1902-1967
Who Was Langston Hughes?
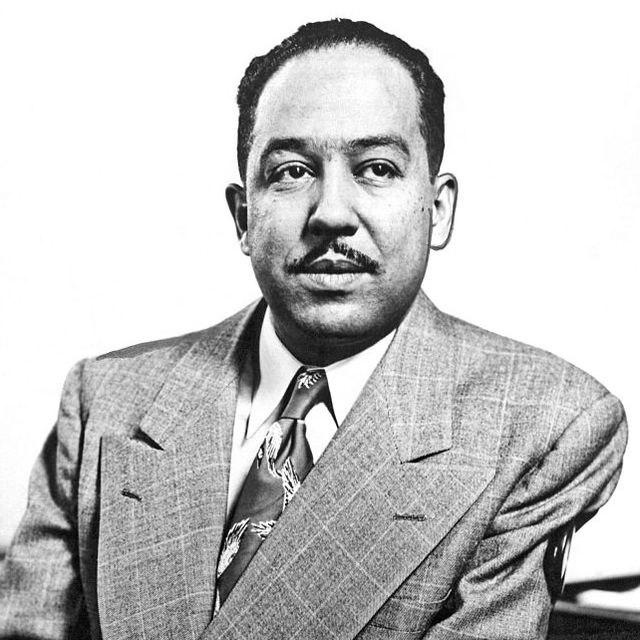
Poet and writer Langston Hughes became a leading figure of the Harlem Renaissance after his first poem was published in 1921. His first book of poetry followed five years later, in 1926. One of the first Black Americans to earn a living as a writer, Hughes went on to compose many more works of poetry, prose, and plays that center the 20th century African American experience and remain influential today. Some of his most famous poems are “Dreams,” “I, Too,” and “Harlem.” Additionally, he wrote a popular column for the Chicago Defender. In May 1967, Hughes died in his mid-60s from prostate cancer.
Quick Facts
FULL NAME: James Mercer Langston Hughes
BORN: c. February 1, 1901
DIED: May 22, 1967
BIRTHPLACE: Joplin, Missouri
ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Aquarius
Early Life
James Mercer Langston Hughes, better known as Langston Hughes, was born in Joplin, Missouri. His birth date—likely February 1, 1901—is the subject of some debate. For decades, scholars believed his birthday was February 1, 1902, but archived newspaper evidence found in 2018 suggests Hughes was born one year earlier.
Whatever the year, his parents, James Hughes and Carrie Langston, separated soon after his birth, and his father moved to Mexico.
While Carrie moved around during his youth, Hughes was raised primarily by his maternal grandmother, Mary, until she died when he was in his early teens. From that point, he went to live with his mother, and they moved to several cities before eventually settling in Cleveland.
It was during this time that Hughes first began to write poetry, and one of his teachers introduced him to the poetry of Carl Sandburg and Walt Whitman, both of whom Hughes later cited as primary influences.
Hughes was also a regular contributor to his school’s literary magazine and frequently submitted to other poetry magazines, though they ultimately rejected his work.
Harlem Renaissance
Hughes graduated from high school in 1920 and spent the following year in Mexico with his father. In 1921, Hughes had his first poem published; “The Negro Speaks of Rivers” appeared in The Crisis magazine and was highly praised.
Also that year, Hughes returned to the United States and enrolled at Columbia University where he studied briefly. In New York City, he quickly became a part of Harlem’s burgeoning cultural movement, what is commonly known as the Harlem Renaissance.
The young poet dropped out of Columbia in 1922 and worked various odd jobs around New York for the following year, before signing on as a steward on a freighter that took him to Africa and Spain. He left the ship in 1924 and lived for a brief time in Paris, where he continued to develop and publish his poetry.
Poems, Books, and Other Works
Hughes was one of the first Black Americans to earn a living as writer. Following his first published poem, “The Negro Speaks of Rivers,” in 1921, he wrote hundreds more. His poems appeared in 16 volumes of poetry during his lifetime, starting with The Weary Blues (1926). These poetry books account for roughly half of the more than 35 books Hughes published. He also wrote short story collections, novels, plays, two autobiographies, and even children’s books. His work centers the experiences of everyday African American in the 20th century.
“Dreams”
In 1923, the New York City magazine The World Tomorrow published Hughes’ poem “Dreams.”
“The Weary Blues”
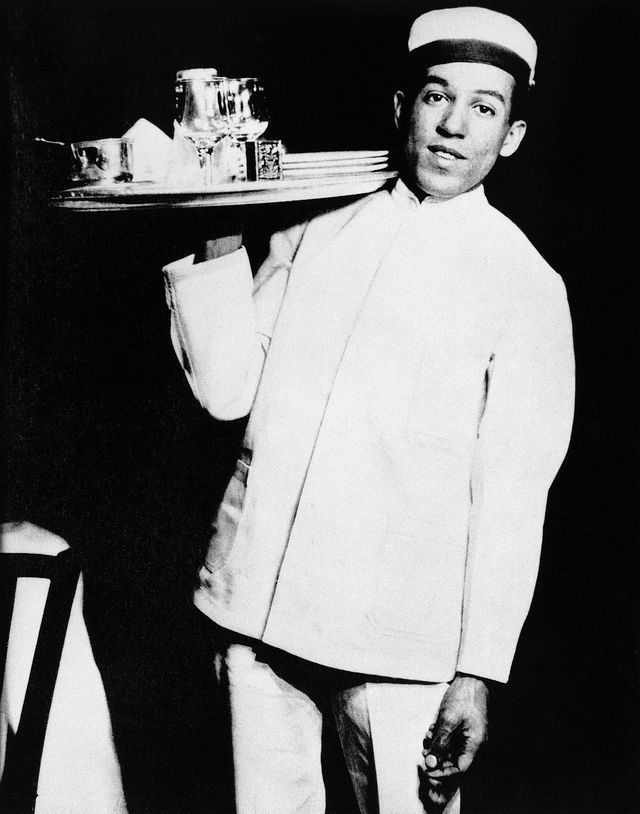
By November 1924, Hughes had returned to the United States and worked various jobs. In 1925, he was working as a busboy in a Washington, D.C., hotel restaurant when he met American poet Vachel Lindsay. Hughes showed some of his poems to Lindsay, who was impressed enough to use his connections to promote Hughes’ poetry and ultimately bring it to a wider audience.
That same year, Hughes’ poem “The Weary Blues” won first prize in the Opportunity magazine literary competition, and Hughes also received a scholarship to attend Lincoln University, a historically Black institution in southeast Pennsylvania.
While studying at Lincoln, Hughes’ poetry came to the attention of novelist and critic Carl Van Vechten, who used his connections to help get Hughes’ first book of poetry, The Weary Blues, published by Knopf in 1926. The book had popular appeal and established both his poetic style and his commitment to Black themes and heritage.
“I, Too”
One of the poems comprising The Weary Blues was “I, Too,” which examined the relationship of African Americans to the larger culture and society in the early 20th century. Parts of the poem are now engraved on a wall of the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, D.C.
Hughes was also among the first to use jazz rhythms and dialect to depict the life of urban Black people in his work. He published a second volume of poetry, Fine Clothes to the Jew, in 1927.
Not Without Laughter
After his graduation from Lincoln in 1929, Hughes published his first novel, Not Without Laughter, the next year. The book was commercially successful enough to convince Hughes that he could make a living as a writer.
During the 1930s, Hughes frequently traveled the United States on lecture tours, as well as abroad to the Soviet Union, Japan, and Haiti. He continued to write and publish poetry and prose during this time, and in 1934, he published his first collection of short stories, The Ways of White Folks.
“Let America Be America Again”
In July 1936, the writer published one of his most celebrated poems, “Let America Be America Again” in Esquire magazine. The poem examines the unrealized hopes and dreams of the country’s lower class and disadvantaged, expressing a sense of hope that the American Dream will one day arrive.
Hughes later revised and republished “Let America Be America Again” in a small anthology of poems called A New Song.
In 1937, he served as a war correspondent for several American newspapers during the Spanish Civil War.
Simple Character and Stage Work
In 1940, Hughes’ autobiography up to age 28, The Big Sea, was published.
Also around this time, Hughes began contributing a column to the Chicago Defender, for which he created a comic character named Jesse B. Semple, better known as “Simple,” a Black Everyman that Hughes used to further explore urban, working-class Black themes and to address racial issues. The columns were highly successful, and “Simple” was later the focus of several of Hughes’ books and plays.
In the late 1940s, Hughes contributed the lyrics for a Broadway musical titled Street Scene, which featured music by Kurt Weill. The success of the musical earned Hughes enough money that he was finally able to buy a house in Harlem. Around this time, he also taught creative writing at Atlanta University (today Clark Atlanta University) and was a guest lecturer at a university in Chicago for several months.
Over the next two decades, Hughes continued his prolific output. In 1949, he wrote a play that inspired the opera Troubled Island and published yet another anthology of work titled The Poetry of the Negro.
“Harlem”
In 1951, Hughes published another acclaimed poem titled “Harlem,” also known as “A Dream Deferred” based on its opening line. According to the Poetry Foundation, Hughes conceived “Harlem” as part of a book-length sequence of poems eventually titled Montage of a Dream Deferred. The collection also featured the poems “Theme for English B” and “Ballad of the Landlord.”
“Harlem” examines how the American Dream can fall short for African Americans. It opens:
What happens to a dream deferred?
Does it dry up
like a raisin in the sun?
The poem inspired the title of Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun, and Martin Luther King Jr. referenced it in a number of his speeches.
During the 1950s and 1960s, Hughes published countless other works, including several books in his “Simple” series, English translations of the poetry of Federico García Lorca and Gabriela Mistral, another anthology of his own poetry, and the second installment of his autobiography, I Wonder as I Wander.
Tambourines to Glory
In 1956, Hughes began writing a play called Tambourines to Glory: A Play with Songs. Mixing story and song, Tambourines tells the story of two female street preachers in Harlem whose success allows them to open up a church.
Hughes told The New York Times he tried to sell the play to producers for a couple of years, eventually adapting the story into a novel—his second. It published in 1958 and received acclaim, garnering new interest in a stage production. The play debuted at the Little Theater in November 1963 with cast members including Louis Gossett Jr., Clara Ward, Hilda Simms, and Rosetta LeNoire.
Sexuality
Literary scholars have debated Hughes’ sexuality for years, with many claiming the writer was gay and had included a number of coded references to male lovers in his poems (as did Hughes’ major influence Walt Whitman.
Hughes never married, nor was he romantically linked to any of the women in his life. And several of Hughes’ friends and traveling companions were known or believed to be gay, including Zell Ingram, Gilbert Price, and Ferdinand Smith.
Others have refuted these claims, including Hughes’ primary biographer, who believed him to be likely asexual. But because of Hughes’ secrecy and the era’s homophobia surrounding openly gay men, there is no concrete evidence of Hughes’ sexuality.
Accusations of Communism
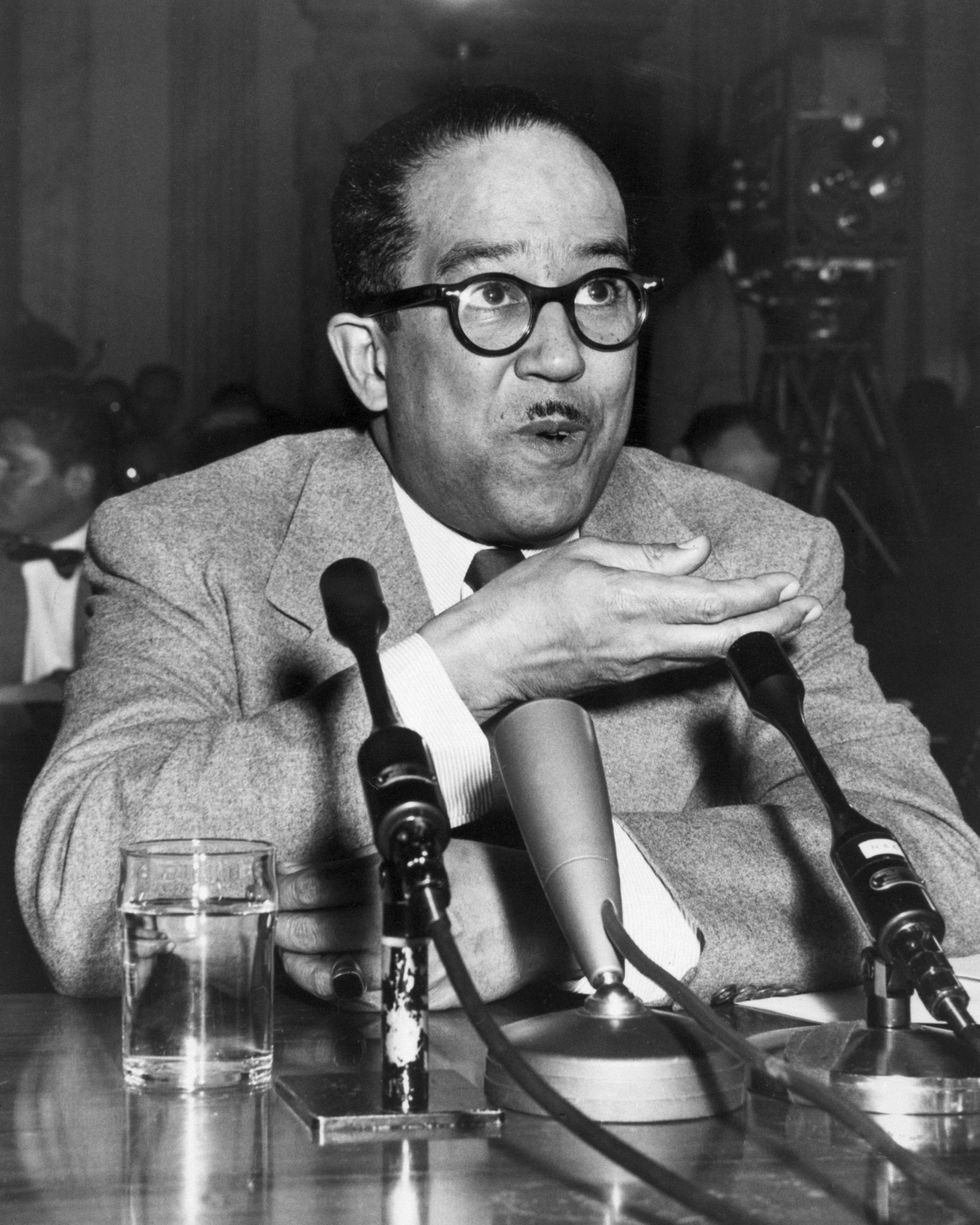
According to The New York Times, the House Un-American Activities Committee accused Hughes of being affiliated at one time or another with 91 different communist organizations. In March 1953, the writer was called to testify in front of Senator Joseph McCarthy’s Subcommittee on Investigations to answer questions about communist influences in his writings.
Although Hughes admitted his works might have been influenced by the ideology, he denied ever being a believer in or member of the communist party and didn’t implicate anyone else in his testimony. “My feeling, sir, is that I have believed in the entire philosophies of the left at one period in my life, including socialism, communism, Trotsky-ism. All -isms have influenced me one way or another, and I can not answer to any specific -ism, because I am not familiar with the details of them and have not read their literature,” Hughes told counsel Roy Cohn, according to transcripts.
Death and Legacy
On May 22, 1967, Hughes died from complications of prostate cancer at age 66.
A tribute to his poetry, his funeral contained little in the way of spoken eulogy but was filled with jazz and blues music. Hughes’ ashes were interred beneath the entrance of the Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture in Harlem. The inscription marking the spot features a line from Hughes’ poem “The Negro Speaks of Rivers.” It reads: “My soul has grown deep like the rivers.”
Hughes’ Harlem home, on East 127th Street, received New York City Landmark status in 1981 and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1982. Volumes of his work continue to be published and translated throughout the world.
Langston Hughes High School, completed in 2009 and located in Fairburn, Georgia, is named after the poet. The library at Hughes’ alma mater Lincoln University also bears his name.
Quotes
- An artist must be free to choose what he does, certainly, but he must also never be afraid to do what he might choose.
- I have discovered in life that there are ways of getting almost anywhere you want to go, if you really want to go.
- We Negro writers, just by being Black, have been on the Blacklist all our lives. Censorship for us begins at the color line.
- Humor is laughing at what you haven’t got when you ought to have it.
- Let the rain kiss you. Let the rain beat upon your head with silver liquid drops. Let the rain sing you a lullaby.
- The first two or three days, on the way home from school, little white kids, kids my age, 6 and 7 years old, who would throw stones at me. There were other little white kids, 6 and 7 years old, who picked up stones and threw them back at their fellow classmates and defend me and saw that I got home safely. So, I learned very early in life that our race problem is not really of Black against white and white against Black. It’s a problem of people who are not very knowledgeable, or have small minds, or small spirits.
- Negroes—sweet and docile, meek, humble and kind: Beware the day—they change their mind.
- I swear to the Lord, I can’t see why democracy means everybody but me.
- Like welcome summer rain, humor may suddenly cleanse and cool the earth, the air and you.
- Negro blood is sure powerful, because just one drop of Black blood makes a colored man. One drop you are a Negro!... Black is powerful.
- Hold fast to dreams, for if dreams die, life is a broken winged bird that cannot fly.
- Life is a system of half-truths and lies, opportunistic, convenient evasion.
- No woman can be handsome by the force of features alone, any more that she can be witty by only the help of speech.
- Jessie Fauset at The Crisis, Charles Johnson at Opportunity, and Alain Locke in Washington were the three people who midwifed the so-called “New Negro Literature” into being. Kind and critical—but not too critical for the young—they nursed us along until our books were born.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us!
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Tyler Piccotti first joined the Biography.com staff as an Associate News Editor in February 2023, and before that worked almost eight years as a newspaper reporter and copy editor. He is a graduate of Syracuse University. When he's not writing and researching his next story, you can find him at the nearest amusement park, catching the latest movie, or cheering on his favorite sports teams.