Boggle (Find all possible words in a board of characters) | Set 1
Last Updated :
15 Apr, 2024
Given a dictionary, a method to do lookup in dictionary and a M x N board where every cell has one character. Find all possible words that can be formed by a sequence of adjacent characters. Note that we can move to any of 8 adjacent characters, but a word should not have multiple instances of same cell.
Example:
Input: dictionary[] = {"GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"};
boggle[][] = {{'G', 'I', 'Z'},
{'U', 'E', 'K'},
{'Q', 'S', 'E'}};
isWord(str): returns true if str is present in dictionary
else false.
Output: Following words of dictionary are present
GEEKS
QUIZ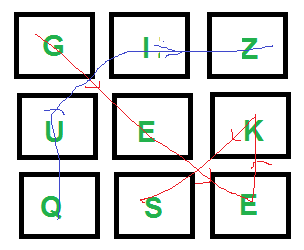
The idea is to consider every character as a starting character and find all words starting with it. All words starting from a character can be found using Depth First Traversal. We do depth-first traversal starting from every cell. We keep track of visited cells to make sure that a cell is considered only once in a word.
C++
// C++ program for Boggle game
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define M 3
#define N 3
// Let the given dictionary be following
string dictionary[] = { "GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO" };
int n = sizeof(dictionary) / sizeof(dictionary[0]);
// A given function to check if a given string is present in
// dictionary. The implementation is naive for simplicity. As
// per the question dictionary is given to us.
bool isWord(string& str)
{
// Linearly search all words
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (str.compare(dictionary[i]) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// A recursive function to print all words present on boggle
void findWordsUtil(char boggle[M][N], bool visited[M][N], int i,
int j, string& str)
{
// Mark current cell as visited and append current character
// to str
visited[i][j] = true;
str = str + boggle[i][j];
// If str is present in dictionary, then print it
if (isWord(str))
cout << str << endl;
// Traverse 8 adjacent cells of boggle[i][j]
for (int row = i - 1; row <= i + 1 && row < M; row++)
for (int col = j - 1; col <= j + 1 && col < N; col++)
if (row >= 0 && col >= 0 && !visited[row][col])
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, row, col, str);
// Erase current character from string and mark visited
// of current cell as false
str.erase(str.length() - 1);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
// Prints all words present in dictionary.
void findWords(char boggle[M][N])
{
// Mark all characters as not visited
bool visited[M][N] = { { false } };
// Initialize current string
string str = "";
// Consider every character and look for all words
// starting with this character
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, str);
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
char boggle[M][N] = { { 'G', 'I', 'Z' },
{ 'U', 'E', 'K' },
{ 'Q', 'S', 'E' } };
cout << "Following words of dictionary are present\n";
findWords(boggle);
return 0;
}
// Java program for Boggle game
class GFG {
// Let the given dictionary be following
static final String dictionary[] = { "GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GUQ", "EE" };
static final int n = dictionary.length;
static final int M = 3, N = 3;
// A given function to check if a given string is present in
// dictionary. The implementation is naive for simplicity. As
// per the question dictionary is given to us.
static boolean isWord(String str)
{
// Linearly search all words
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (str.equals(dictionary[i]))
return true;
return false;
}
// A recursive function to print all words present on boggle
static void findWordsUtil(char boggle[][], boolean visited[][], int i,
int j, String str)
{
// Mark current cell as visited and append current character
// to str
visited[i][j] = true;
str = str + boggle[i][j];
// If str is present in dictionary, then print it
if (isWord(str))
System.out.println(str);
// Traverse 8 adjacent cells of boggle[i][j]
for (int row = i - 1; row <= i + 1 && row < M; row++)
for (int col = j - 1; col <= j + 1 && col < N; col++)
if (row >= 0 && col >= 0 && !visited[row][col])
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, row, col, str);
// Erase current character from string and mark visited
// of current cell as false
str = "" + str.charAt(str.length() - 1);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
// Prints all words present in dictionary.
static void findWords(char boggle[][])
{
// Mark all characters as not visited
boolean visited[][] = new boolean[M][N];
// Initialize current string
String str = "";
// Consider every character and look for all words
// starting with this character
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, str);
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void main(String args[])
{
char boggle[][] = { { 'G', 'I', 'Z' },
{ 'U', 'E', 'K' },
{ 'Q', 'S', 'E' } };
System.out.println("Following words of dictionary are present");
findWords(boggle);
}
}
# Python3 program for Boggle game
# Let the given dictionary be following
dictionary = ["GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"]
n = len(dictionary)
M = 3
N = 3
# A given function to check if a given string
# is present in dictionary. The implementation is
# naive for simplicity. As per the question
# dictionary is given to us.
def isWord(Str):
# Linearly search all words
for i in range(n):
if (Str == dictionary[i]):
return True
return False
# A recursive function to print all words present on boggle
def findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, Str):
# Mark current cell as visited and
# append current character to str
visited[i][j] = True
Str = Str + boggle[i][j]
# If str is present in dictionary,
# then print it
if (isWord(Str)):
print(Str)
# Traverse 8 adjacent cells of boggle[i,j]
row = i - 1
while row <= i + 1 and row < M:
col = j - 1
while col <= j + 1 and col < N:
if (row >= 0 and col >= 0 and not visited[row][col]):
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, row, col, Str)
col+=1
row+=1
# Erase current character from string and
# mark visited of current cell as false
Str = "" + Str[-1]
visited[i][j] = False
# Prints all words present in dictionary.
def findWords(boggle):
# Mark all characters as not visited
visited = [[False for i in range(N)] for j in range(M)]
# Initialize current string
Str = ""
# Consider every character and look for all words
# starting with this character
for i in range(M):
for j in range(N):
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, Str)
# Driver Code
boggle = [["G", "I", "Z"], ["U", "E", "K"], ["Q", "S", "E"]]
print("Following words of", "dictionary are present")
findWords(boggle)
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
// C# program for Boggle game
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Let the given dictionary be following
static readonly String []dictionary = { "GEEKS", "FOR",
"QUIZ", "GUQ", "EE" };
static readonly int n = dictionary.Length;
static readonly int M = 3, N = 3;
// A given function to check if a given string
// is present in dictionary. The implementation is
// naive for simplicity. As per the question
// dictionary is given to us.
static bool isWord(String str)
{
// Linearly search all words
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (str.Equals(dictionary[i]))
return true;
return false;
}
// A recursive function to print all words present on boggle
static void findWordsUtil(char [,]boggle, bool [,]visited,
int i, int j, String str)
{
// Mark current cell as visited and
// append current character to str
visited[i, j] = true;
str = str + boggle[i, j];
// If str is present in dictionary,
// then print it
if (isWord(str))
Console.WriteLine(str);
// Traverse 8 adjacent cells of boggle[i,j]
for (int row = i - 1; row <= i + 1 && row < M; row++)
for (int col = j - 1; col <= j + 1 && col < N; col++)
if (row >= 0 && col >= 0 && !visited[row, col])
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, row, col, str);
// Erase current character from string and
// mark visited of current cell as false
str = "" + str[str.Length - 1];
visited[i, j] = false;
}
// Prints all words present in dictionary.
static void findWords(char [,]boggle)
{
// Mark all characters as not visited
bool [,]visited = new bool[M, N];
// Initialize current string
String str = "";
// Consider every character and look for all words
// starting with this character
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, str);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
char [,]boggle = { { 'G', 'I', 'Z' },
{ 'U', 'E', 'K' },
{ 'Q', 'S', 'E' } };
Console.WriteLine("Following words of " +
"dictionary are present");
findWords(boggle);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
<script>
// JavaScript program for Boggle game
// Let the given dictionary be following
var dictionary = ["GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"];
var n = dictionary.length;
var M = 3,
N = 3;
// A given function to check if a given string
// is present in dictionary. The implementation is
// naive for simplicity. As per the question
// dictionary is given to us.
function isWord(str)
{
// Linearly search all words
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) if (str == dictionary[i]) return true;
return false;
}
// A recursive function to print all words present on boggle
function findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, str)
{
// Mark current cell as visited and
// append current character to str
visited[i][j] = true;
str = str + boggle[i][j];
// If str is present in dictionary,
// then print it
if (isWord(str)) document.write(str + "<br>");
// Traverse 8 adjacent cells of boggle[i,j]
for (var row = i - 1; row <= i + 1 && row < M; row++)
for (var col = j - 1; col <= j + 1 && col < N; col++)
if (row >= 0 && col >= 0 && !visited[row][col])
findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, row, col, str);
// Erase current character from string and
// mark visited of current cell as false
str = "" + str[str.length - 1];
visited[i][j] = false;
}
// Prints all words present in dictionary.
function findWords(boggle)
{
// Mark all characters as not visited
var visited = Array.from(Array(M), () => new Array(N).fill(0));
// Initialize current string
var str = "";
// Consider every character and look for all words
// starting with this character
for (var i = 0; i < M; i++)
for (var j = 0; j < N; j++) findWordsUtil(boggle, visited, i, j, str);
}
// Driver Code
var boggle = [
["G", "I", "Z"],
["U", "E", "K"],
["Q", "S", "E"],
];
document.write("Following words of " + "dictionary are present <br>");
findWords(boggle);
// This code is contributed by rdtank.
</script>
OutputFollowing words of dictionary are present
GEEKS
QUIZ
Note that the above solution may print the same word multiple times. For example, if we add “SEEK” to the dictionary, it is printed multiple times. To avoid this, we can use hashing to keep track of all printed words.
To improve time complexity, we can use unordered_set(in C++) or dictionary(in Python) which takes constant search time. Now Time Complexity, Since we are doing depth-first traversal for every position in the array so n*m( time for one DFS) = n*m( |V| + |E|) where |V| is the total number of nodes and |E| is the total number of edges which are equal to n*m. So,
Time Complexity: O(N2 *M2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N*M)
Optimized Approach :
Instead of generating all strings from the grid and then checking whether it exists in dictionary or not , we can simply run a DFS on all words present in dictionary and check whether we can make that word from grid or not. This Approach is more optimised then the previous one.
Below is the implementation of above Approach.
C++
// C++ program for Boggle game
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define M 3
#define N 3
bool dfs(vector<vector<char> >& board, string &s, int i, int j, int n, int m, int idx){
if(i<0 || i>=n||j<0||j>=m){
return false;
}
if(s[idx]!= board[i][j]){
return false;
}
if(idx == s.size()-1){
return true;
}
char temp = board[i][j];
board[i][j]='*';
bool a = dfs(board,s,i,j+1,n,m,idx+1);
bool b= dfs(board,s,i,j-1,n,m,idx+1);
bool c = dfs(board,s,i+1,j,n,m,idx+1);
bool d = dfs(board,s,i-1,j,n,m,idx+1);
bool e = dfs(board,s,i+1,j+1,n,m,idx+1);
bool f = dfs(board,s,i-1,j+1,n,m,idx+1);
bool g = dfs(board,s,i+1,j-1,n,m,idx+1);
bool h = dfs(board,s,i-1,j-1,n,m,idx+1);
board[i][j]=temp;
return a||b||c||e||f||g||h||d;
}
void wordBoggle(vector<vector<char> >& board, vector<string>& dictionary) {
int n= board.size();
int m = board[0].size();
vector<string> ans;
set<string> store;
for(int i=0;i<dictionary.size();i++){
string s = dictionary[i];
int l = s.size();
for(int j = 0 ; j < n;j++){
for(int k=0;k<m;k++){
if(dfs(board,s,j,k,n,m,0)){
store.insert(s);
}
}
}
}
for(auto i:store){
cout<<i<<"\n";
}
return ;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
vector<vector<char>> boggle{ { 'G', 'I', 'Z' },
{ 'U', 'E', 'K' },
{ 'Q', 'S', 'E' } };
// Let the given dictionary be following
vector<string> dictionary{ "GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO" };
cout << "Following words of dictionary are present\n";
wordBoggle(boggle,dictionary);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Arpit Jain
// Java program for Boggle game
import java.util.*;
public class BoggleGame {
private static final int M = 3;
private static final int N = 3;
private static boolean dfs(char[][] board, String s, int i, int j, int n, int m, int idx) {
if (i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m) {
return false;
}
if (s.charAt(idx) != board[i][j]) {
return false;
}
if (idx == s.length() - 1) {
return true;
}
char temp = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '*';
boolean a = dfs(board, s, i, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean b = dfs(board, s, i, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean c = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean d = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean e = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean f = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean g = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
boolean h = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
board[i][j] = temp;
return a || b || c || e || f || g || h || d;
}
private static void wordBoggle(char[][] board, String[] dictionary) {
int n = board.length;
int m = board[0].length;
Set<String> ans = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> store = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : dictionary) {
int l = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (dfs(board, s, i, j, n, m, 0)) {
store.add(s);
}
}
}
}
for (String i : store) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] boggle = {
{'G', 'I', 'Z'},
{'U', 'E', 'K'},
{'Q', 'S', 'E'}
};
// Let the given dictionary be following
String[] dictionary = {"GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"};
System.out.println("Following words of dictionary are present");
wordBoggle(boggle, dictionary);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivamsharma215
def dfs(board, s, i, j, n, m, idx):
if i < 0 or i >= n or j < 0 or j >= m:
return False
if s[idx] != board[i][j]:
return False
if idx == len(s) - 1:
return True
temp = board[i][j]
board[i][j] = '*'
a = dfs(board, s, i, j+1, n, m, idx+1)
b = dfs(board, s, i, j-1, n, m, idx+1)
c = dfs(board, s, i+1, j, n, m, idx+1)
d = dfs(board, s, i-1, j, n, m, idx+1)
e = dfs(board, s, i+1, j+1, n, m, idx+1)
f = dfs(board, s, i-1, j+1, n, m, idx+1)
g = dfs(board, s, i+1, j-1, n, m, idx+1)
h = dfs(board, s, i-1, j-1, n, m, idx+1)
board[i][j] = temp
return a or b or c or e or f or g or h or d
def wordBoggle(board, dictionary):
n = len(board)
m = len(board[0])
store = set()
# Let the given dictionary be following
for word in dictionary:
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if dfs(board, word, i, j, n, m, 0):
store.add(word)
for word in store:
print(word)
boggle = [['G', 'I', 'Z'],
['U', 'E', 'K'],
['Q', 'S', 'E']]
dictionary = ["GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"]
print("Following words of dictionary are present:")
wordBoggle(boggle, dictionary)
# This code is contributed by vikramshirsath177
// C# program for Boggle game
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Boggle
{
static int M = 3;
static int N = 3;
static bool dfs(char[][] board, string s, int i, int j, int n, int m, int idx)
{
if (i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m)
{
return false;
}
if (s[idx] != board[i][j])
{
return false;
}
if (idx == s.Length - 1)
{
return true;
}
char temp = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '*';
bool a = dfs(board, s, i, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
bool b = dfs(board, s, i, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
bool c = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j, n, m, idx + 1);
bool d = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j, n, m, idx + 1);
bool e = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
bool f = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
bool g = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
bool h = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
board[i][j] = temp;
return a || b || c || e || f || g || h || d;
}
static void wordBoggle(char[][] board, string[] dictionary)
{
int n = board.Length;
int m = board[0].Length;
List<string> ans = new List<string>();
HashSet<string> store = new HashSet<string>();
for (int i = 0; i < dictionary.Length; i++)
{
string s = dictionary[i];
int l = s.Length;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++)
{
if (dfs(board, s, j, k, n, m, 0))
{
store.Add(s);
}
}
}
}
foreach (string i in store)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
return;
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void Main()
{
char[][] boggle = new char[][] {
new char[] { 'G', 'I', 'Z' },
new char[] { 'U', 'E', 'K' },
new char[] { 'Q', 'S', 'E' }
};
// Let the given dictionary be following
string[] dictionary = new string[] {"GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"};
Console.WriteLine("Following words of dictionary are present");
wordBoggle(boggle, dictionary);
}
}
//This code is contributed by shivamsharma215
// Javascript program for Boggle game
function dfs(board, s, i, j, n, m, idx) {
if (i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m) {
return false;
}
if (s[idx] != board[i][j]) {
return false;
}
if (idx == s.length - 1) {
return true;
}
temp = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = "*";
a = dfs(board, s, i, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
b = dfs(board, s, i, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
c = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j, n, m, idx + 1);
d = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j, n, m, idx + 1);
e = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
f = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j + 1, n, m, idx + 1);
g = dfs(board, s, i + 1, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
h = dfs(board, s, i - 1, j - 1, n, m, idx + 1);
board[i][j] = temp;
return a || b || c || e || f || g || h || d;
}
function wordBoggle(board, dictionary) {
n = board.length;
m = board[0].length;
let ans = new Array();
let store = new Set();
for (let i = 0; i < dictionary.length; i++) {
s = dictionary[i];
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (let k = 0; k < m; k++) {
if (dfs(board, s, j, k, n, m, 0)) {
store.add(s);
}
}
}
}
console.log(store);
return;
}
// Driver program to test above function
boggle = [
["G", "I", "Z"],
["U", "E", "K"],
["Q", "S", "E"],
];
//Let the given dictionary be following
dictionary = ["GEEKS", "FOR", "QUIZ", "GO"];
console.log("Following words of dictionary are present");
wordBoggle(boggle, dictionary);
OutputFollowing words of dictionary are present
GEEKS
QUIZ
Time Complexity: O(N*W + R*C^2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N*W + R*C)
In below set 2, we have discussed Trie based optimized solution:
Boggle | Set 2 (Using Trie)
Please Login to comment...