You can find information about the history of Structural Engineering Before Christ here: Interesting History of Structural Engineering - BC
Intro
The 16th and 17th centuries saw a dramatic shift in scientific ideas known as the Scientific Revolution. Before the Scientific Revolution, no one doubted the claim that the center of the universe was the Earth. Nicolaus Copernicus challenged that system, and from him, the Scientific Revolution began.
During the Scientific Revolution era, we will encounter truly famous figures like Galileo Galilei. You might think there is no connection between structural engineering and these individuals, but their research and writings have greatly influenced structural engineering. The theories they left behind are still used in structural engineering today.
History of Structural Engineering Timeline
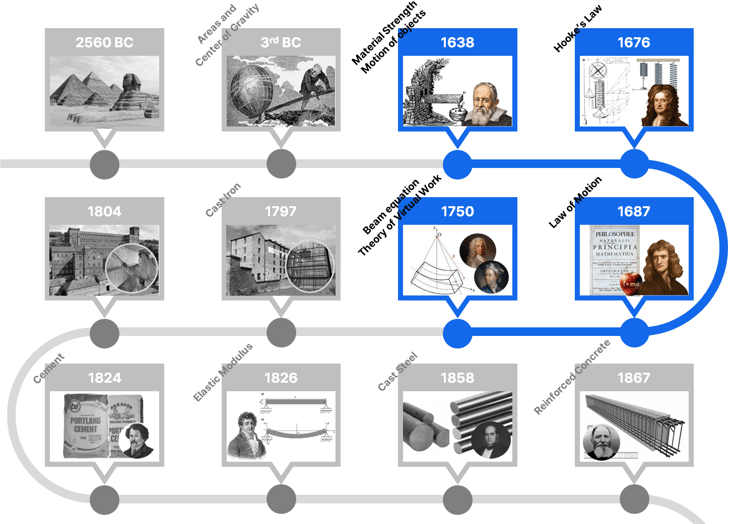 History of Structural Engineering Timeline
History of Structural Engineering Timeline
2. Scientific Revolution
1638 BC Material Strength Motion of objects | Galileo Galilei

Galileo Galilei was an Italian philosopher, scientist, physicist, and astronomer. This genius also influenced structural engineering. He described the disciplines of material strength and object motion in his publication Dialogues Relating to Two New Sciences. This work marked the beginning of the structural analysis. Surprisingly, as seen in the picture below, he made the first effort at quantifying the load response of a simple cantilever beam.
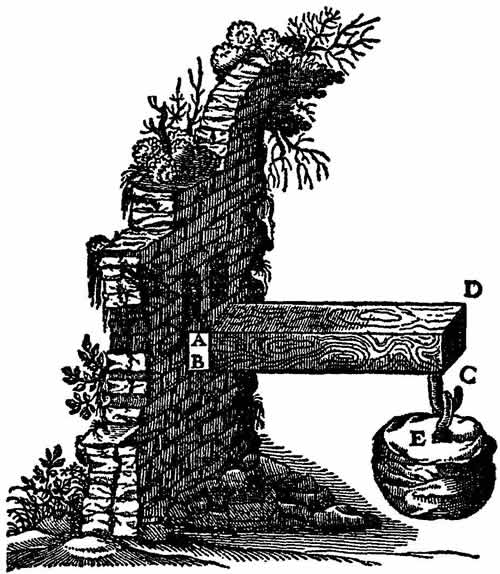 Galileo's cantilever beam in his publication Dialogues Relating to Two New Sciences
Galileo's cantilever beam in his publication Dialogues Relating to Two New Sciences
1676 Hooke’s Law | Robert Hooke
.png?width=1280&height=720&name=Robert%20Hooke%20(1635%20%E2%80%93%201703).png)
Some engineers say they 'can live from by Hooke's Law.' Among structural engineers, there is no one who does not know Hooke's Law. In many elastic materials, there is a proportional relationship between the restoring force and the amount of deformation when the deformation is small. Expressed in equation form, it is as follows: Fs=kx, where Fs is the restoring spring force. This formular is named after British physicist Robert Hooke. He provided a scientific explanation of elasticity of materials and their behavior under load.
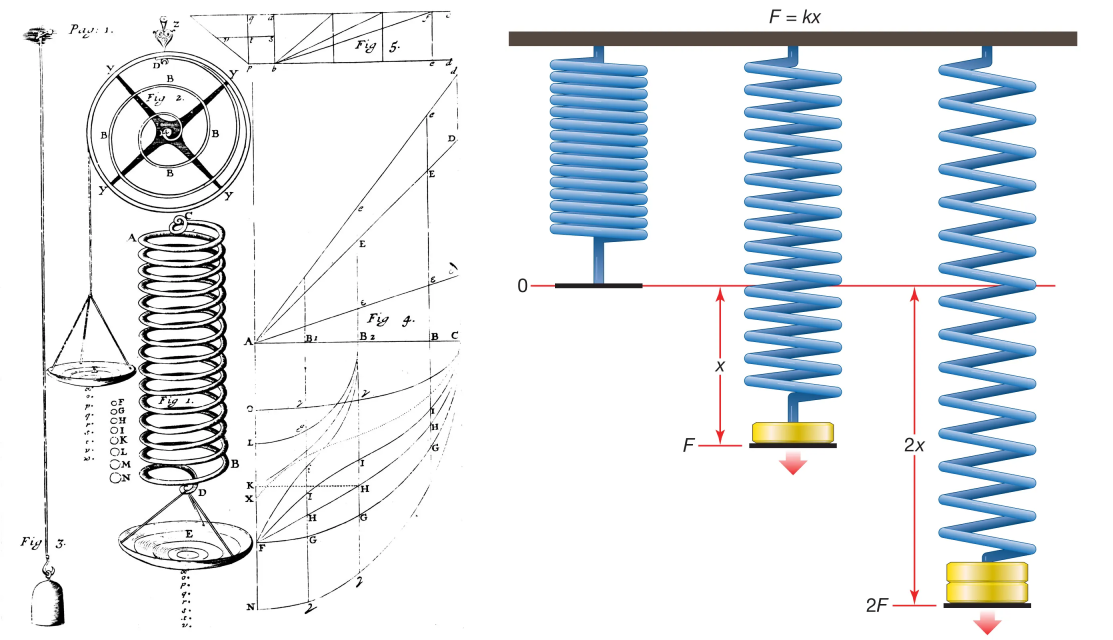 Hooke’s law, law of elasticity discovered by the English scientist Robert Hooke in 1660
Hooke’s law, law of elasticity discovered by the English scientist Robert Hooke in 1660
1687 Law of Motion | Isaac Newton
.png?width=640&height=771&name=Isaac%20Newton%20(1642%20%E2%80%93%201727).png)
Every structural engineer knows Hooke. Everyone knows Isaac Newton because he discovered the law of universal gravitation after seeing an apple fall. With the publication of Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, Sir Isaac Newton gave us a grasp of the underlying laws governing built structures. One of the most significant mathematical tools in engineering is the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, independently developed by Newton and Gottfried Leibniz.
 Isaac Newton’s revolutionary work: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica
Isaac Newton’s revolutionary work: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica
1750 Beam equation, Theory of Virtual Work | Leonhard Euler and David Bernoulli
%20and%20Daniel%20Bernoulli%20(1700%20-%201782).png?width=1160&height=737&name=Leonhard%20Euler%20(1707%20%E2%80%93%201783)%20and%20Daniel%20Bernoulli%20(1700%20-%201782).png)
The Euler-Bernoulli Beam Equation, which was created by Leonhard Euler and David Bernoulli, is the basic theory that guides the majority of structural engineering designs. Additionally, Daniel and Jean Bernoulli created the Theory of Virtual Work, a method for resolving structural issues that makes use of geometric compatibility and force balance. If you were a college student dreaming of becoming a structural engineer, around your first or second year, you would find yourself calculating this formula by hand.
The post on the history of structural engineering in the 19th and 20th Centuries will be uploaded soon.
References
1638 BC Material Strength Motion of objects | Galileo Galilei
ResearchGate - Galileo's cantilever beam [Kurrer, 2008]
1676 Hooke’s Law | Robert Hooke
Facts.net - 15 Astonishing Facts About Robert Hooke [Julissa Richie, 2024]
1750 Beam equation, Theory of Virtual Work | Leonhard Euler and David Bernoulli
Wikipedia - Portrait of Daniel Bernoulli [Bammesk - Basel Historical Museum, 2022]
Topics
#StructuralEngineering
#CivilEngineering
#Infrastructure
#Getmotivated
/Jegeon%20240_240.png)
Hello, I am Jegeon Ryu, a Project Manager responsible for developing MOTIVE for engineers dedicated to creating a safer and better world. During my two years of military service, I learned that creating a safer world is achievable through the sharing of technology and motivating each other. My goal is to contribute to the happiness of the world by creating a global platform that facilitates mutual knowledge sharing and growth.
Profile: Jegeon Ryu
※ Click on the keywords below 'Topics' to view related content.

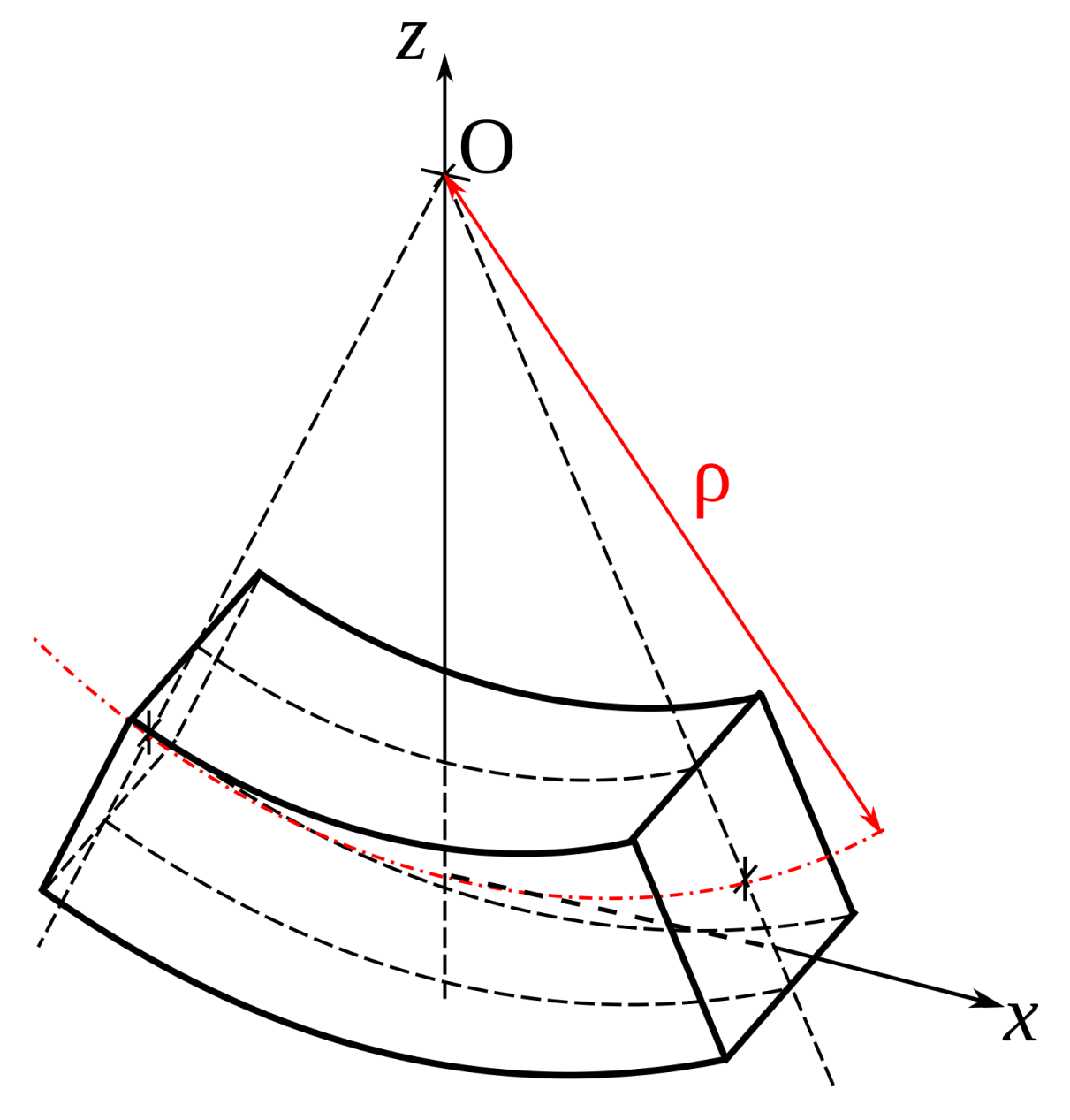 Euler–Bernoulli beam theory
Euler–Bernoulli beam theory 
/%EC%A0%84%EA%B7%9C%EC%8B%9D.jpg)