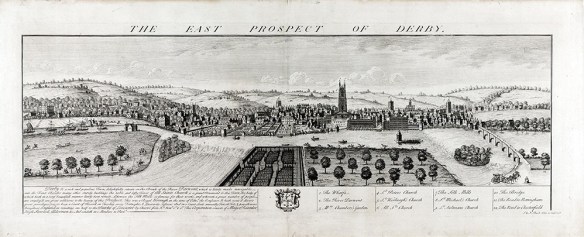
Samuel and Nathantial Buck’s engraving of Derby shows the town dominated by the tower of All Saints Church which was constructed at the turn of the sixteenth century and in the middle by Exeter House, owned by the Earl and Countess of Exeter. Exeter was not at home when Bonnie Prince Charlie arrived on 4 December 1745.
But who was the Earl of Exeter and why did he have a house in Derby? Brownlow Cecil, Lord Burghley had only recently succeeded his father, similarly named, as the 9th Earl of Exeter. It turns out that Brownlow’s mother, Hannah Chambers, was from Derby. Her father Thomas Chambers who ran his business from London was a merchant in copper and lead – which immediately provides the Derbyshire connection as well as a reason for the marriage of the younger son of an earl with the younger daughter of a ‘gent’. In short they were very wealthy. The 8th Earl’s elder brother died within two years of Hannah’s marriage and she became a countess.
Hannah’s grandfather is buried in All Saints. By then the family extended their home in Derby with the pleasure grounds depicted on the near side of the river to the viewer but it doesn’t seem that the earl and his countess spent much time in their Derby residence.
Having provided accommodation for the Jacobites it was sold in 1758 to the then Mayor of Derby.
Incidentally, the long narrow plots of land are the footprints of the Anglo-Saxon burgage plots – what’s not to love? A burgage consists of a long narrow plot with a house fronting on to the street – usually burgage plots were rented for cash rather than service although the latter was possible. Tenantry of a burgage plot also often accrued voting rights. Obviously Exeter House involved the purchase and amalgamation of two burgage plots because of the width of the house when the area became fashionable.

