most populous city is Quezon City; both are part of Metro Manila. To the north of the Philippines across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan; Vietnam sits west across the South China Sea; southwest is the island of Borneo across the Sulu Sea, and to the south the Celebes Sea separates it from other islands of Indonesia; while to the east it is bounded by the Philippine Sea and the island-nation of Palau. Its location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world's greatest biodiversity. At approximately 300,000 square kilometers, the Philippines is the 64th-largest country in the world.More Philippines
- Dig Deeper...Terrifying Monsters And Urban Myths From The Philippines
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #43 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- DublinIreland, also known as the Republic of Ireland, is a sovereign state in western Europe occupying about five-sixths of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, located in the eastern part of the island, whose metropolitan area is home to around a third of the country's 4.6 million inhabitants. The state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, a part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, Saint George's Channel to the south east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic with an elected president serving as head of state. The head of government, the Taoiseach, is nominated by the lower house of parliament, Dáil Éireann. The Irish Free State was created in 1922 as a result of the Anglo-Irish Treaty. It effectively became a republic, with an elected president, under the constitution of 1937, in which it was named "Ireland". It was officially declared a republic in 1949. Ireland became a member of the United Nations in December 1955. It joined the European Economic Community, predecessor of the European Union, in 1973.More Republic of Ireland
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #94 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- FreetownSierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Guinea in the north-east, Liberia in the south-east, and the Atlantic Ocean in the south-west. Sierra Leone has a tropical climate, with a diverse environment ranging from savannah to rainforests. Sierra Leone has a total area of 71,740 km² and an estimated population of 6 million. Freetown is the capital, largest city, and its economic and political centre. Bo is the second largest city and second major economic center in the country. The country is divided into four geographical regions: the Northern Province, Eastern Province, Southern Province and the Western Area, which are further divided into fourteen districts. About sixteen ethnic groups inhabit Sierra Leone, each with their own language and custom. The two largest and most influential are the Temne and the Mende people. The Temne are predominantly found in the north of the country, while the Mende are predominant in the south-east.More Sierra Leone
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #197 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
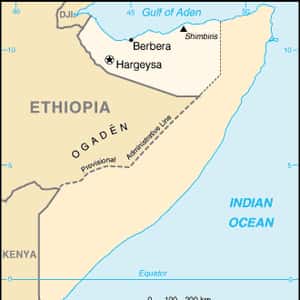
- HargeisaSomaliland is a self-declared independent state that is internationally recognized as an autonomous region of Somalia. The government of Somaliland regards itself as the successor state to the former British Somaliland protectorate, which as the State of Somaliland united as scheduled on 1 July 1960 with the Trust Territory of Somaliland to form the Somali Republic. Somaliland lies in northwestern Somalia, on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden. It is bordered by the autonomous Puntland region of Somalia to the east, Djibouti to the northwest, and Ethiopia to the south and west. Its claimed territory has an area of 137,600 square kilometres, with approximately 3.5 million residents. The capital and the largest city is Hargeisa, with the population of around 750,000 residents. In 1988, the Siad Barre regime launched a clampdown against the Hargeisa-based Somali National Movement and other rebel outfits, which were among the events that led to the Somali Civil War. The conflict left the economic and military infrastructure severely damaged.
- Washington, D.C.The United States of America, commonly referred to as the United States or America, is a federal republic consisting of 50 states and a federal district. The 48 contiguous states and Washington, D.C., are in central North America between Canada and Mexico. The state of Alaska is located in the northwestern part of North America and the state of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific. The country also has five populated and numerous unpopulated territories in the Pacific and the Caribbean. At 3.80 million square miles and with over 320 million people, the United States is the world's fourth-largest country by total area and third most populous. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many countries. The geography and climate of the United States are also extremely diverse, and the country is home to a wide variety of wildlife. Paleo-Indians migrated from Eurasia to what is now the U.S. mainland around 15,000 years ago, with European colonization beginning in the 16th century. The United States emerged from 13 British colonies located along the East Coast.
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Computers In Use: World's Top 15 Countries In PC Usage
- #19 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Sana'aYemen, officially known as the Republic of Yemen, is an Arab country in Southwest Asia, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. Yemen is the second largest country in the peninsula, occupying 527,970 km². The coastline stretches for about 2,000 km. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea to the south, and Oman to the east. Although Yemen's constitutionally stated capital is the city of Sana'a, the city has been under rebel control since February 2015. Because of this, Yemen's capital has been temporarily relocated to the port city of Aden, on the southern coast. Yemen's territory includes more than 200 islands, the largest of these is Socotra. Yemen was home of the Sabaeans, a trading state that flourished for over a thousand years and probably also included parts of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. In 275 AD, the region came under the rule of the later Jewish influenced Himyarite Kingdom. Christianity arrived in the 4th century AD whereas Judaism and local paganism were already established.More Yemen
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #175 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World