Units of Sound
What is Sound?
Characteristics of Sound
Sound has several key characteristics:
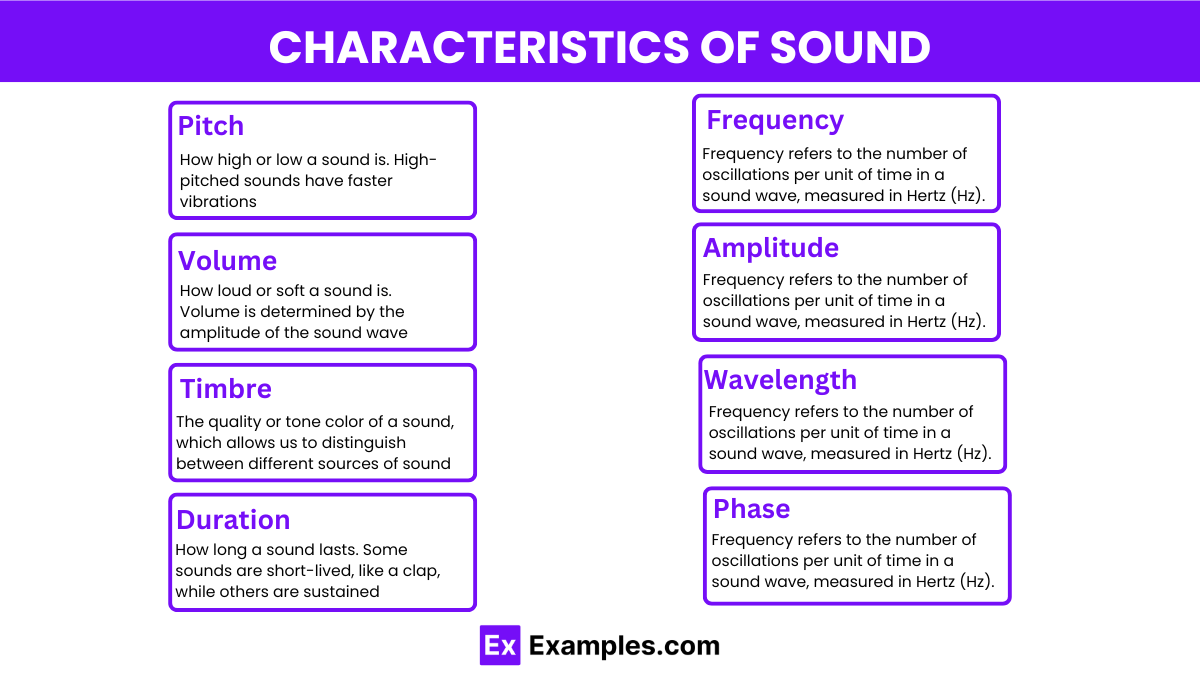
Pitch: How high or low a sound is. High-pitched sounds have faster vibrations, while low-pitched sounds have slower vibrations in physics.
Volume: How loud or soft a sound is. Volume is determined by the amplitude of the sound wave – larger amplitudes result in louder sounds.
Timbre: The quality or tone color of a sound, which allows us to distinguish between different sources of sound, such as different musical instruments or voices.
Duration: How long a sound lasts. Some sounds are short-lived, like a clap, while others are sustained, like a continuous tone from a musical instrument.
Frequency: Frequency refers to the number of oscillations per unit of time in a sound wave, measured in Hertz (Hz). It determines the pitch of the sound, with higher frequencies corresponding to higher pitches and vice versa.
Amplitude: Amplitude is the maximum displacement of particles in the medium through which sound waves travel. It corresponds to the loudness or intensity of the sound, with greater amplitudes producing louder sounds.
Wavelength: Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points in a sound wave that are in phase (e.g., two consecutive peaks or troughs). It is inversely related to frequency, with higher frequencies having shorter wavelengths and vice versa.
Phase: Phase refers to the relative position of a point on a sound wave compared to a reference point at a given instant in time. It is often used to describe the relationship between multiple sound waves or to analyze the temporal characteristics of a single wave.
These characteristics help us perceive and understand the world around us through the sense of hearing.
What are the Units of Sound?
Units of sound are typically measured in decibels (dB), which quantify the intensity or loudness of sound. Additionally, frequency, the pitch of sound, is measured in hertz (Hz), indicating the number of vibrations per second. These units help quantify and characterize the various aspects of sound, aiding in its analysis and understanding.
SI Unit of Sound
It measures the intensity or loudness of sound. The decibel scale is logarithmic, with each increase of 10 dB representing a tenfold increase in sound intensity.
CGS Unit of Sound
In the CGS (Centimeter-Gram-Second) system, the unit of sound intensity is typically expressed in ergs per second per square centimeter (erg/s/cm²). This unit measures the energy transferred through sound waves per unit area over time and is commonly used in scientific and engineering contexts.
How is Sound Measured?
Sound is measured using instruments called sound level meters or decibel meters. These devices quantify the intensity of sound waves in units called decibels (dB). Sound level meters have a microphone that detects sound waves, and then they convert the detected pressure variations into electrical signals. These signals are processed to determine the sound pressure level (SPL) in decibels, which represents the loudness of the sound. Sound can also be analyzed in terms of frequency using spectrum analyzers, which measure the distribution of sound energy across different frequencies.
List of Units of Sound
| Unit | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Decibel (dB) | dB | Measures sound intensity or loudness. |
| Hertz (Hz) | Hz | Measures sound frequency or pitch. |
| Sound Pressure Level (SPL) | SPL | Measures the pressure level of sound waves relative to a reference level. |
| Phon | Measures subjective loudness perception of sound by the human ear. | |
| Weighted Decibel (dBA, dBC) | Decibels adjusted to account for the sensitivity of the human ear at different frequencies. | |
| Sound Exposure Level (SEL) | SEL | Measures the total sound energy exposure over a period. |
| Sound Power Level (SWL) | SWL | Measures the total acoustic power emitted by a source. |
| Octave | Measures the frequency band that spans a doubling or halving of a given frequency. | |
| Bel (B) | B | A logarithmic unit used in the past, now mostly replaced by the decibel (dB). |
Decibel (dB)
The decibel is the standard unit for measuring sound intensity or loudness. It represents the logarithmic ratio of a sound’s intensity to a reference level.
Hertz (Hz)
Hertz is the unit of frequency, measuring the number of vibrations per second in a sound wave. It determines the pitch of the sound, with higher frequencies corresponding to higher pitches.
Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
SPL measures the pressure level of sound waves relative to a reference level. It provides an objective measure of the physical intensity of sound.
Phon
The phon is used to measure the subjective loudness perception of sound by the human ear. It takes into account factors such as frequency and duration to assess perceived loudness.
Weighted Decibel (dBA, dBC)
Weighted decibels are decibels adjusted to account for the sensitivity of the human ear at different frequencies. This weighting is often used in noise measurement to reflect human perception accurately.
Sound Exposure Level (SEL)
SEL measures the total sound energy exposure over a specified period, typically used to assess noise exposure in occupational settings.
Sound Power Level (SWL)
SWL measures the total acoustic power emitted by a sound source, providing an indication of its overall loudness output.
Octave
An octave represents a doubling or halving of a given frequency band, commonly used in music and sound engineering to describe frequency ranges.
Conversion of Units of Sound
| From Unit | To Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Decibel (dB) | Sound Pressure Level (SPL) | Often used interchangeably, representing the same quantity—the intensity or loudness of sound. |
| Hertz (Hz) | Octave | Each octave corresponds to a doubling or halving of the frequency in Hertz (Hz). |
| Phon | Decibel (dB) | Conversion depends on specific sound frequency and duration as perceived by the human ear. |
| Weighted Decibel (dBA, dBC) | Decibel (dB) | Adjust for the sensitivity of the human ear at different frequencies, providing a more accurate representation of perceived loudness. |
| Sound Exposure Level (SEL) | Sound Pressure Level (SPL) | Measures total sound energy exposure over time, while SPL quantifies instantaneous pressure level of sound waves relative to a reference level. |
FAQ’s
What are the units of sound frequency?
Units of sound frequency are typically measured in Hertz (Hz), representing the number of oscillations per second in a sound wave. Hertz is commonly used to quantify pitch and frequency in sound analysis.
What is the unit used to measure speed of sound?
The unit used to measure the speed of sound is meters per second (m/s). It represents the rate at which sound waves travel through a medium, indicating how quickly sound propagates through air, water, or other substances.


