London Borough of Lewisham
London Borough of Lewisham | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Lewisham shown within Greater London | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | London |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Created | 1 April 1965 |
| Admin HQ | Catford |
| Government | |
| • Type | London borough council |
| • Body | Lewisham London Borough Council |
| • Leadership | Mayor & Cabinet (Labour) |
| • Mayor | Brenda Dacres (Labour) |
| • London Assembly | Len Duvall AM for Greenwich and Lewisham |
| • MPs | Ellie Reeves (Labour) Vicky Foxcroft (Labour) Janet Daby (Labour) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 13.57 sq mi (35.15 km2) |
| • Rank | 271st (of 296) |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 299,810 |
| • Rank | 46th (of 296) |
| • Density | 22,000/sq mi (8,500/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Postcodes | |
| Area code | 020 |
| ONS code | 00AZ |
| GSS code | E09000023 |
| Police | Metropolitan Police |
| Website | Council Website |
Lewisham (/ˈluːɪʃəm/ ⓘ LOO-ish-əm) is a London borough in south-east London, England. It forms part of Inner London. The principal settlement of the borough is Lewisham. The local authority is Lewisham London Borough Council, based in Catford. The Prime Meridian passes through Lewisham. Blackheath, Goldsmiths, University of London and Millwall F.C. are located within the borough.
History[edit]
The borough was formed in 1965, by the London Government Act 1963, as an amalgamation of the former area of the Metropolitan Borough of Lewisham and the Metropolitan Borough of Deptford, which had been created in 1900 as divisions of the County of London.[1]
Minor boundary changes have occurred since its creation. The most significant amendments were made in 1996, when the former area of the Royal Docks in Deptford was transferred from the London Borough of Greenwich.[2]
The metropolitan borough of Lewisham corresponded to the ancient parishes of Lee and Lewisham and the borough of Deptford corresponded to the parish of Deptford St Paul, including Hatcham. Prior to becoming part of the County of London in 1889, Hatcham was part of Surrey and the rest was part of Kent.
Geography[edit]

The borough is surrounded by the Royal Borough of Greenwich to the east (where the border runs between Deptford and Horn Park), the London Borough of Bromley to the south (where the border runs between Horn Park and Crystal Palace Park), and the London Borough of Southwark to the west ( where the border runs between Crystal Palace Park and Rotherhithe). The River Thames forms a short section of northern boundary with the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Deptford Creek, Pool River, River Quaggy and River Ravensbourne pass through the borough. Major landmarks include All Saints Church in Blackheath, the Citibank Tower in Lewisham, Dietrich Bonhoeffer Church (Sydenham's German Church, technically located in Forest Hill) and the Horniman Museum in Forest Hill. Millwall F.C. are based in the borough, their stadium The Den being located in South Bermondsey.
Demographics[edit]

According to the 2011 census,[3] Lewisham has a population of 275,885, is 53% white and 47% BME, and 43% of households are owner-occupiers.
A 2017 report by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute found that Lewisham has a poverty rate of 26%, close to the London-wide figure of 27%.[4]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 16,640 | — |
| 1811 | 19,728 | +18.6% |
| 1821 | 24,474 | +24.1% |
| 1831 | 27,329 | +11.7% |
| 1841 | 32,589 | +19.2% |
| 1851 | 41,593 | +27.6% |
| 1861 | 76,958 | +85.0% |
| 1871 | 112,324 | +46.0% |
| 1881 | 147,689 | +31.5% |
| 1891 | 173,229 | +17.3% |
| 1901 | 217,295 | +25.4% |
| 1911 | 272,600 | +25.5% |
| 1921 | 299,022 | +9.7% |
| 1931 | 328,010 | +9.7% |
| 1941 | 314,953 | −4.0% |
| 1951 | 302,420 | −4.0% |
| 1961 | 285,431 | −5.6% |
| 1971 | 269,401 | −5.6% |
| 1981 | 230,504 | −14.4% |
| 1991 | 240,649 | +4.4% |
| 2001 | 248,924 | +3.4% |
| 2011 | 275,885 | +10.8% |
| 2015 | 297,325 | +7.8% |
| Note:[5] | ||
Ethnicity[edit]
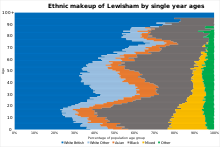
| Ethnic Group | Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 estimations[6] | 1991[7] | 2001[8] | 2011[9] | 2021[10] | ||||||
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | 193,492 | 84.9% | 180,234 | 78% | 164,098 | 65.8% | 147,686 | 53.6% | 154,749 | 51.5% |
| White: British | – | – | – | – | 141,814 | 56.9% | 114,446 | 41.5% | 111,726 | 37.2% |
| White: Irish | – | – | – | – | 5,206 | 1.9% | 6,990 | 2.8% | 5,055 | 1.7% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | – | – | – | – | 208 | 0.1% | 116 | 0.0% | ||
| White: Roma | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,033 | 0.3% |
| White: Other | – | – | – | – | 15,294 | 6.1% | 27,826 | 10.1% | 36,819 | 12.3% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | – | – | 9,576 | 4.1% | 12,881 | 5.2% | 25,534 | 9.3% | 26,927 | 9% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | – | – | 2,790 | 3,487 | 1.4% | 4,600 | 1.7% | 5,046 | 1.7% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | – | – | 739 | 1,090 | 0.4% | 1,596 | 0.6% | 2,361 | 0.8% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | – | – | 636 | 1,229 | 0.5% | 1,388 | 0.5% | 1,826 | 0.6% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | – | – | 2,380 | 3,431 | 1.4% | 6,164 | 2.2% | 6,296 | 2.1% | |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | – | – | 3,031 | 3,644 | 1.4% | 11,786 | 4.3% | 11,398 | 3.8% | |
| Black or Black British: Total | – | – | 37,524 | 16.2% | 58,260 | 23.4% | 74,942 | 27.2% | 80,473 | 26.8% |
| Black or Black British: African | – | – | 8,554 | 22,571 | 9.0% | 32,025 | 11.6% | 37,834 | 12.6% | |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | – | – | 23,229 | 10% | 30,543 | 12.3% | 30,854 | 11.2% | 31,883 | 10.6% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | – | – | 5,741 | 5,146 | 2.1% | 12,063 | 4.4% | 10,756 | 3.6% | |
| Mixed or British Mixed: Total | – | – | – | – | 10,399 | 4.1% | 20,472 | 7.4% | 24,253 | 8.2% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | – | – | – | – | 4,760 | 1.9% | 8,539 | 3.1% | 8,726 | 2.9% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | – | – | – | – | 1,599 | 0.6% | 3,559 | 1.3% | 3,774 | 1.3% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | – | – | 1,565 | 0.6% | 3,045 | 1.1% | 4,359 | 1.5% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | – | – | 2,475 | 1.0% | 5,329 | 1.9% | 7,394 | 2.5% |
| Other: Total | – | – | 3,649 | 1.5% | 3,284 | 1.3% | 7,341 | 2.6% | 14,151 | 4.8% |
| Other: Arab | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1,456 | 0.5% | 1671 | 0.6% |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | – | – | 3,649 | 1.5% | 3,284 | 1.3% | 5,795 | 2.1% | 12,480 | 4.2% |
| Ethnic minority: Total | 34,463 | 15.1% | 50,749 | 21.8% | 84,824 | 34.2% | 128,289 | 46.4% | 145,804 | 48.5% |
| Total | 227,955 | 100% | 230,983 | 100% | 248,922 | 100.00% | 275,885 | 100.00% | 300,553 | 100% |
Religion[edit]
The following table shows the religious identity of residents residing in Lewisham according to 2021 census results
| Religion | 2021[11] | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
| Christian | 131,706 | 43.8 |
| Muslim | 22,264 | 7.4 |
| Jewish | 826 | 0.3 |
| Hindu | 6,459 | 2.1 |
| Sikh | 720 | 0.2 |
| Buddhism | 3,270 | 1.1 |
| Other religion | 2,269 | 0.8 |
| No religion | 110,379 | 36.7 |
| Religion not stated | 22,660 | 7.5 |
| Total | 300,553 | 100.0 |
Age and sex[edit]
The male population in Lewisham is 157,820, and the female population is 142,733. The average age of people living in Lewisham is 37 years old.[12]
The following table shows the age distributions of residents residing in Lewisham according to 2021 census results.
| Age | 2021[11] | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
| Below 14 | 54,877 | 18.26 |
| Between 15 and 24 | 34,479 | 11.47 |
| Between 25 and 34 | 58,434 | 19.44 |
| Between 35 and 44 | 51,254 | 17.05 |
| Between 45 and 54 | 40,770 | 13.56 |
| Between 55 and 64 | 32,091 | 10.68 |
| Between 65 and 74 | 16,092 | 5.35 |
| Between 75 and 100 | 12,557 | 4.18 |
| Total | 300,553 | 100.0 |
Civic affairs[edit]

Motto[edit]
The motto of the borough is "Salus Populi Suprema Lex", which means (roughly translated) "The welfare of the people [is] the highest law."
Administration[edit]
The current Chief Executive is Kim Wright.[13] The borough is administered by the four directorates of the council: Children and Young People, Community Services, Customer Services, and Resources & Regeneration.
Twinning[edit]
The borough is twinned with the following towns:
The borough has also signed a "friendship link" with Ekurhuleni, near Johannesburg, South Africa.
Freedom of the Borough[edit]
The honour of Freedom of the Borough has been awarded to:
- Alan Milner Smith, Town Clerk (9 December 1971)
- Frederick William Winslade, appointed OBE for services to local government in Lewisham and Camberwell New Year Honours 1967[14] and CBE for services to local government in Lewisham Birthday Honours 1978[15](28 November 1975)
- Daisy Amelia Elizabeth Hurren (10 October 1985)
- Alfred Anderson Hawkins (30 March 1990)
- Desmond Tutu (4 May 1990)
- Terry Waite (16 November 1992)
- Sybil Theodora Phoenix,(8 March 1996)
- Dame Cicely Saunders, (10 March 2000)
- James Leslie Hicks ('Les') Eytle (8 June 2007)
- Dame Erica Pienaar (2013)
- Baroness (Doreen) Lawrence of Clarendon, (2014)
- Dame Joan Ruddock (2016)
- Bridget Prentice (2016)
Politics[edit]
Wards[edit]

The London Borough of Lewisham is divided into 18 wards, first used in the 2002 elections, they are:
- Bellingham
- Blackheath
- Brockley
- Catford
- Crofton Park
- Downham
- Evelyn
- Forest Hill
- Grove Park
- Ladywell
- Lee Green
- Lewisham Central
- New Cross
- Perry Vale
- Rushey Green
- Sydenham
- Telegraph Hill
- Whitefoot
New wards will be adopted at the 2022 election.[16]
Previous wards[edit]

Previously the borough was divided into 26 wards and 6 areas, used for elections from 1978 to 1998. Some of these former wards had the same names as the present wards, but their borders were different. When the wards were revised for 2002, some became larger, absorbing parts of other previous wards, the number of wards changed from 26 to 18. The previous wards and areas used from 1978 to 1998 were:
|
Lewisham Central
Lewisham North East
Lewisham North West
|
Lewisham South Lewisham South East
Lewisham South West
|
London Borough Council[edit]
Lewisham's council, unlike most English councils, is led by a directly elected mayor. The first mayoral election was in 2002 and was won by the Labour Party candidate, Steve Bullock, who was re-elected in 2006, 2010 and 2014. Following the 2018 council elections, there are 54 Labour Party councillors and none for other parties. The Mayor of Lewisham until January 2024 was Labour MP Damien Egan, who was succeeded in a by-election by Brenda Dacres who became the first black woman directly elected mayor in England.[17]
Westminster Parliament[edit]
The borough includes the constituencies of Lewisham Deptford, Lewisham West and Penge and Lewisham East.
These are the MPs who have represented constituencies covered by the borough since its formation in 1964. Constituencies change their boundaries over time, even where names remain the same.
| MP | Party | Represented | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heidi Alexander | Labour | Lewisham East | 2010–2018 |
| Christopher Chataway | Conservative | Lewisham North | 1964–66 |
| Janet Daby | Labour | Lewisham East | 2018–present |
| James Dickens | Labour | Lewisham West | 1966–70 |
| Jim Dowd | Labour | Lewisham West | 1992–2017 |
| Vicky Foxcroft | Labour | Lewisham, Deptford | 2015–present |
| John Selwyn Gummer | Conservative | Lewisham West | 1970–74 (Feb) |
| Carol Johnson | Labour | Lewisham South | 1964–74 (Feb) |
| Patrick McNair-Wilson | Conservative | Lewisham West | 1964–66 |
| John Maples | Conservative | Lewisham West | 1983–92 |
| Roland Moyle | Labour | Lewisham North Lewisham East |
1966–74 (Feb) 1974 (Feb)-79 |
| Colin Moynihan | Conservative | Lewisham East | 1983–92 |
| Bridget Prentice | Labour | Lewisham East | 1992–2010 |
| Christopher Price | Labour | Lewisham West | 1974 (Feb)-79 |
| Ellie Reeves | Labour | Lewisham West | 2017–present |
| John Silkin | Labour | Deptford Lewisham, Deptford |
1964–74 (Feb) 1974 (Feb)-87 |
Greater London representation[edit]
For elections to the Greater London Council, the borough formed the Lewisham electoral division, electing three members. In 1973 it was divided into the single-member Deptford, Lewisham East and Lewisham West electoral divisions.[18] The Greater London Council was abolished in 1986.
Since 2000, for elections to the London Assembly, the borough forms part of the Greenwich and Lewisham constituency.
Education[edit]
The London's Poverty Profile, a report by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute, found that 42% of 19-year-olds in Lewisham lack level 3 qualifications. This is the 3rd worst rate out of 32 boroughs.[19]
In 2018, Lewisham had the third highest rate of exclusions of pupils from secondary schools of any area in England.[20]
Transport[edit]

Lewisham station, once known as Lewisham Junction, is located at the junction of the lines to Dartford and Hayes, and is also the terminus of the southern branch of the Docklands Light Railway.
The East London Line (on the London Underground network) terminated at New Cross and New Cross Gate until December 2007. An extension to this line opened on 23 May 2010, serving Brockley, Honor Oak Park, Forest Hill, and Sydenham. This forms part of the London Overground network.
The South London Line runs along the extreme North West of the borough, at present there are no stations that are within the borough. There is a proposal for a new station at New Bermondsey providing a link to Clapham Junction.
Railway stations[edit]
|
|
DLR stations[edit]
- Deptford Bridge – on the border between Lewisham and Greenwich.
- Elverson Road – on the border between Lewisham and Greenwich.
- Lewisham
London Underground[edit]
There are no Tube stations currently in the borough, as the East London Line has been part of London Overground since 2006. However, an extension of the Bakerloo line beyond Elephant & Castle to Lewisham and Hayes has been proposed.[21]
Cycling[edit]
Quietway one links Lewisham to Greenwich and in toward central London
One Cycle Superhighways will operate through Lewisham in the future.
- CS4 – Will along Deptford's Evelyn Street (A200). Will operate between Greenwich and Tower Bridge. Construction will start in Summer 2019
Main roads[edit]
- A2 from the border with Old Kent Road in the west to Kidbrooke in the east.
- A20 from New Cross to the border with Eltham in the east.
- A21 from Lewisham to the border with Bromley in the south.
- A202 from New Cross Gate to the border with Peckham in the west.
- A205 (South Circular Road) passes through the centre of the borough from the border with Dulwich in the west to Eltham in the east. Except for a short section in Lee as it approaches Eltham, it is purely a one-lane-each-way road.
Travel to work[edit]
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: train, 18.6% of all residents aged 16–74; driving a car or van, 11.2%; bus, minibus or coach, 11.2%; underground, metro, light rail, tram, 9.7%; on foot, 4.3%; work mainly at or from home, 2.8%; bicycle, 2.6%.[22]
48% of households in the borough are car free, compared to 42% across Greater London.[23]
Culture[edit]
Lewisham won London Borough of Culture for 2020. The prestigious award, is a major initiative launched by the Mayor of London in June 2017, will see Lewisham receive £1.35 million to stage an ambitious, year-long programme of cultural events celebrating the wealth of creative talent in the borough and delivering lasting social change.
Sport and leisure[edit]
Millwall Football Club was originally formed in 1885, in Millwall on the Isle of Dogs, East London. They retained the name, even though they moved across the river to New Cross, South London in 1910. In 1993 they moved to their current stadium, The Den which is in Bermondsey, but falls under the Borough of Lewisham. The Borough has a Non-League football club Lewisham Borough Football Club, who play at the Ladywell Arena, Catford.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Vision of Britain Archived 11 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine – Lewisham LB
- ^ OPSI – The Greenwich and Lewisham (London Borough Boundaries) Order 1993
- ^ "2011 Census Second Release December 2012" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 March 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ^ "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- ^ "Lewisham: Total Population". A Vision of Britain Through Time. Great Britain Historical GIS Project. Retrieved 6 September 2011.
- ^ "Ethnic minorities in Britain: statistical information on the pattern of settlement". Commission for Racial Equality: Table 2.2. 1985.
- ^ "1991 census – theme tables". NOMIS. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- ^ "KS006 - Ethnic group". NOMIS. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "Ethnic Group by measures". NOMIS. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ "Ethnic group - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ a b "Religion - Religion by local authorities, ONS".
- ^ "Lewisham Area Information - Map | Demographics". postcodeinfo.uk. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ "The chief executive". Lewisham Council.
- ^ Supplement to the London Gazette 1 January 1967, p. 15
- ^ "Supplement to the London Gazette 3 June 1978, p. 6237" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 November 2012.
- ^ "Political map of Lewisham set to change". Local Government Boundary Commission for England. 25 June 2019.
- ^ "First black woman wins directly elected mayoralty". BBC News. 8 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- ^ Boothroyd, David. "Greater London Council Election results: Lewisham". United Kingdom Election Results. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 8 September 2023.
- ^ "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Archived from the original on 3 July 2018. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- ^ Children and Young People Select Committee (5 September 2018). "Exclusions from school – an in-depth review" (PDF). London Borough of Lewisham. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 July 2019.
- ^ "Bakerloo line extension". Transport for London.
- ^ "2011 Census: QS701EW Method of travel to work, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 November 2013. Percentages are of all residents aged 16–74 including those not in employment. Respondents could only pick one mode, specified as the journey’s longest part by distance.
- ^ 2011 Census, Car or Van Availability (QS416EW)



