Skip Counting is a method of counting forward or backward by numbers other than 1. It involves counting by skipping through a particular number of places in the counting sequence. For example, when skip counting by 5, you start from 0 and count 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25
In this article, we will discuss what is skip counting, including its various examples, types, table, etc.
What is Skip Counting?
Skip counting is a method of counting numbers by skipping a consistent number of values each time. Instead of counting by ones (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.), skip counting involves counting by a certain interval or “skip” (e.g., by twos, threes, fives, tens, etc.).
For example,
- Skip counting by twos: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, . . .
- Skip counting by threes: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, . . .
- Skip counting by fives: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, . . .
- Skip counting by tens: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, . . .
Skip Counting on Number Line
Skip counting on a Number Line involves counting by a certain interval or “skip” while visually representing the numbers on a line. The following illustration shows the skip counting by 2’s on the number line:

Skip Counting Rule
Rule for skip counting is to add the same number each time to the previous number to get the next number in the sequence.
For Example:
- Skip Counting by Twos: Start with a number (e.g., 1) and add 2 to it to get the next number (1 + 2 = 3), then add 2 again to get the following number (3 + 2 = 5), and continue this process to generate the sequence i.e., 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, . . .
- Skip Counting by Fives: Begin with a number (e.g., 5) and add 5 to it to obtain the next number (5 + 5 = 10), then add 5 again to get the following number (10 + 5 = 15), and continue this pattern to create the sequence i.e., 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, . . .
Skip Counting Table (2 to 10)
Table for Skip counting from 2 to 10 is given as follows:
|
By 2s
|
2
|
4
|
6
|
8
|
10
|
12
|
14
|
16
|
18
|
20
|
|
By 3s
|
3
|
6
|
9
|
12
|
15
|
18
|
21
|
24
|
27
|
30
|
|
By 4s
|
4
|
8
|
12
|
16
|
20
|
24
|
28
|
32
|
36
|
40
|
|
By 5s
|
5
|
10
|
15
|
20
|
25
|
30
|
35
|
40
|
45
|
50
|
|
By 6s
|
6
|
12
|
18
|
24
|
30
|
36
|
42
|
48
|
54
|
60
|
|
By 7s
|
7
|
14
|
21
|
28
|
35
|
42
|
49
|
56
|
63
|
70
|
|
By 8s
|
8
|
16
|
24
|
32
|
40
|
48
|
56
|
64
|
72
|
80
|
|
By 9s
|
9
|
18
|
27
|
36
|
45
|
54
|
63
|
72
|
81
|
90
|
|
By 10s
|
10
|
20
|
30
|
40
|
50
|
60
|
70
|
80
|
90
|
100
|
Types of Skip Counting
- Forward Skip Counting
- Backward Skip Counting
Forward Skip Counting
Forward skip counting refers to counting numbers in a sequence by increasing values with a consistent interval or “skip.”
In simple words, we count or add numbers in the forward direction to a number when we do a forward skip count. For example, if you’re forward skip counting by threes starting from 0, the sequence would be: 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, . . .
Similarly, if you’re forward skip counting by fives starting from 10, the sequence would be: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, . . .
Backward Skip Counting
Backward skip counting involves counting numbers in a sequence by decreasing values with a consistent interval or “skip.”
In simple words, we subtract a certain number when we perform a backward skip count. For example, if you’re backward skip counting by twos starting from 10, the sequence would be:
10, 8, 6, 4, 2, 0, . . .
Similarly, if you’re backward skip counting by fives starting from 25, the sequence would be 25, 20, 15, 10, 5, 0, . . .
Various Examples of Skip Counting
Some of the common skip counting examples are:
- Skip Counting By 2’s
- Skip Counting By 3’s
- Skip Counting By 4’s
- Skip Counting By 5’s
- Skip Counting By 10’s
Skip Counting By 2’s
Skip counting by 2’s means counting numbers while skipping one number in between each count. Skip counting by 2’s is given as follows:
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, . . .
And it continues in the same pattern, adding 2 to the previous number each time. Following illustration help us understand Skip Counting By 2’s.

Skip Counting By 3’s
Skip counting by 3 is a method of counting numbers by skipping two numbers in between and directly jumping on the third number. Starting from 0, we keep adding 3 to each previous number to obtain the next number in the list. Here’s a list of numbers when counting by 3’s:
3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 51, 54, 57, 60, . . .
You continue this pattern by adding 3 to the previous number each time.

Skip Counting By 4’s
To count in intervals of 4 or skip counting by 4, we start with 4, add 4, and then keep adding 4 to the previous number to maintain counting by 4. Here’s a list of numbers when counting by 4’s:
4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64, 68, 72, 76, 80, . . .
You continue this pattern by adding 4 to the previous number each time.
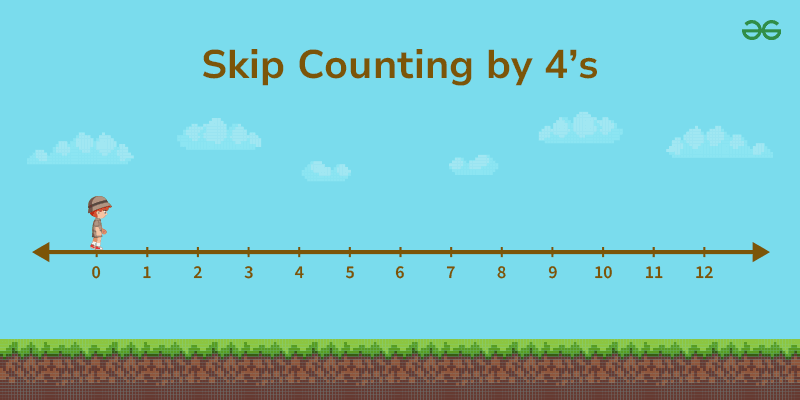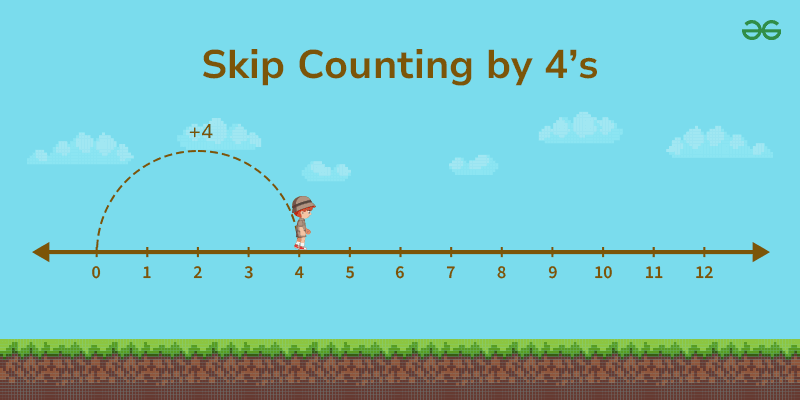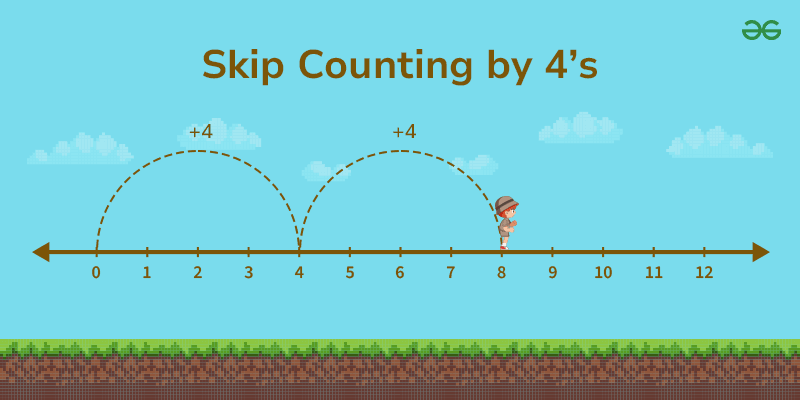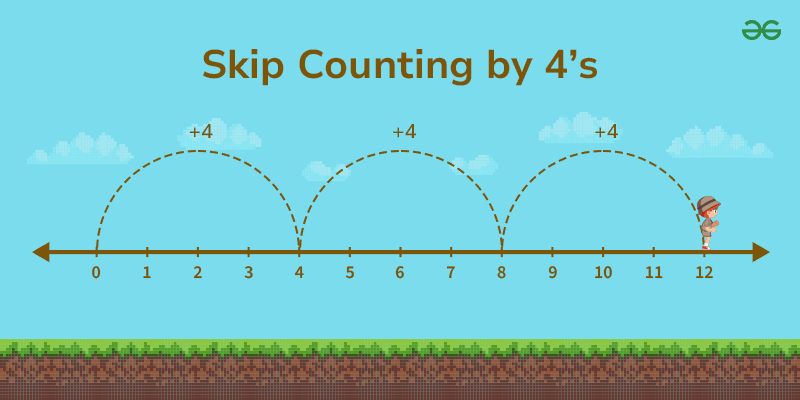
Skip Counting By 5’s
Skip counting by 5’s is a method of counting by increments of 5, where each successive number is obtained by adding 5 to the previous number. For example,
- If you start with 0.
- Add 5 to get the next number: 0 + 5 = 5.
- Add 5 again to get the next number: 5 + 5 = 10.
Continue this pattern to generate the sequence as follows:
5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100, . . .

Skip Counting By 10’s
Skip counting by 10’s is a method of counting where you add a fixed number (in this case, 10) to the previous number to get the next number in the sequence. It’s called “skip” counting because you’re skipping over the numbers in between. For example, if you start with 0 and skip count by 10’s, you would get:
10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200, . . .
Each number is 10 more than the previous one, and you’re “skipping” over the numbers in between.

Skip Counting by Bigger Numbers
We can skip count using any bigger number but bigger the number is harder it is to skip count. Some of the common bigger number which used in skip counting are
- Skip Counting by 25
- Skip Counting by 50
- Skip Counting by 100
- Skip Counting by 200
Following table shows first 20 terms in the skip counting of all the numbers mention above:
Skip Counting By 25
|
Skip Counting By 50
|
Skip Counting By 100
|
Skip Counting By 200
|
| 25 |
50 |
100 |
200 |
| 50 |
100 |
200 |
400 |
| 75 |
150 |
300 |
600 |
| 100 |
200 |
400 |
800 |
| 125 |
250 |
500 |
1000 |
| 150 |
300 |
600 |
1200 |
| 175 |
350 |
700 |
1400 |
| 200 |
400 |
800 |
1600 |
| 225 |
450 |
900 |
1800 |
| 250 |
500 |
1000 |
2000 |
| 275 |
550 |
1100 |
2200 |
| 300 |
600 |
1200 |
2400 |
| 325 |
650 |
1300 |
2600 |
| 350 |
700 |
1400 |
2800 |
| 375 |
750 |
1500 |
3000 |
| 400 |
800 |
1600 |
3200 |
| 425 |
850 |
1700 |
3400 |
| 450 |
900 |
1800 |
3600 |
| 475 |
950 |
1900 |
3800 |
| 500 |
1000 |
2000 |
4000 |
| 525 |
1050 |
2100 |
4200 |
| 550 |
1100 |
2200 |
4400 |
| 575 |
1150 |
2300 |
4600 |
| 600 |
1200 |
2400 |
4800 |
| 625 |
1250 |
2500 |
5000 |
| 650 |
1300 |
2600 |
5200 |
| 675 |
1350 |
2700 |
5400 |
| 700 |
1400 |
2800 |
5600 |
| 725 |
1450 |
2900 |
5800 |
| 750 |
1500 |
3000 |
6000 |
| 775 |
1550 |
3100 |
6200 |
| 800 |
1600 |
3200 |
6400 |
Skip Counting Worksheet
The below worksheet contains problems based on Skip Counting – Skip counting by 2s, 5s, 10s and Multiple skip counting:
Part 1: Skip Counting by 2s
- 2, 4, __, 8, 10, __, 14, __, 18, 20
- __, 6, 8, __, 12, 14, __, 18, 20, __
- 20, 18, __, 14, 12, __, 8, __, 4, 2
Part 2: Skip Counting by 5s
- 5, 10, __, 20, 25, __, 35, __, 45, 50
- __, 55, 60, __, 70, 75, __, 85, 90, __
- 100, 95, __, 85, 80, __, 70, __, 60, 55
Part 3: Skip Counting by 10s
- 10, 20, __, 40, 50, __, 70, __, 90, 100
- __, 110, 120, __, 140, 150, __, 170, 180, __
- 200, 190, __, 170, 160, __, 140, __, 120, 110
Part 4: Challenge – Mixed Skip Counting
- Skip counting by 3s: 3, __, 9, __, 15, 18, __, 24, __, 30
- Skip counting by 4s: 4, __, 12, __, 20, 24, __, 32, __, 40
- Skip counting by 7s: 7, __, 21, __, 35, 42, __, 56, __, 70
Conclusion – Skip Counting
Skip counting is a very easy and helpful way to assist students in learning to interact with numbers using addition and multiplication. In the early days of education, students learn this method to sharpen their calculations. In this article, we have explored the concept of skip counting, including its various examples and types, which help students understand counting numbers.
People Also Read:
FAQs on Skip Counting
What is Skip Counting?
Skip counting is a mathematical technique where numbers are counted by skipping a fixed number of places in the counting sequence, instead of counting by 1.
Why is it called Skip Counting?
Because while counting, we skip some numbers by going forward in the count with the value of another number.
What is the Rule for Skip Counting?
The rule for skip counting is essentially to count by a consistent interval or increment. This means that instead of counting by one (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …), you count by a predetermined number or sequence of numbers.
What is Skip Count by 2’s from 1 to 20?
Skip counting by 2’s from 1 to 20 is 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19.
What are the Real-life Examples of Skip Counting?
In our everyday lives, we often skip counting when we are talking about time, counting money, scoring points in games like basketball, and there are many more examples that can be observed.
Can we do Backward Skip Counting?
Yes, skip counting can be done either forward or backward by a number other than 1.
Please Login to comment...