Explore the origins, formation, and history of Hesse from the Middle Ages to the modern era in this comprehensive blog post.
Origins of Hesse
Contents
The origins of Hesse can be traced back to the ancient Germanic tribes that inhabited the region. The first recorded mention of Hesse dates back to the 8th century when Charlemagne’s son, Louis the Pious, established the County of Hesse. The region continued to develop over the centuries, with the establishment of the Landgraviate of Hesse in the 13th century marking a significant milestone in its history.
Under the rule of the House of Hesse, the region emerged as a prominent political and cultural center in the Holy Roman Empire. Hessian territory expanded and contracted over the years, with periods of prosperity and turmoil shaping the region’s identity. The Thirty Years’ War in the 17th century and the Napoleonic Wars in the 19th century had a significant impact on Hesse, leading to changes in its territorial boundaries and political landscape.
Throughout its history, Hesse has been a melting pot of different cultures and influences, with its rich tapestry of traditions and customs reflecting its diverse heritage. Today, the state of Hesse is a vibrant and dynamic region that continues to honor its historical origins while embracing the opportunities and challenges of the modern world.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 8th century | First recorded mention of Hesse |
| 13th century | Establishment of the Landgraviate of Hesse |
| 17th century | Impact of the Thirty Years’ War |
| 19th century | Napoleonic Wars and territorial changes |
Formation of Hesse state
The formation of Hesse state dates back to the early 16th century, during the time of the Holy Roman Empire. It was during this period that Hesse emerged as an independent state, with its own distinct political and cultural identity. The origins of Hesse can be traced back to the medieval era, when it was part of the Franconian Empire. Over time, the region of Hesse gained autonomy and eventually became a sovereign state.
In the 15th and 16th centuries, Hesse went through a process of consolidation and expansion, as various territories within the region were united under a single ruler. This period saw the rise of the powerful Landgraviate of Hesse, which played a key role in the formation of the Hesse state. The rulers of Hesse were able to assert their authority and establish a strong central government, leading to the creation of a unified Hessian state.
The formation of Hesse state was also influenced by the political and religious developments of the time. The Protestant Reformation, led by Martin Luther, had a significant impact on the region, as many of the rulers of Hesse embraced the new religious movement. This played a crucial role in shaping the identity of the Hesse state and its relationship with other European powers.
By the end of the 16th century, the formation of Hesse state was complete, and the region had established itself as a prominent player in the politics of the Holy Roman Empire. The state of Hesse continued to evolve and adapt to the changing realities of European politics, ultimately becoming an integral part of the German nation-state in the 19th century.
Hesse in the Middle Ages
The Middle Ages in Hesse was a time of great change and growth. During this period, Hesse was made up of various small territories and was heavily influenced by the Holy Roman Empire. The region was marked by conflict and shifting alliances, with local rulers vying for power and influence.
One of the most significant developments during the Middle Ages was the rise of trade and commerce in Hesse. The region’s central location made it a hub for trade routes and the exchange of goods. Towns and cities flourished as markets and fairs became common, and the economy of Hesse began to thrive.
The religious landscape of Hesse also underwent significant changes during the Middle Ages. The spread of Christianity brought about the construction of numerous churches and monasteries, which played a central role in the spiritual and cultural life of the region. The influence of the church extended into politics and society, shaping the values and beliefs of the people of Hesse.
As the Middle Ages drew to a close, new social and political structures began to emerge in Hesse. Feudalism gave way to more centralized forms of government, and the influence of the Holy Roman Empire waned. The region began to assert its independence and develop its own identity, laying the groundwork for the modern state of Hesse.
Hesse during the Renaissance
Hesse during the Renaissance was a period of great cultural and intellectual growth for the region. This era, which lasted from the 14th to the 17th century, saw the flourishing of art, literature, and science in Hesse. The Renaissance was a time of rebirth and renewal, as the people of Hesse looked back to the classical civilizations of Greece and Rome for inspiration. This period also saw the rise of new technologies and the exploration of new lands, which had a profound impact on the development of Hesse.
One of the most significant developments during the Renaissance in Hesse was the patronage of the arts by the ruling families. The Landgraves of Hesse were known for their support of artists, musicians, and scholars, which helped to foster a vibrant cultural scene in the region. The University of Marburg, founded in 1527, became a center for humanist learning and played a crucial role in the dissemination of Renaissance ideas in Hesse and beyond.
Trade and commerce also flourished during the Renaissance, bringing new wealth to Hesse and transforming its cities into vibrant centers of economic and cultural activity. The city of Kassel, for example, became a hub for the trade of goods and ideas, attracting merchants, artists, and thinkers from across Europe. This influx of new people and new ideas helped to enrich the cultural landscape of Hesse during the Renaissance.
Another important aspect of the Renaissance in Hesse was the development of new scientific and philosophical ideas. The mathematician and astronomer Johannes Kepler, who was born in Weil der Stadt, made significant contributions to the fields of mathematics, astronomy, and physics during this period. His work had a lasting impact on the scientific community and helped to shape the intellectual climate of Hesse during the Renaissance.
| Key takeaways from the Hesse Renaissance: | |
|---|---|
| Patronage of the arts: The support of artists and scholars by the ruling families of Hesse helped to foster a vibrant cultural scene. | |
| Trade and commerce: The flourishing of trade and commerce brought new wealth to Hesse and transformed its cities into vibrant centers of activity. | |
| Development of new scientific and philosophical ideas: The Renaissance in Hesse saw the rise of new technologies and the exploration of new lands, which had a profound impact on the development of the region. |
Modern history of Hesse
The modern history of Hesse covers the period from the early 19th century to the present day. This era saw significant changes in the region, including industrialization, the rise of political movements, and its role in the unification of Germany.
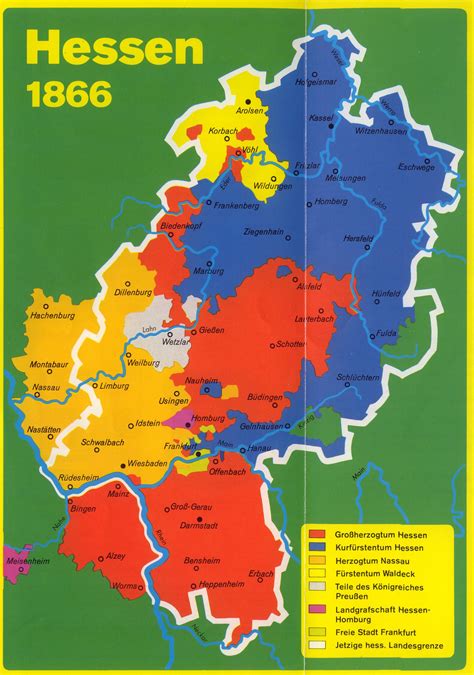
Following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, Hesse was reorganized into two separate states: Hesse-Kassel and Hesse-Darmstadt. The two states went through various political changes and alliances, including the incorporation into the German Confederation and later, the North German Confederation.
During the latter part of the 19th century, Hesse experienced rapid industrialization, particularly in the areas of manufacturing, mining, and transportation. This economic growth transformed Hesse into a significant player in the German economy.
After the defeat of Germany in World War I, Hesse became a republic and went through a period of political instability. However, the state eventually stabilized and became a strong supporter of the Weimar Republic.
During the 20th century, Hesse played a key role in the reconstruction of Germany after World War II, with cities like Frankfurt becoming major financial centers. It also became a center for the arts and culture, attracting a diverse population and contributing to the growth of the state.