The Difference Between Hepatitis A, B and C

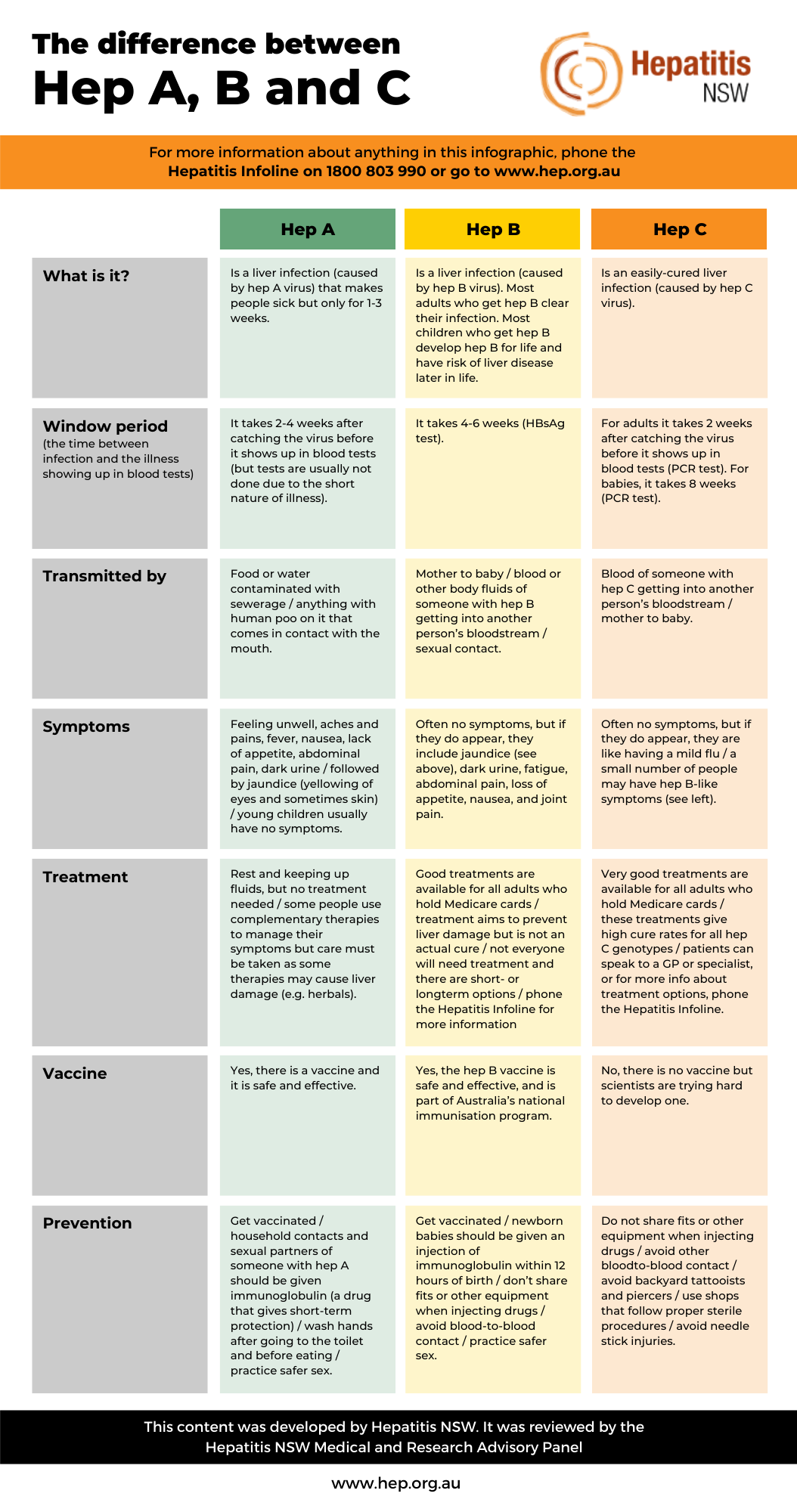
- Hepatitis A, B and C are all liver infections caused by a virus.
- You get hep A from anything that has poo on or in it, that then has contact with your mouth. The poo has to contain the hep A virus. Hep A infection lasts a short time and most people recover quickly, but some get seriously sick.
- Hep B is most often passed on from mother to baby during childbirth.
Hep B lives in blood and sexual fluids.
Hep B can’t yet be cured.
You can live a healthy life with hep B, with 6-monthly visits to your doctor. - Hep C is only passed on through blood-to-blood contact, when blood from someone with hep C gets into someone else’s bloodstream.
Hep C is easily cured. - There is a vaccination for hepatitis A and B. There is no vaccine for hep C.
If you’ve heard about the different types of hepatitis and are wondering what’s the difference between them, read on. This clear guide to the difference between Hepatitis A, B and C, will answer all your questions.
All About Hepatitis A
What is it?
Hepatitis A is a liver infection (caused by hep A virus) that makes people sick but only for 1-3 weeks.
When should you test for Hepatitis A?
It takes 2-4 weeks after catching the virus before it shows up in blood tests (but tests are usually not done due to the short nature of illness).
How is Hepatitis A transmitted?
Food or water contaminated with sewerage /anything with human poo on it that comes in contact with the mouth.
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis A?
Feeling unwell, aches and pains, fever, nausea, lack of appetite, abdominal pain, dark urine. This may be followed by jaundice (yellowing of eyes and sometimes skin). Young children usually have no symptoms.
Can hepatitis A be treated? What treatments are available?
Rest and keeping up fluids, but no treatment needed. Some people use complementary therapies to manage their symptoms but care must be taken as some therapies may cause liver damage (e.g. herbals).
Is there a vaccine for Hepatitis A?
Yes, there is a vaccine and it is safe and effective.
How to prevent Hepatitis A?
Get vaccinated. Household contacts and sexual partners of someone with hep A should be given immunoglobulin (a drug that gives short-term protection). Wash hands after going to the toilet and before eating. Practice safer sex.
All About Hepatitis B
What is it?
Is a liver infection (caused by hep B virus). Most adults who get hep B clear their infection. Most children who get hep B develop hep B for life and have risk of liver disease later in life. Read more about Hepatitis B here.
When should you test for Hepatitis B?
It takes 4-6 weeks after getting hep B, for hep B to show up in blood tests. There are 3 hep B tests for hep B – you should make sure your doctor does all of them. They show if you have hep B, if you are protected against hep B (e.g. from a vaccination), and if you have ever come into contact with hep B. Getting all three tests is important to help you and our doctor understand your hep B status. Our hep B testing chart can explain each test.
How is Hepatitis B transmitted?
Most often, hep B is passed on from mother to baby. Hep B can be passed on through blood or other body fluids of someone with hep B getting into another person’s bloodstream (including exual contact). Learn more about hep B transmission.
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis B?
Often no symptoms, but if they do appear, they include jaundice (see above), dark urine, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, and joint pain.
Can hepatitis B be treated? What treatments are available?
Good treatments are available for all adults who hold Medicare cards. Treatment aims to prevent liver damage but is not an actual cure. Not everyone will need
treatment and there are short- or long term options. Please phone the Hepatitis Infoline on 1800 803 990 for more information. Read more about monitoring and treatment of hep B.
Is there a vaccine for Hepatitis B?
Yes, the hep B vaccine is safe and effective, and is part of Australia’s national immunisation program. You can get vaccinated for hep B at your doctor’s clinic or a sexual health centre. Learn all about hep B vaccination here.
How to prevent Hepatitis B?
Getting vaccinated is an effective way to prevent hep B. Newborn babies should be given an injection of immunoglobulin within 12 hours of birth. Don’t share fits or other equipment when injecting drugs. Avoid blood-to-blood contact. Practice safer sex.
All About Hepatitis C
What is it?
It is an easily-cured liver infection (caused by hep C virus). Hep C can cause long-term health problems if left untreated, particularly for the liver.
When should you test for Hepatitis C?
For adults it takes 2 weeks after getting the virus before it shows up in blood tests (PCR test). For babies, it takes 8 weeks (PCR test).
How is Hepatitis C transmitted?
Hep C is transmitted through blood-to-blood contact. This is when the blood of someone with hep C gets into your bloodstream. Hep C can also be passed on from mother to baby, during childbirth, but this isn’t very common. Visit our ‘hep C Transmission and Prevention’ info page to learn more.
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis C?
Often no symptoms, but if they do appear, they are like having a mild flu. A small number of people may have jaundice (see above), dark urine, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, and joint pain.
Can hepatitis C be treated? What treatments are available?
Hep C is easily cured! Very good treatments are available to everyone in Australia who holds a Medicare card or Health Care Concession Card. peak to your doctor or specialist, or for more info about treatment options, phone the Hepatitis
Infoline on 1800 803 990. You can learn all about hep C treatment here.
Is there a vaccine for Hepatitis C?
No, there is no vaccine but scientists are trying hard to develop one.
How to prevent Hepatitis C?
Avoid blood-to-blood contact and use your own sterile (new) injecting equipment. If you get a tattoo or body piercing, have it done at a licensed studio.
Have more questions? Get in touch with our friendly team
For more information, phone the Hepatitis Infoline on 1800 803 990 today or go to https://www.hep.org.au/contact-us/.
You can download the below chart at this link >>