The syntax is a vital component of written language. Syntax defines the rules, principles, and the processes that need to be followed when structuring words, phrases, and sentences. The way you structure phrases and sentences determines the kind of content you will end up with. It is fundamental to structure your words and sentences in a manner that your readers will find it easy to read and understand. That is where syntax comes in.
Table of Contents
Syntax
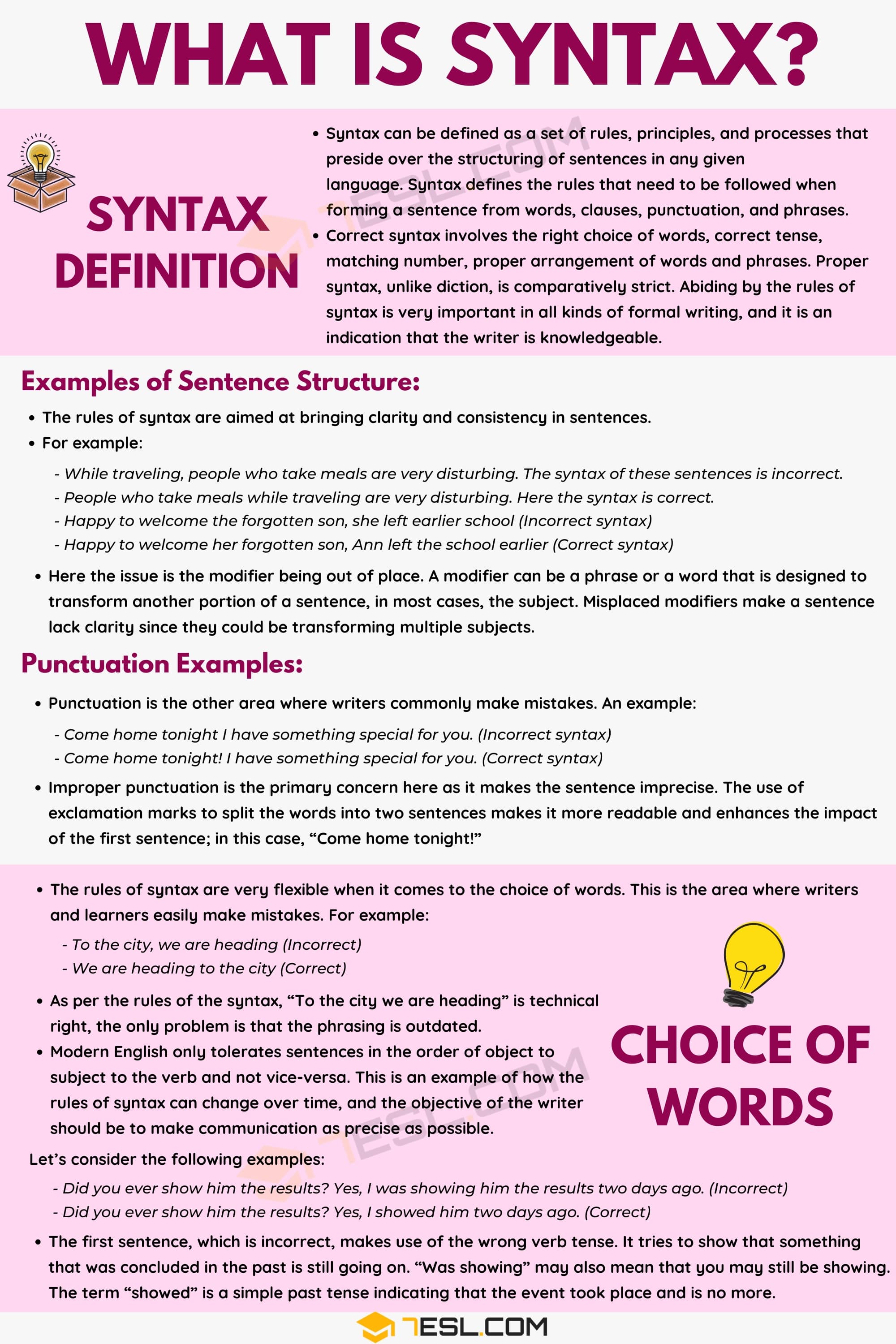
Syntax Definition
Syntax can be defined as a set of rules, principles, and processes that preside over the structuring of sentences in any given language. Syntax defines the rules that need to be followed when forming a sentence from words, clauses, punctuation, and phrases.
Correct syntax involves the right choice of words, correct tense, matching number, proper arrangement of words and phrases. Proper syntax, unlike diction, is comparatively strict. Abiding by the rules of syntax is very important in all kinds of formal writing, and it is an indication that the writer is knowledgeable.
Basic Syntax Concepts
Words
Words are the most basic unit of language, representing individual concepts or ideas. They can be classified into different categories or parts of speech, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. In syntax, it’s crucial to understand the proper placement and function of words within sentences to maintain clarity and proper grammatical structure.
Phrases
Phrases are groups of words that work together to convey a specific meaning. They can consist of various combinations of words and serve different roles within a sentence. Common types of phrases include noun phrases, verb phrases, and adjective phrases. Understanding how phrases function in a sentence helps create well-formed, meaningful sentences.
- Noun phrases: Typically consist of a noun and any accompanying modifiers. Example: The happy dog
- Verb phrases: Comprise a main verb and any helping or auxiliary verbs. Example: has been swimming
- Adjective phrases: Include an adjective and any associated modifiers. Example: very tall
Sentences
Sentences are language units that consist of one or more words and express a complete thought or idea. They begin with a capital letter and end with a punctuation mark, usually a period, question mark, or exclamation point. Proper syntax ensures that sentences follow specific rules and structures for coherence and comprehension. There are different types of sentences, usually distinguished by their structure or purpose.
- Declarative sentences: Make a statement or convey information. Example: She reads the book.
- Interrogative sentences: Pose a question. Example: Do you like ice cream?
- Imperative sentences: Give a command or request. Example: Close the door.
- Exclamatory sentences: Express strong feelings or emotions. Example: I can’t believe it!
In summary, basic syntax concepts include understanding the roles and functions of words, phrases, and sentences within language. Proper syntax is crucial for clear and effective communication, as it organizes words and phrases into coherent sentences that convey specific meanings and ideas.
Syntax Examples
Examples of Sentence Structure
The syntax is more of a structure. The rules of syntax are aimed at bringing clarity and consistency in sentences. There are all sorts of common syntactical mistakes, and they are all easy to correct once the writer finds out what they are not doing right. For example:
- While traveling, people who take meals are very disturbing. The syntax of these sentences is incorrect.
- People who take meals while traveling are very disturbing. Here the syntax is correct.
- Happy to welcome the forgotten son, she left earlier school (Incorrect syntax)
- Happy to welcome her forgotten son, Ann left the school earlier (Correct syntax)
Here the issue is the modifier being out of place. A modifier can be a phrase or a word that is designed to transform another portion of a sentence, in most cases, the subject. Misplaced modifiers make a sentence lack clarity since they could be transforming multiple subjects.
In the other incorrect example, the sentence states that “she left earlier school” (subject) was “happy to welcome her forgotten son,” which is not meaningful at all. Instead, it is “Ann” who is happy to welcome her forgotten son, as illustrated in the correct sentence.
Consider yet another example:
- When evaluating the test, more than one area needed to be corrected. (Incorrect)
- When evaluating the test, the examiner noted the areas to be corrected. (Correct)
The incorrect sentence does not have a subject. A sentence can only be meaningful if something or someone is performing the action it describes. It’s all about dependent and independent clauses.
Punctuation Examples
Punctuation is the other area where writers commonly make mistakes. An example:
- Come home tonight I have something special for you. (Incorrect syntax)
- Come home tonight! I have something special for you. (Correct syntax)
Improper punctuation is the primary concern here as it makes the sentence imprecise. The use of exclamation marks to split the words into two sentences makes it more readable and enhances the impact of the first sentence; in this case, “Come home tonight!”
- Before we embark on our mission. (Incorrect)
- We need a break before we embark on our mission. (Correct)
The problem with this sentence is different from others, as it is a sentence fragment. Sentence fragment occurs when a sentence doesn’t express a complete thought. For instance, “Before we embark on our mission” is not a complete sentence. With the addition of “We need a break,” the reader can now understand the intent of the writer.
The following is another example of a sentence with a similar problem but needs to be addressed differently.
- We can’t embark on our mission. Or get rewarded with no results. (Incorrect)
- We can’t embark on our mission or get rewarded with no results. (Correct)
The first sentence is improperly structured. “We can’t embark on our mission” can be a complete sentence on its own; the only problem is that it is followed by a phrase that depends on it to express a complete thought.
The solution to an incomplete sentence is to link up the pieces instead of adding more information.
Inappropriate use of punctuation is the other issue that messes the syntax of a sentence. For example:
- The room is disorganized unclean, and filthy. (Incorrect)
- The room is cluttered, messy, and dirty. (Correct)
The first sentence, which is incorrect, does not make use of a comma to separate the words describing the room. At least one comma is needed to separate a group of three items. The room is disorganized, unclean, and filthy.
Syntax: Choice of Words
The rules of syntax are very flexible when it comes to the choice of words. This is the area where writers and learners easily make mistakes. For example:
- To the city, we are heading (Incorrect)
- We are heading to the city (Correct)
As per the rules of the syntax, “To the city we are heading” is technical right, the only problem is that the phrasing is outdated.
Modern English only tolerates sentences in the order of object to subject to the verb and not vice-versa. This is an example of how the rules of syntax can change over time, and the objective of the writer should be to make communication as precise as possible.
Let’s consider the following examples:
- Did you ever show him the results? Yes, I was showing him the results two days ago. (Incorrect)
- Did you ever show him the results? Yes, I showed him two days ago. (Correct)
The first sentence, which is incorrect, makes use of the wrong verb tense. It tries to show that something that was concluded in the past is still going on. “Was showing” may also mean that you may still be showing. The term “showed” is a simple past tense indicating that the event took place and is no more.
Syntactical issues can also arise as a result of mild little prepositions such as “to.” An example
- Her brother-in-law requested her make a call and congratulate her younger sister. (Incorrect)
- Her brother-in-law requested him call and congratulate his younger sister. (Correct)
The syntax is fundamental in any form of writing. Every piece of writing, including a thank you note, demands syntactical selections. The most crucial aspect of persuasive writing is to understand how to use syntax correctly.
Syntax in Context
Literature
In the realm of literature, syntax plays a vital role in shaping a writer’s style and voice. The arrangement of words and phrases allows writers to convey meanings and evoke emotions in readers. Authors may utilize varying sentence structures, lengths, and patterns to create distinct literary styles. For instance, some writers choose to employ complex sentences in order to create a more intricate, sophisticated atmosphere, while others might use simpler sentences to communicate ideas clearly and directly. Syntax, as an essential component of language, greatly impacts the way literature is perceived and interpreted by readers.
Business
In the context of business, clear and concise syntax is crucial for effective communication. Well-structured sentences help to convey ideas and messages accurately while minimizing the risk of misinterpretation. In professional writing, such as emails, reports, and presentations, using proper syntax demonstrates professionalism and credibility. Bullet points, tables, and other formatting tools can be employed to aid readability and foster better comprehension. Consistent attention to syntax in business communication ensures that stakeholders, clients, and team members alike are able to understand and act upon the information provided.
Industry
Syntax is also integral in various industries, particularly those that rely on technological systems and coding. In computer programming, for example, the proper ordering of symbols and codes is necessary for computers to understand and execute the provided instructions. Much like in literature and business, the arrangement of these elements shapes the functionality and efficiency of the code. Adhering to the specific syntax rules of a programming language is essential for successful implementation and error-free running of software applications. In this way, syntax serves as a foundational pillar in the development and maintenance of various industry solutions.
Syntax Infographic
FAQs on Syntax
What is Syntax?
Syntax refers to the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language. It encompasses the rules that govern the structure of a sentence, such as the order of subjects, verbs, and objects.
What are the different types of sentences?
There are various types of sentences based on their structure:
- Simple sentences consist of a single independent clause with a subject and a verb.
- Compound sentences contain two or more independent clauses, usually connected by coordinating conjunctions like ‘and,’ ‘but,’ or ‘so.’
- Complex sentences consist of one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses, connected by subordinating conjunctions like ‘because,’ ‘although,’ or ‘since.’
- Compound-complex sentences are a combination of compound and complex sentences, containing at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
What are the key parts of a sentence?
A well-constructed sentence typically includes:
- Subject: The person, place, thing, or idea performing the action in the sentence.
- Verb: The action or state of being that the subject performs.
- Object: The person, place, thing, or concept affected by the action of the verb.
How does proper syntax contribute to effective communication?
Using proper syntax ensures that sentences are clear, logical, and easy to understand. By following the rules of syntax, speakers and writers can effectively convey their intended meaning to their audience. Proper syntax also helps avoid ambiguity and miscommunication.
How can someone improve their syntax skills?
To improve syntax skills, one can:
- Practice reading and writing regularly to become familiar with sentence structure and various ways to combine phrases and clauses.
- Study grammar rules and examples to better understand the underlying structure of a language.
- Seek feedback from teachers, tutors, or peers on written work to identify and correct syntax errors.
- Hypocritical Meaning: What Does This Term Mean? - January 27, 2024
- SWAG Meaning: What Does it Mean? - January 25, 2024
- Hypocrisy Meaning: What Does it Mean? - January 20, 2024

Need to study for my course E304 Grammar. Which is all about (SFL) Systemic Functional Linguistics ( Michael Halliday ). Ideational, Textual, and Interpersonal Metafunctions ( processes, participants, and circumstances. it is about Field, Mode, and Tenor. I did not find any kind of these on your page.
Very informative and easy to understand.
Thank you for an excellent grammar resource
So helpful thanks
Nice