Countries Ruled by A Parliamentary System
List of countries, nations and states governed or ruled by a parliamentary system, sorted alphabetically. In some cases nations may have multiple ruling bodies or government types, meaning they're not exclusively countries that are governed by parliamentary system. This list of countries that use parliamentary system as their form of government contains various bits of information about each nation, such as the official language or currency of the country. If you're looking for the names of countries with parliamentary system governments then you're in the right place.
List features items like Israel and Luxembourg.
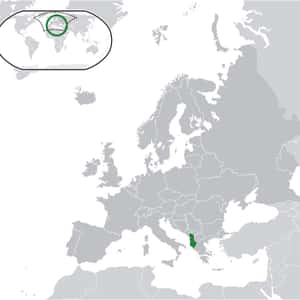
This list answers the questions, "Which countries are ruled by parliamentary system?" and "Which countries are governed by parliamentary system?"- TiranaAlbania, officially known as the Republic of Albania, is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east, and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the west and on the Ionian Sea to the southwest. It is less than 72 km from Italy, across the Strait of Otranto which links the Adriatic Sea to the Ionian Sea. Albania is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Council of Europe and the World Trade Organization. It is one of the founding members of the Energy Community and the Union for the Mediterranean. It is also an official candidate for membership in the European Union. The modern-day territory of Albania was at various points in history part of the Roman provinces of Dalmatia, Macedonia, and Moesia Superior. The modern Republic became independent after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in Europe following the Balkan Wars. Albania declared independence in 1912 and was recognized the following year.More Albania
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #13 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
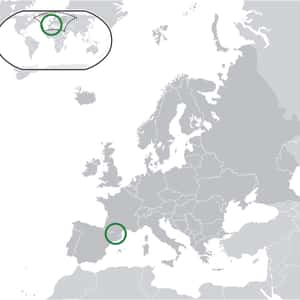
- Andorra la VellaAndorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, is a sovereign landlocked microstate in Southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe, having an area of 468 km² and a population of ca. 85,000. Its capital, Andorra la Vella, is the highest capital city in Europe, at an elevation of 1,023 metres above sea level. The official language is Catalan, although Spanish, Portuguese, and French are also commonly spoken. Created under a charter in A.D. 988, the present Principality was formed in A.D. 1278. It is known as a principality as it is a monarchy headed by two Co-Princes – the Spanish/Roman Catholic Bishop of Urgell and the President of France. Andorra's tourism services an estimated 10.2 million visitors annually. It is not a member of the European Union, but the euro is the de facto currency. It has been a member of the United Nations since 1993. The people of Andorra have one of the highest life expectancies in the world and as of December 2014, according to The Lancet, has the highest in the world - 81 years in 2013.More Andorra
- Dig Deeper...The Top 50 Healthcare Systems Around The World
- And Deeper...Countries Where Gay Marriage is Legal
- #133 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
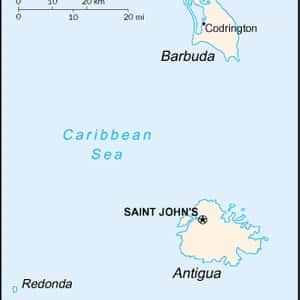
- St. John'sAntigua and Barbuda is a twin-island country lying between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It consists of two major inhabited islands, Antigua and Barbuda, and a number of smaller islands. The permanent population numbers about 81,800 and the capital and largest port and city is St. John's, on Antigua. Separated by a few nautical miles, Antigua and Barbuda are in the middle of the Leeward Islands, part of the Lesser Antilles, roughly at 17°N of the equator. The country is nicknamed "Land of 365 Beaches" due to the many beaches surrounding the islands. Its governance, language, and culture have all been strongly influenced by the British Empire, of which the country was formerly a part.More Antigua and Barbuda
- Dig Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #131 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- #42 of 114 onThe Top Travel Destinations in the World
- CanberraAustralia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is an Oceanian country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area. Neighbouring countries include Indonesia, East Timor and Papua New Guinea to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. For at least 40,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century, Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians, who spoke languages grouped into roughly 250 language groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, Australia's eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades; the continent was explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies were established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia.More Australia
- Dig Deeper...The Funniest Australian Movies Ever Made
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #45 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- DhakaBangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia; and is bordered by India to its west, north and east; Burma to its southeast and separated from Nepal and Bhutan by the Chicken’s Neck corridor. To its south, it faces the Bay of Bengal. Bangladesh is the world's eighth-most populous country, with over 160 million people, and among the most densely populated countries. It forms part of the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal, along with the neighbouring Indian states of West Bengal and Tripura. The present-day borders of Bangladesh took shape during the Partition of Bengal and British India in 1947, when the region came to be known as East Pakistan, as a part of the newly formed state of Pakistan. It was separated from West Pakistan by 1,400 km of Indian territory. Due to political exclusion, ethnic and linguistic discrimination and economic neglect by the politically dominant western wing, nationalism, popular agitation and civil disobedience led to the Bangladesh Liberation War and independence in 1971. After independence, the new state endured poverty, famine, political turmoil and military coups.More Bangladesh
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #206 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BridgetownBarbados is a sovereign island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is 34 kilometres in length and up to 23 kilometres in width, covering an area of 432 square kilometres. It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about 168 kilometres east of the islands of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and 400 kilometres north-east of Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is outside of the principal Atlantic hurricane belt. Barbados was visited by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century and claimed for the Spanish Crown. It first appears on a Spanish map from 1511. The Portuguese visited the island in 1536, but they left it unclaimed, with their only remnants being an introduction of wild hogs for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the Olive Blossom, arrived in Barbados in 1625; its men took possession of it in the name of King James I. In 1627 the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and it became an English and later British colony. In 1966 Barbados became an independent state and Commonwealth realm, retaining Queen Elizabeth II as Head of State.More Barbados
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...The Fattest Countries In The World
- #35 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BelmopanBelize is a nation-state on the eastern coast of Central America. It is the only country in Central America whose official language is English, though Belizean Creole and Spanish are also commonly spoken. Belize is bordered on the north by Mexico, on the south and west by Guatemala, and on the east by the Caribbean Sea. Its mainland is about 290 km long and 110 km wide. With 22,800 square kilometres of land and as of 2014 a population of 340,844, Belize has the lowest population density in Central America. The country's population growth rate of 1.97% per year is the second highest in the region and one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere. Belize's abundance of terrestrial and marine species and its diversity of ecosystems give it a key place in the globally significant Mesoamerican Biological Corridor. Belize has a diverse society, composed of many cultures and languages that reflect its rich history. Originally part of the British Empire, it shares a common colonial history with other Anglophone Caribbean countries. From 1862 to 1973 the area went by the name of British Honduras.More Belize
- Dig Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #160 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ThimphuBhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia at the eastern end of the Himalayas. It is bordered to the north by China and to the south, east and west by India. To the west, it is separated from Nepal by the Indian state of Sikkim, while farther south it is separated from Bangladesh by the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal. Bhutan's capital and largest city is Thimphu. At that time the lama and military leader Ngawang Namgyal, the first Zhabdrung Rinpoche, who was fleeing religious persecution in Tibet, unified the area and cultivated a distinct Bhutanese .More Bhutan
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #20 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- SofiaBulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. With a territory of 110,994 square kilometres, Bulgaria is Europe's 16th-largest country. Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period.More Bulgaria
- Dig Deeper...The Best Tennis Players from Bulgaria
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #188 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Phnom PenhCambodia, officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia and once known as the Khmer Empire, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Its total landmass is 181,035 square kilometres, bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, and the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. With a population of over 15 million, Cambodia is the 69th most populous country in the world. The official religion is Theravada Buddhism, practiced by approximately 95 percent of the population. The country's minority groups include Vietnamese, Chinese, Chams, and 30 hill tribes. The capital and largest city is Phnom Penh, the political, economic, and cultural center of Cambodia. The kingdom is a constitutional monarchy with Norodom Sihamoni, a monarch chosen by the Royal Throne Council, as head of state. The head of government is Hun Sen, who is currently the longest serving non-royal leader in South East Asia and has ruled Cambodia for over 25 years. Cambodia's ancient name is "Kambuja".More Cambodia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- #76 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- OttawaCanada is a country in North America consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean. Covering 9.98 million square kilometres in total, Canada is the world's second-largest country by total area and the fourth-largest country by land area. Its common border with the United States forms the world's longest land border. The land that is now Canada has been inhabited for millennia by various Aboriginal peoples. Beginning in the late 15th century, British and French colonies were established on the region's Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various conflicts, the United Kingdom gained and lost North American territories until left, in the late 18th century, with what mostly comprises Canada today. Pursuant to the British North America Act, on July 1, 1867, three colonies joined to form the autonomous federal Dominion of Canada. This began an accretion of provinces and territories to the new self-governing Dominion.More Canada
- Dig Deeper...The Top Stadiums in Canada
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #6 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
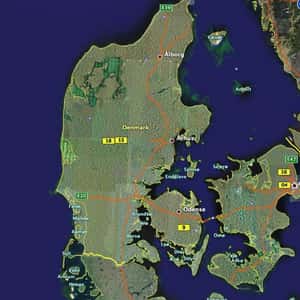
- CopenhagenDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The southernmost of the Nordic countries, it is located southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark is a sovereign state that comprises Denmark and two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark proper has an area of 43,094 square kilometres, and a population of 5,659,715. The country consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and the Danish archipelago of 443 named islands, of which around 70 are inhabited. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate. The unified kingdom of Denmark emerged in the 10th century as a proficient seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea. Danish rule over the personal Kalmar Union, established in 1397, ended with Swedish secession in 1523. However, Denmark still kept a union over Norway which lasted until its dissolution in 1814. Denmark inherited an expansive colonial empire from this union, of which the Faroe Islands and Greenland are remnants.
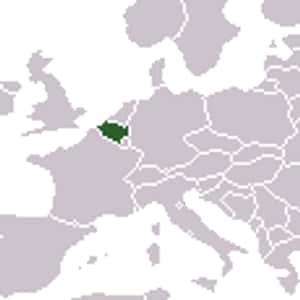
Flanders
Flanders today normally refers to the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium. It is one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. Historically, the name referred to a region located in the northwestern part of present-day Belgium and adjacent parts of France and the Netherlands. Both in the historical and the contemporary meaning, the demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. Brussels is the capital of Flanders, though it is also autonomous, predominantly French-speaking and only partially under Flanders' jurisdiction. Over the course of history, the geographical territory that was called "Flanders" has varied, and usage in English was at most periods much vaguer and imprecise than in the region itself. From around 1000 AD, Flanders historically meant the land situated along the North Sea from the Strait of Dover to the Scheldt estuary, with ill-defined southern borders. It came to refer specifically to the County of Flanders, lasting from 862 to 1795, whose territory was situated in the northwestern part of what is now Belgium, and what are now parts of northern France, and the Netherlands.- St. George'sGrenada is an island country consisting of Grenada itself and six smaller islands at the southern end of the Grenadines in the southeastern Caribbean Sea. Grenada is located northwest of Trinidad and Tobago, northeast of Venezuela, and southwest of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Grenada is also known as the "Island of Spice" because of the production of nutmeg and mace crops of which it is one of the world's largest exporters. Its size is 344 square kilometres, with an estimated population of 110,000. Its capital is St. George's. The national bird of Grenada is the critically endangered Grenada dove.More Grenada
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #208 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- New DelhiIndia, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the south-west, and the Bay of Bengal on the south-east, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north-east; and Burma and Bangladesh to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia. Home to the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation and a region of historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian subcontinent was identified with its commercial and cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism—originated here, whereas Zoroastrianism and the abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam arrived in the 1st millennium CE and also helped shape the region's diverse culture.More India
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #29 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
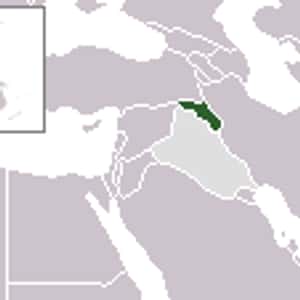
- ErbilIraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan, also known as the Kurdistan Region, is the autonomous region of Iraq. It borders the Kurdish regions of Iran to the east, Turkey to the north, and Syria to the west, along with the rest of Iraq to the south. The regional capital is Erbil. The region is officially governed by the Kurdistan Regional Government. Kurdistan is a parliamentary democracy with a regional assembly that consists of 111 seats. The current president is Masoud Barzani, who was initially elected in 2005 and re-elected in 2009. In August 2013 the parliament extended his presidency for another two years. The new Iraqi constitution defines Iraqi Kurdistan as a federal entity of Iraq, and establishes Kurdish and Arabic as Iraq's joint official languages. The four governorates of Duhok, Hawler, Silemani, and Halabja comprise around 41,710 square kilometres and have a population of 8.35 million. In 2014, during the 2014 Iraq Crisis, Iraqi Kurdistan's forces also took over much of the disputed territories of Northern Iraq.
- DouglasThe Isle of Man, otherwise known simply as Mann, is a self-governing British Crown dependency located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is represented by a Lieutenant Governor, but its foreign relations and defence are the responsibility of the British Government. The island has been inhabited by humans since before 6500 BC. Gaelic cultural influence began in the 5th century AD, and the Manx language, a branch of the Gaelic languages, gradually emerged. In 627, Edwin of Northumbria conquered the Isle of Man along with most of Mercia. In the 9th century, the Norse began to settle there. Norse people from Scotland then established the Kingdom of the Isles. The King's title would then carry the suffix, "and the Isles". Magnus III, the King of Norway, was also known as "King of Mann and the Isles" as part of the Hebrides civilization between 1099 and 1103. A Norse-Gaelic culture arose and the island came under Norse control. In 1266, the island became part of Scotland, as formalised by the Treaty of Perth.More Isle of Man
- Dig Deeper...Countries Where Gay Marriage is Legal
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #93 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- JerusalemIsrael or, officially the State of Israel, is a country in Western Asia, situated at the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea. It shares land borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria in the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories comprising the West Bank and Gaza Strip on the east and southwest, respectively, and Egypt and the Gulf of Aqaba in the Red Sea to the south. It contains geographically diverse features within its relatively small area. Israel's financial center is Tel Aviv, while Jerusalem is both its designated capital and the most populous individual city under the country's governmental administration. Israeli sovereignty over Jerusalem is internationally disputed. On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly recommended the adoption and implementation of the Partition Plan for Mandatory Palestine. Borders for a new Jewish state were specified by the UN but ultimately not recognized by either Israel or neighboring countries. The end of the British Mandate for Palestine was set for midnight on 14 May 1948.More Israel
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Israel
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #44 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
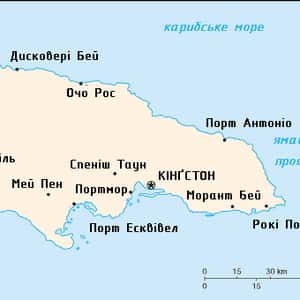
- KingstonJamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea, comprising the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles. The island, 10,990 square kilometres in area, lies about 145 kilometres south of Cuba, and 191 kilometres west of Hispaniola, the island containing the nation-states of Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Jamaica is the fifth-largest island country in the Caribbean. Once a Spanish possession known as Santiago, in 1655 it came under the rule of England, and was called Jamaica. It achieved full independence from the United Kingdom on 6 August 1962. With 2.8 million people, it is the third most populous Anglophone country in the Americas, after the United States and Canada. Kingston is the country's largest city and its capital, with a population of 937,700. Jamaica has a large diaspora around the world, due to emigration from the country. Jamaica is a Commonwealth realm, with Queen Elizabeth II as its monarch and head of state. Her appointed representative in the country is the Governor-General of Jamaica, currently Patrick Allen. The head of government and Prime Minister of Jamaica is Portia Simpson-Miller.More Jamaica
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Jamaica
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #17 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- TokyoJapan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. The Kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and Japan is often called "Land of the Rising Sun". Japan is a stratovolcanic archipelago of 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku, which make up about ninety-seven percent of Japan's land area. Japan's population of 126 million is the world's tenth largest. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes the de facto capital of Tokyo and several surrounding prefectures, is the world's largest metropolitan area, with over 30 million residents. Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period. The first written mention of Japan is in Chinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly Imperial China, followed by periods of isolation, later from Western European influence, has characterized Japan's history.More Japan
- Dig Deeper...The Most WTF Japan Photos Ever
- And Deeper...The Craziest Japanese Fashion Trends
- And Deeper...14 Locations in Japan You Must Visit If You're An Anime Fan
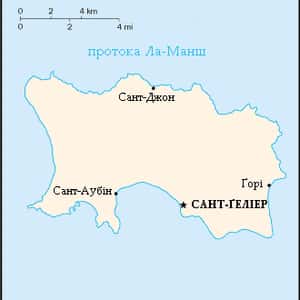
- Saint HelierJersey, officially the Bailiwick of Jersey, is a possession of the Crown in right of Jersey, off the coast of Normandy, France. The bailiwick consists of the island of Jersey, along with surrounding uninhabited islands and rocks collectively named Les Dirouilles, Les Écréhous, Les Minquiers, Les Pierres de Lecq, and other reefs. Jersey was part of the Duchy of Normandy, whose dukes went on to become kings of England from 1066. After Normandy was lost by the kings of England in the thirteenth century, and the ducal title surrendered to France, Jersey and the other Channel Islands remained attached to the English crown. Jersey is a self-governing parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy, with its own financial, legal and judicial systems, and the power of self-determination. The island of Jersey is the largest of the Channel Islands. Although the Bailiwicks of Jersey and Guernsey are often referred to collectively as the Channel Islands, the "Channel Islands" are not a constitutional or political unit. Jersey has a separate relationship to the British Crown from the other Crown dependencies of Guernsey and the Isle of Man.More Jersey
- Dig Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #164 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- #168 of 186 onThe Countries with the Best Food
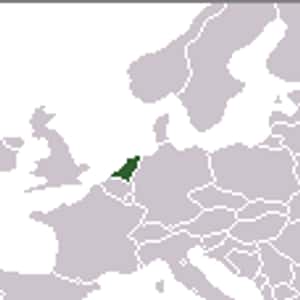
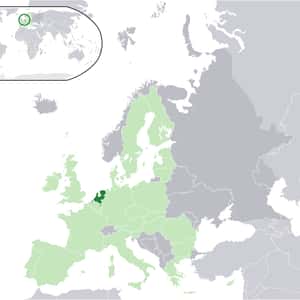
- AmsterdamThe Kingdom of the Netherlands, commonly known as the Netherlands, is a sovereign state and constitutional monarchy with territory in western Europe and in the Caribbean. The Kingdom is celebrating its 200 years in a series of festive occasions spanning from 2013 to 2015, the actual year of the anniversary. The four parts of the Kingdom – Aruba, Curaçao, the Netherlands, and Sint Maarten – are separate countries and participate on a basis of equality as partners in the Kingdom. In practice, however, most of the Kingdom affairs are administered by the Netherlands – which comprises roughly 98% of the Kingdom's land area and population – on behalf of the entire Kingdom. Consequently, the countries of Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten are dependent on the Netherlands for matters like foreign policy and defence, although they are autonomous to a certain degree with their own parliaments. The vast majority in land area of the constituent country of the Netherlands is located in Europe, with the exception of its three special municipalities that are located in the Caribbean. The constituent countries of Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten are located in the Caribbean as well.
- BeirutLebanon, officially the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south. Lebanon's location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has dictated its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious and ethnic diversity. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back more than seven thousand years, predating recorded history. Lebanon was the home of the Phoenicians and their kingdom, a maritime culture that flourished for over a thousand years. In 64 BC, the region came under the rule of the Roman Empire, and eventually became one of the Empire's leading centers of Christianity. In the Mount Lebanon range a monastic tradition known as the Maronite Church was established. As the Arab Muslims conquered the region, the Maronites held onto their religion and identity. However, a new religious group, the Druze, established themselves in Mount Lebanon as well, a religious divide that would last for centuries. During the Crusades, the Maronites re-established contact with the Roman Catholic Church and asserted their communion with Rome.More Lebanon
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #57 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
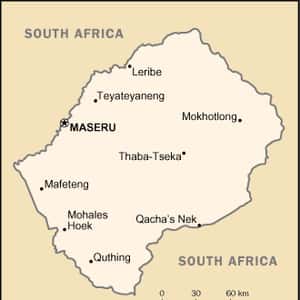
- MaseruLesotho, officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is an enclaved landlocked country completely surrounded by South Africa. It is just over 30,000 km² in size and has a population slightly over two million. Its capital and largest city is Maseru. Lesotho is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The name Lesotho translates roughly into the land of the people who speak Sesotho. About 40% of the population lives below the international poverty line of US $1.25 a day.
- VaduzLiechtenstein, officially the Principality of Liechtenstein, is a doubly landlocked German-speaking microstate in Central Europe. It is a constitutional principality headed by the Prince of Liechtenstein. Liechtenstein is bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and Austria to the east and north. It has an area of just over 160 square kilometres and an estimated population of 35,000. Divided into 11 municipalities, its capital is Vaduz and largest town Schaan. Economically, Liechtenstein has the highest gross domestic product per person in the world when adjusted by purchasing power parity. It is also the 2nd richest country in the world, after Qatar, and has one of the lowest unemployment rates at 1.5%. An alpine country, Liechtenstein is mainly mountainous, making it a winter sports destination. Many cultivated fields and small farms are found both in the south and north. The country has a strong financial sector centered in Vaduz, and has been identified as a tax haven. It is a member of the European Free Trade Association and part of the European Economic Area and the Schengen Area, but not of the European Union.
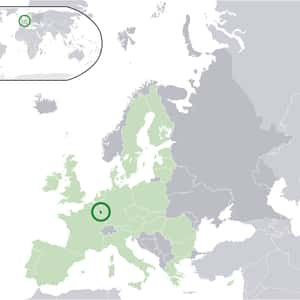
- LuxembourgLuxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. It comprises two principal regions: the Oesling in the north as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south. Luxembourg had a population of 524,853 in October 2012 and has an area of 2,586 square kilometres, making it one of the smallest sovereign nations in Europe. As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by a grand duke, Henri, Grand Duke of Luxembourg, and is the world's only remaining grand duchy. Luxembourg is a developed country, with an advanced economy and the world's second highest GDP per capita, according to the World Bank. Its central location has historically made it of great strategic importance to numerous powers, dating back to its founding as a Roman fortress, its hosting of a vital Frankish castle during the Early Middle Ages, and its role as a bastion for the Spanish Road between 16th and 17th centuries.More Luxembourg
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #154 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- Kuala LumpurMalaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy located in Southeast Asia. It consists of thirteen states and three federal territories and has a total landmass of 329,847 square kilometres separated by the South China Sea into two similarly sized regions, Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime border with Thailand and maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia and a maritime border with the Philippines. The capital city is Kuala Lumpur, while Putrajaya is the seat of the federal government. By 2015, with a population of over 30 million, Malaysia became the 43rd most populous country in the world. The southernmost point of continental Eurasia, Tanjung Piai, is in Malaysia, located in the tropics. It is one of 17 megadiverse countries on earth, with large numbers of endemic species. Malaysia has its origins in the Malay kingdoms present in the area which, from the 18th century, became subject to the British Empire.More Malaysia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #95 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- AmsterdamThe Netherlands is the main constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It is a small, densely populated country, lying mainly in Western Europe, but also including three islands in the Caribbean. The European part of the Netherlands borders Germany to the east, Belgium to the south, and the North Sea to the northwest, sharing maritime borders with Belgium, the United Kingdom and Germany. The largest and most important cities in the Netherlands are Amsterdam, The Hague and Rotterdam. Amsterdam is the country's capital, while The Hague holds the Dutch seat of government and parliament. The port of Rotterdam is the largest port in Europe – as large as the next three largest combined. The Netherlands' name literally means "Low Country", inspired by its low and flat geography, with only about 50% of its land exceeding one metre above sea level. Most of the areas below sea level are man-made. Since the late 16th century, large areas have been reclaimed from the sea and from lakes, amounting to nearly 17% of the country's current land mass.More Netherlands
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From The Netherlands
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #81 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- WellingtonNew Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses – that of the North Island, or Te Ika-a-Māui, and the South Island, or Te Waipounamu – and numerous smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long isolation, New Zealand developed a distinctive biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life. The country's varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland. Polynesians settled New Zealand in 1250–1300 CE and developed a distinctive Māori culture. Abel Tasman, a Dutch explorer, was the first European to sight New Zealand in 1642. In 1840, representatives of the British Crown and Māori Chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, making New Zealand a British colony.More New Zealand
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from New Zealand
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #37 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- NiameyNiger, officially the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. Niger covers a land area of almost 1,270,000 km², making it the largest nation in West Africa, with over 80 percent of its land area covered by the Sahara desert. The country's predominantly Islamic population of 17,138,707 is mostly clustered in the far south and west of the nation. The capital city is Niamey, located in the far-southwest corner of Niger. Niger is a developing country, and is consistently one of the lowest-ranked in the United Nations' Human Development Index; it was ranked last at 187th for 2013. Much of the non-desert portions of the country are threatened by periodic drought and desertification. The economy is concentrated around subsistence and some export agriculture clustered in the more fertile south, and the export of raw materials, especially uranium ore. Niger faces serious challenges to development due to its landlocked position, desert terrain, poor education and poverty of its people, lack of infrastructure, poor health care, and environmental degradation.
- OsloNorway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a sovereign and unitary monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula plus Jan Mayen and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard. The Antarctic Peter I Island and the sub-Antarctic Bouvet Island are dependent territories and thus not considered part of the Kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land. Until 1814, the Kingdom included the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. Norway has a total area of 385,252 square kilometres and a population of 5,109,059 people. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden. Norway is bordered by Finland and Russia to the north-east, and the Skagerrak Strait to the south, with Denmark on the other side. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. King Harald V of the House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg is the current monarch of Norway. Erna Solberg became Prime Minister in 2013, replacing Jens Stoltenberg. A constitutional monarchy since 1814, state power is divided between the Parliament, the King and his Council, and the Supreme Court.More Norway
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Norway
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #18 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- IslamabadPakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a sovereign country in South Asia. With a population exceeding 180 million people, it is the sixth most populous country and with an area covering 796,095 km², it is the 36th largest country in the world in terms of area. Pakistan has a 1,046-kilometre coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by the nations of India to the east, Afghanistan to the west, Iran to the southwest and China in the far northeast respectively. It is separated from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's narrow Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a marine border with Oman. The territory that now constitutes Pakistan was previously home to several ancient cultures, including the Mehrgarh of the Neolithic and the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation, and was later home to kingdoms ruled by people of different faiths and cultures, including Hindus, Indo-Greeks, Muslims, Turco-Mongols, Afghans and Sikhs.More Pakistan
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from Pakistan
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #70 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- RamallahThe Palestinian National Authority was the interim self-government body established to govern Areas A and B of the West Bank and Gaza Strip as a consequence of the 1993 Oslo Accords. Following elections in 2006 and the subsequent Gaza conflict between the Fatah and Hamas parties, its authority had extended only as far as the West Bank. Since January 2013, the Fatah-controlled Palestinian Authority rebranded itself as the State of Palestine in official documents, after the United Nations voted to recognize Palestine as a non-member UN observer state. The Palestinian Authority was formed in 1994, pursuant to the Oslo Accords between the Palestine Liberation Organization and the government of Israel, as a five-year interim body. Further negotiations were then meant to take place between the two parties regarding its final status. As of 2013, more than eighteen years following the formulation of the Authority, this status has yet to be reached. According to the Oslo Accords, the Palestinian Authority was designated to have exclusive control over both security-related and civilian issues in Palestinian urban areas and only civilian control over Palestinian rural areas.
- Port MoresbyPapua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an Oceanian country that occupies the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The western half of New Guinea forms the Indonesian provinces of Papua and West Papua. Papua New Guinea is one of the most culturally diverse countries in the world; 848 languages are listed for the country, of which 12 have no known living speakers. Most of the population of over 7 million people live in customary communities, which are as diverse as the languages. It is also one of the most rural, as only 18 per cent of its people live in urban centres. The country is one of the world's least explored, culturally and geographically, and many undiscovered species of plants and animals are thought to exist in the interior. Strong growth in Papua New Guinea's mining and resource sector has led to the country becoming the sixth fastest-growing economy in the world as of 2011.
- LisbonPortugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country in southwest Europe. It is located on the Iberian Peninsula, and it is the westernmost country of mainland Europe, being bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and south and by Spain to the north and east. Aside from continental Portugal, the Portuguese Republic holds sovereignty over the Atlantic archipelagos of Azores and Madeira, which are autonomous regions of Portugal. The country is named after its second largest city, Porto, whose name derives from a combination of Latin "Portus", and the Celtic place-name Cale., The land within the borders of the current Portuguese Republic has been continually fought over and settled since prehistoric times. The Celts and the Romans were followed by the Visigothic and the Suebi Germanic peoples, who were themselves later invaded by the Moors. These Muslim peoples were eventually expelled during the Christian Reconquista of the peninsula. By 1139, Portugal established itself as a kingdom independent from León.More Portugal
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From Portugal
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #23 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
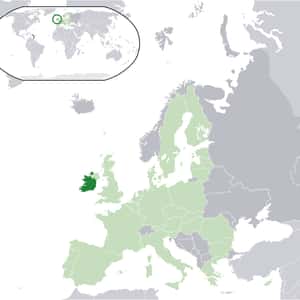
- DublinIreland, also known as the Republic of Ireland, is a sovereign state in western Europe occupying about five-sixths of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, located in the eastern part of the island, whose metropolitan area is home to around a third of the country's 4.6 million inhabitants. The state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, a part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, Saint George's Channel to the south east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic with an elected president serving as head of state. The head of government, the Taoiseach, is nominated by the lower house of parliament, Dáil Éireann. The Irish Free State was created in 1922 as a result of the Anglo-Irish Treaty. It effectively became a republic, with an elected president, under the constitution of 1937, in which it was named "Ireland". It was officially declared a republic in 1949. Ireland became a member of the United Nations in December 1955. It joined the European Economic Community, predecessor of the European Union, in 1973.More Republic of Ireland
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #94 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BasseterreThe Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island country in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population. The country is a Commonwealth realm, with Elizabeth II as its head of state. The capital city and headquarters of government for the federated state is Basseterre on the larger island of Saint Kitts. The smaller island of Nevis lies about 2 miles southeast of Saint Kitts, across a shallow channel called "The Narrows." Historically, the British dependency of Anguilla was also a part of this union, which was then known collectively as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. Saint Kitts and Nevis are considered to be geographically part of the Leeward Islands. To the north-northwest lie the islands of Sint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten and Anguilla. To the east and northeast are Antigua and Barbuda, and to the southeast is the small uninhabited island of Redonda, and the island of Montserrat, which currently has an active volcano. Saint Kitts and Nevis were among the first islands in the Caribbean to be settled by Europeans.
- CastriesSaint Lucia is a sovereign island country in the eastern Caribbean Sea on the boundary with the Atlantic Ocean. Part of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique. It covers a land area of 617 km² and has a population of 174,000. Its capital is Castries. One of the Windward Islands, Saint Lucia was named after Saint Lucy of Syracuse by the French, the island's first European settlers. They signed a treaty with the native Carib Indians in 1660. England took control of the island from 1663 to 1667. In ensuing years, it was at war with France 14 times, and rule of the island changed frequently. In 1814, the British took definitive control of the island. Because it switched so often between British and French control, Saint Lucia was also known as the "Helen of the West Indies". Representative government came about in 1840. From 1958 to 1962, the island was a member of the Federation of the West Indies. On 22 February 1979, Saint Lucia became an independent state of the Commonwealth of Nations associated with the United Kingdom.More Saint Lucia
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #106 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- KingstownSaint Vincent and the Grenadines is an island country in the Lesser Antilles Island arc, in the southern portion of the Windward Islands, which lie at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea where the latter meets the Atlantic Ocean. The country is also known as St. Vincent. Its 389 km² territory consists of the main island of Saint Vincent and the northern two-thirds of the Grenadines, which are a chain of smaller islands stretching south from Saint Vincent Island to Grenada. The main island of Saint Vincent measures 26 km long, 15 km in width and 344 km² in area. From the most northern to the most southern points, the Grenadine islands belonging to Saint Vincent span 60.4 km with a combined area of 45 km². Most of the nation lies within the Hurricane Belt. To the north of Saint Vincent lies Saint Lucia, to the east Barbados. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a densely populated country with approximately 120,000 inhabitants. Its capital is Kingstown, also its main port.
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #185 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- ApiaSamoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa, formerly known as Western Samoa, is an Oceanian country encompassing the western part of the Samoan Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. It became independent from New Zealand in 1962. The two main islands of Samoa are Upolu and Savai'i, one of the biggest islands in Polynesia. The capital city, Apia, and Faleolo International Airport are situated on the island of Upolu. Samoa was admitted to the United Nations on 15 December 1976. The entire island group, which includes American Samoa, was called "Navigator Islands" by European explorers before the 20th century because of the Samoans' seafaring skills. The language spoken is Samoan language or Gagana Fa'asāmoa. This is the same language spoken in American Samoa.More Samoa
- Dig Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- And Deeper...Kingdoms And Monarchs Of The World
- #55 of 186 onThe Countries with the Best Food
- BelgradeSerbia, officially the Republic of Serbia, is a sovereign state situated at the crossroads between Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans. Serbia is landlocked and borders Hungary to the north; Romania and Bulgaria to the east; Macedonia to the south; and Croatia, Bosnia, and Montenegro to the west; it also claims a border with Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. The capital of Serbia, Belgrade, is one of the largest cities in Southeast Europe. As of a 2011 census, Serbia had a total population of 7.2 million. Following the Slavic migrations to the Balkans from the 6th century onwards, Serbs established several states in the early Middle Ages. The Serbian Kingdom obtained recognition by Rome and Constantinople in 1217; it reached its peak in 1346 as a relatively short-lived Serbian Empire. By the mid-16th century, the entire territory of modern-day Serbia was annexed by the Ottoman Empire, at times interrupted by the Habsburgs. In the early 19th century, the Serbian Revolution established the nation-state as the region's first constitutional monarchy, which subsequently expanded its territory.
- Bloemfontein, Cape Town, PretoriaSouth Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa, is a country located in Southern Africa. It has 2,798 kilometres of coastline that stretches along the South Atlantic and Indian oceans. To the north lie the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana and Zimbabwe; to the east are Mozambique and Swaziland; and within it lies Lesotho, an enclave surrounded by South African territory. South Africa is the 25th-largest country in the world by land area, and with close to 53 million people, is the world's 25th-most populous nation. South Africa is a multiethnic society encompassing a wide variety of cultures, languages, and religions. Its pluralistic makeup is reflected in the constitution's recognition of 11 official languages, which is among the highest number of any country in the world. Two of these languages are of European origin: Afrikaans developed from Dutch and serves as the first language of most white and coloured South Africans, based on history; English reflects the legacy of British colonialism, and is commonly used in public and commercial life, though it is fourth-ranked as a spoken first language.More South Africa
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players from South Africa
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #26 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- MadridSpain, officially the Kingdom of Spain, is a sovereign state located on the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe. Its mainland is bordered to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea except for a small land boundary with Gibraltar; to the north and northeast by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west and northwest by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Along with France and Morocco, it is one of only three countries to have both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines. Spain's 1,214 km border with Portugal is the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. Spanish territory also includes two archipelagos; the Balearic Islands, in the Mediterranean Sea, and the Canary Islands, in the Atlantic Ocean off the African coast; two major exclaves, Ceuta and Melilla, in continental North Africa; and the islands and peñones of Alborán, Alhucemas, Chafarinas and Vélez de la Gomera. With an area of 505,990 km², Spain is the second largest country in Western Europe and the European Union, and the fourth largest country in Europe. By population, Spain is the sixth largest in Europe and the fifth in the European Union.More Spain
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From Spain
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #24 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- StockholmSweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. Sweden borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres, Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of about 9.7 million. Sweden has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre, with the population mostly concentrated in the southern half of the country. About 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the collective geographical group of nations Fennoscandia. Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats/Götar and Swedes/Svear and contributing to the sea peoples known as the Vikings. Sweden emerged as an independent and unified country during the Middle Ages. In the 17th century, the country expanded its territories to form the Swedish Empire. The empire grew to be one of the great powers of Europe in the 17th and early 18th centuries.More Sweden
- Dig Deeper...The Best Swedish Soccer Players of All Time
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #42 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- BernSwitzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt. The country is situated in Western and Central Europe, where it is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is a landlocked country geographically divided between the Alps, the Swiss Plateau and the Jura, spanning an area of 41,285 km².More Switzerland
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From Switzerland
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #55 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
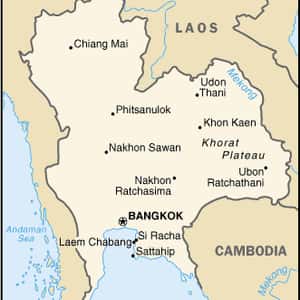
- BangkokThailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand, formerly known as Siam, is a country at the centre of the Indochina peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the southern extremity of Burma. Its maritime boundaries include Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast, and Indonesia and India on the Andaman Sea to the southwest. Thailand is a monarchy headed by King Bhumibol Adulyadej, Rama IX, and governed by a military junta that took power in May 2014. The king is the ninth of the House of Chakri, and has reigned since 1946 as the world's longest-serving current head of state and the country's longest-reigning monarch. The King of Thailand's titles include Head of State, Head of the Armed Forces, Adherent of Buddhism, and Upholder of religions. Although a constitutional system was established in 1932, the monarchy and military have continued to intervene periodically in politics.More Thailand
- Dig Deeper...The Best Kpop Idols From Thailand, Ranked
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #142 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- NassauThe Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country of the Lucayan Archipelago consisting of more than 700 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean; north of Cuba and Hispaniola; northwest of the Turks and Caicos Islands; southeast of the U.S. state of Florida and east of the Florida Keys. Its capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The designation of "Bahamas" can refer to either the country or the larger island chain that it shares with the Turks and Caicos Islands. As stated in the mandate/manifesto of the Royal Bahamas Defence Force, the Bahamas territory encompasses 470,000 km² of ocean space. Originally inhabited by the Lucayan, a branch of the Arawakan-speaking Taino people, the Bahamas were the site of Columbus' first landfall in the New World in 1492. Although the Spanish never colonized the Bahamas, they shipped the native Lucayans to slavery in Hispaniola. The islands were mostly deserted from 1513 until 1648, when English colonists from Bermuda settled on the island of Eleuthera. The Bahamas became a British Crown colony in 1718, when the British clamped down on piracy.More Bahamas
- Dig Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- And Deeper...Countries with Best Sanitation Facilities
- #100 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
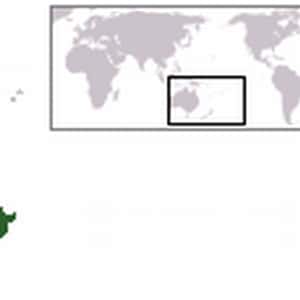
Tuvalu
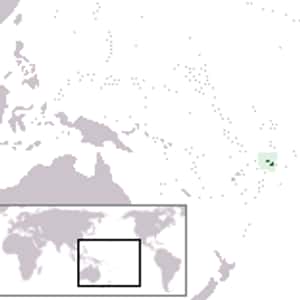
FunafutiTuvalu, formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is a Polynesian island nation located in the Pacific Ocean, midway between Hawaii and Australia. It comprises three reef islands and six true atolls spread out between the latitude of 5° to 10° south and longitude of 176° to 180°, west of the International Date Line. Its nearest neighbours are Kiribati, Nauru, Samoa and Fiji. Tuvalu has a population of 10,837. The total land area of the islands of Tuvalu is 26 square kilometres. The first inhabitants of Tuvalu were Polynesians. The pattern of settlement that is believed to have occurred is that the Polynesians spread out from Samoa and Tonga into the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone to migration into the Polynesian Outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia. In 1568 Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to sail through the archipelago, sighting the island of Nui during his expedition in search of Terra Australis. In 1819 the island of Funafuti was named Ellice's Island; the name Ellice was applied to all nine islands after the work of English hydrographer Alexander George Findlay.More Tuvalu- Dig Deeper...World Poverty: The Poorest Countries In The World
- And Deeper...Life Expectancy by Country | Life Expectancy Trends
- #109 of 186 onThe Countries with the Best Food
- KyivUkraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the largest country entirely within Europe. Ukraine borders Russia to the east and northeast, Belarus to the northwest, Poland, Slovakia and Hungary to the west, Romania and Moldova to the southwest, and the Black Sea and Sea of Azov to the south and southeast, respectively. The territory of modern Ukraine has been inhabited by humans since 32,000 BC. During the Middle Ages, the area was a key center of East Slavic culture, with the powerful state of Kievan Rus' forming the basis of Ukrainian identity. Following its fragmentation in the 13th century, the territory was contested, ruled and divided by a variety of powers, including Lithuania, Poland, the Ottoman Empire, Austro-Hungary, and Russia. A Cossack republic emerged and prospered during the 17th and 18th centuries, but Ukraine's territories remained divided until they were consolidated into a Soviet republic in the 20th century. It became independent in 1991. Ukraine has long been a global breadbasket because of its extensive, fertile farmlands, and it remains one of the world's largest grain exporters.
- LondonThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom or Britain, is a sovereign state in Europe. Lying off the north-western coast of the European mainland, the country includes the island of Great Britain—a term also applied loosely to refer to the whole country—the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands. Northern Ireland is the only part of the UK that shares a land border with another state. Apart from this land border, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to its west and north, the North Sea to its east and the English Channel to its south. The Irish Sea lies between Great Britain and Ireland. The UK has an area of 93,800 square miles, making it the 80th-largest sovereign state in the world and the 11th-largest in Europe. The United Kingdom is the 22nd-most populous country, with an estimated 64.5 million inhabitants. It is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of governance. Its capital city is London, an important global city and financial centre with an urban population of 10,310,000, the fourth-largest in Europe and second-largest in the European Union.More United Kingdom
- Dig Deeper...The Best Soccer Players From England
- And Deeper...The Most Corrupt Countries in the World
- #4 of 223 onThe Prettiest Flags in the World
- HarareZimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. The capital and largest city is Harare. What is now Zimbabwe was historically the site of many prominent kingdoms and empires, as well as a major route for migration and trade. The present territory was first demarcated by Cecil Rhodes' British South Africa Company during the 1890s, becoming the self-governing colony of Southern Rhodesia in 1923. In 1965 the conservative white minority government unilaterally declared independence as Rhodesia. The unrecognized state endured international isolation and a 15-year guerrilla war with black nationalist forces; this culminated in a peace agreement that established universal enfranchisement and de jure sovereignty in April 1980. An ethnically diverse country of roughly 13 million people, Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, with English, Shona and Ndebele being most common. President Robert Mugabe is head of state and government, and commander-in-chief of the armed forces.