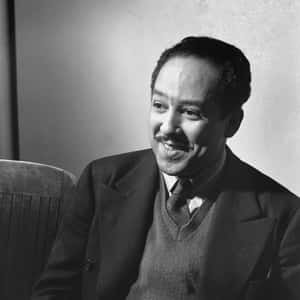Famous Essayists from the United States
- Dec. at 86 (1925-2012)Eugene Luther Gore Vidal (; born Eugene Louis Vidal, October 3, 1925 – July 31, 2012) was an American writer and public intellectual known for his patrician manner, epigrammatic wit, and polished style of writing.Vidal was born into a political family; his maternal grandfather, Thomas Pryor Gore, served as United States senator from Oklahoma (1907–1921 and 1931–1937). Vidal himself was a Democratic Party politician who twice sought elected office; first to the United States House of Representatives (New York, 1960), then to the U.S. Senate (California, 1982).As a political commentator and essayist, Vidal's principal subject was the history of the United States and its society, especially how the militaristic foreign policy reduced the country to a decadent empire. His political and cultural essays were published in The Nation, the New Statesman, the New York Review of Books, and Esquire magazines. As a public intellectual, Gore Vidal's topical debates on sex, politics, and religion with other intellectuals and writers occasionally turned into quarrels with the likes of William F. Buckley Jr. and Norman Mailer. Vidal thought all men and women are potentially bisexual.As a novelist, Vidal explored the nature of corruption in public and private life. His polished and erudite style of narration readily evoked the time and place of his stories, and perceptively delineated the psychology of his characters. His third novel, The City and the Pillar (1948), offended the literary, political, and moral sensibilities of conservative book reviewers, centering the plot around a dispassionately presented male homosexual relationship. In the historical novel genre, Vidal re-created the imperial world of Julian the Apostate (r. AD 361–63) in Julian (1964). Julian was the Roman emperor who used general religious toleration to re-establish pagan polytheism to counter the political subversion of Christian monotheism. In social satire, Myra Breckinridge (1968) explores the mutability of gender role and sexual orientation as being social constructs established by social mores. In Burr (1973) and Lincoln (1984), the protagonist is presented as "A Man of the People" and as "A Man" in a narrative exploration of how the public and private facets of personality affect the national politics of the United States.
- Dec. at 62 (1949-2011)Christopher Hitchens, a British-born journalist, essayist, and critic, was widely recognized for his sharp wit and controversial commentary. Born in 1949, he spent the early part of his life in Portsmouth, England, where he developed a passion for politics and literature. After graduating from Balliol College, Oxford University, with a degree in Philosophy, Politics, and Economics, Hitchens began a career in publishing that spanned over four decades. Hitchens's influence reached across the Atlantic when he relocated to the United States in 1981. His acerbic pen found a large audience through his work as a contributing editor to Vanity Fair, where he wrote on a wide array of topics, ranging from politics to literature, and everything in between. A prolific author, Hitchens penned more than twenty books throughout his career, including God is Not Great, a bold critique of religion, and the memoir Hitch-22. His ruthless honesty and intellectual rigor made him a formidable figure in public discourse. Despite being a controversial figure, Hitchens's impact on journalistic integrity and intellectual engagement is undeniable. A self-proclaimed contrarian, he never shied away from expressing unpopular opinions, often challenging the status quo and pushing readers to question their beliefs. Christopher Hitchens passed away in 2011, leaving behind a legacy of independent thought and fearless criticism that continues to inspire journalists and thinkers worldwide.More Christopher Hitchens
- #517 of 559 onPeople We Wish Were Still Alive
- #615 of 752 onThe Greatest Minds of All Time
- #15 of 78 onHistory's Greatest Essayists
- Dec. at 78 (1803-1882)Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803 – April 27, 1882) was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champion of individualism and a prescient critic of the countervailing pressures of society, and he disseminated his thoughts through dozens of published essays and more than 1,500 public lectures across the United States. Emerson gradually moved away from the religious and social beliefs of his contemporaries, formulating and expressing the philosophy of transcendentalism in his 1836 essay "Nature". Following this work, he gave a speech entitled "The American Scholar" in 1837, which Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. considered to be America's "intellectual Declaration of Independence."Emerson wrote most of his important essays as lectures first and then revised them for print. His first two collections of essays, Essays: First Series (1841) and Essays: Second Series (1844), represent the core of his thinking. They include the well-known essays "Self-Reliance", "The Over-Soul", "Circles", "The Poet", and "Experience." Together with "Nature", these essays made the decade from the mid-1830s to the mid-1840s Emerson's most fertile period. Emerson wrote on a number of subjects, never espousing fixed philosophical tenets, but developing certain ideas such as individuality, freedom, the ability for mankind to realize almost anything, and the relationship between the soul and the surrounding world. Emerson's "nature" was more philosophical than naturalistic: "Philosophically considered, the universe is composed of Nature and the Soul." Emerson is one of several figures who "took a more pantheist or pandeist approach by rejecting views of God as separate from the world."He remains among the linchpins of the American romantic movement, and his work has greatly influenced the thinkers, writers and poets that followed him. "In all my lectures," he wrote, "I have taught one doctrine, namely, the infinitude of the private man." Emerson is also well known as a mentor and friend of Henry David Thoreau, a fellow transcendentalist.More Ralph Waldo Emerson
- Dig Deeper...The 365+ Most Famous Geminis
- #111 of 508 onThe 500+ Best Writers of All Time
- #17 of 141 onThe Greatest American Writers Of All Time
- Dec. at 72 (1920-1992)Isaac Asimov (; c. January 2, 1920 – April 6, 1992) was an American writer and professor of biochemistry at Boston University. He was known for his works of science fiction and popular science. Asimov was a prolific writer who wrote or edited more than 500 books and an estimated 90,000 letters and postcards. His books have been published in 9 of the 10 major categories of the Dewey Decimal Classification.Asimov wrote hard science fiction. Along with Robert A. Heinlein and Arthur C. Clarke, Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime. Asimov's most famous work is the "Foundation" series, the first three books of which won the one-time Hugo Award for "Best All-Time Series" in 1966. His other major series are the "Galactic Empire" series and the Robot series. The Galactic Empire novels are set in earlier history of the same fictional universe as the Foundation series. Later, with Foundation and Earth (1986), he linked this distant future to the Robot stories, creating a unified "future history" for his stories much like those pioneered by Robert A. Heinlein and previously produced by Cordwainer Smith and Poul Anderson. He also wrote hundreds of short stories, including the social science fiction novelette "Nightfall", which in 1964 was voted the best short science fiction story of all time by the Science Fiction Writers of America. Asimov wrote the Lucky Starr series of juvenile science-fiction novels using the pen name Paul French.Asimov also wrote mysteries and fantasy, as well as much nonfiction. Most of his popular science books explain concepts in a historical way, going as far back as possible to a time when the science in question was at its simplest stage. Examples include Guide to Science, the three-volume set Understanding Physics, and Asimov's Chronology of Science and Discovery. He wrote on numerous other scientific and non-scientific topics, such as chemistry, astronomy, mathematics, history, biblical exegesis, and literary criticism. He was president of the American Humanist Association. The asteroid 5020 Asimov, a crater on the planet Mars, a Brooklyn elementary school, and a literary award are named in his honor.More Isaac Asimov
- #56 of 508 onThe 500+ Best Writers of All Time
- #3 of 165 onThe Best Science-Fiction Authors
- #21 of 162 onThe Best Fantasy Authors
- Dec. at 65 (1902-1967)James Mercer Langston Hughes (February 1, 1902 – May 22, 1967) was an American poet, social activist, novelist, playwright, and columnist from Joplin, Missouri. He moved to New York City as a young man, where he made his career. One of the earliest innovators of the then-new literary art form called jazz poetry, Hughes is best known as a leader of the Harlem Renaissance. He famously wrote about the period that "the negro was in vogue", which was later paraphrased as "when Harlem was in vogue".Growing up in a series of Midwestern towns, Hughes became a prolific writer at an early age. He graduated from high school in Cleveland, Ohio and soon began studies at Columbia University in New York City. Although he dropped out, he gained notice from New York publishers, first in The Crisis magazine, and then from book publishers and became known in the creative community in Harlem. He eventually graduated from Lincoln University. In addition to poetry, Hughes wrote plays, and short stories. He also published several non-fiction works. From 1942 to 1962, as the civil rights movement was gaining traction, he wrote an in-depth weekly column in a leading black newspaper, The Chicago Defender.More Langston Hughes
- #41 of 141 onThe Greatest American Writers Of All Time
- #100 of 342 onThe Greatest Poets of All Time
- #23 of 123 onThe Best Gay Authors
- Dec. at 63 (1924-1987)James Arthur Baldwin (August 2, 1924 – December 1, 1987) was an American novelist, playwright, and activist. His essays, as collected in Notes of a Native Son (1955), explore intricacies of racial, sexual, and class distinctions in Western societies, most notably in mid-20th-century North America. Some of Baldwin's essays are book-length, including The Fire Next Time (1963), No Name in the Street (1972), and The Devil Finds Work (1976). An unfinished manuscript, Remember This House, was expanded and adapted for cinema as the Academy Award–nominated documentary film I Am Not Your Negro. One of his novels, If Beale Street Could Talk, was adapted into an Academy Award-winning dramatic film in 2018. Baldwin's novels and plays fictionalize fundamental personal questions and dilemmas amid complex social and psychological pressures thwarting the equitable integration of not only African Americans, but also gay and bisexual men, while depicting some internalized obstacles to such individuals' quests for acceptance. Such dynamics are prominent in Baldwin's second novel, Giovanni's Room, written in 1956, well before the gay liberation movement.More James Baldwin
- #196 of 508 onThe 500+ Best Writers of All Time
- #21 of 141 onThe Greatest American Writers Of All Time
- #9 of 123 onThe Best Gay Authors
- Age: 76Lee Earle "James" Ellroy (born March 4, 1948) is an American crime fiction writer and essayist. Ellroy has become known for a telegrammatic prose style in his most recent work, wherein he frequently omits connecting words and uses only short, staccato sentences, and in particular for the novels The Black Dahlia (1987), The Big Nowhere (1988), L.A. Confidential (1990), White Jazz (1992), American Tabloid (1995), The Cold Six Thousand (2001), and Blood's a Rover (2009).More James Ellroy
- #66 of 108 onThe Greatest Living Writers & Most Famous Authors Today
- #15 of 68 onThe Best Crime Authors
- #210 of 429 onHere's a List of Every Known Republican Celebrity
- Age: 88Larry Kramer (born June 25, 1935) is an American playwright, author, film producer, public health advocate, and LGBT rights activist. He began his career rewriting scripts while working for Columbia Pictures, which led him to London where he worked with United Artists. There he wrote the screenplay for the 1969 film Women in Love (1969) and earned an Academy Award nomination for his work. Kramer introduced a controversial and confrontational style in his novel Faggots (1978), which earned mixed reviews and emphatic denunciations from elements within the gay community for Kramer's one-sided portrayal of shallow, promiscuous gay relationships in the 1970s. Kramer witnessed the spread of the disease later known as Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) among his friends in 1980. He co-founded the Gay Men's Health Crisis (GMHC), which has become the world's largest private organization assisting people living with AIDS. Kramer grew frustrated with bureaucratic paralysis and the apathy of gay men to the AIDS crisis, and wished to engage in further action than the social services GMHC provided. He expressed his frustration by writing a play titled The Normal Heart, produced at The Public Theater in New York City in 1985. His political activism continued with the founding of the AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power (ACT UP) in 1987, an influential direct action protest organization with the aim of gaining more public action to fight the AIDS crisis. ACT UP has been widely credited with changing public health policy and the perception of people living with AIDS (PWAs), and with raising awareness of HIV and AIDS-related diseases. Kramer has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize for his play The Destiny of Me (1992), and he is a two-time recipient of the Obie Award.
- Dec. at 84 (1923-2007)Norman Kingsley Mailer (January 31, 1923 – November 10, 2007) was an American novelist, journalist, essayist, playwright, film-maker, actor, and liberal political activist. His novel The Naked and the Dead was published in 1948 and brought him early and wide renown. His 1968 nonfiction novel Armies of the Night won the Pulitzer Prize for non-fiction as well as the National Book Award. His best-known work is widely considered to be The Executioner's Song, the 1979 winner of the Pulitzer Prize for fiction. In over six decades of work, Mailer had eleven best-selling books, at least one in each of the seven decades after World War II—more than any other post-war American writer.Along with Truman Capote, Joan Didion, Hunter S. Thompson, and Tom Wolfe, Mailer is considered an innovator of creative nonfiction, a genre sometimes called New Journalism, which uses the style and devices of literary fiction in fact-based journalism. Mailer was also known for his essays, the most famous and reprinted of which is "The White Negro". He was a cultural commentator and critic, expressing his views through his novels, journalism, essays, and frequent media appearances. In 1955, Mailer and three others founded The Village Voice, an arts- and politics-oriented weekly newspaper distributed in Greenwich Village. In 1960, he was convicted of assault and served a three-year probation after he stabbed his wife, Adele Morales, with a penknife, nearly killing her. In 1969, he ran an unsuccessful campaign to become the mayor of New York. While principally known as a novelist and journalist, Mailer was not afraid to bend genres and venture outside his comfort zone; he lived a life that seemed to embody an idea that echoes throughout his work: "There was that law of life, so cruel and so just, that one must grow or else pay more for remaining the same."More Norman Mailer
- #134 of 296 onThe Best Novelists of All Time
- #109 of 142 onThe Greatest American Writers of All Time
- #6 of 18 onFamous Writers And Artists Who Were Terrible Humans
- Dec. at 47 (1964-2012)David Benjamin Rakoff (November 27, 1964 – August 9, 2012) was a Canadian-born American writer based in New York City, who wrote humorous and sometimes autobiographical non-fiction essays. Rakoff was an essayist, journalist, and actor, and a regular contributor to WBEZ's This American Life. Rakoff described himself as a "New York writer" who also happened to be a "Canadian writer", a "mega Jewish writer", a "gay writer", and an "East Asian Studies major who has forgotten most of his Japanese" writer.More David Rakoff
- Dig Deeper...Famous People Who Died in New York City
- And Deeper...Famous People Who Died of Cancer
- #48 of 66 onCelebrity Deaths: 2012 Famous Deaths
- Dec. at 40 (1876-1916)John Griffith London (born John Griffith Chaney; January 12, 1876 – November 22, 1916) was an American novelist, journalist, and social activist. A pioneer in the world of commercial magazine fiction, he was one of the first writers to become a worldwide celebrity and earn a large fortune from writing. He was also an innovator in the genre that would later become known as science fiction.His most famous works include The Call of the Wild and White Fang, both set in the Klondike Gold Rush, as well as the short stories "To Build a Fire", "An Odyssey of the North", and "Love of Life". He also wrote about the South Pacific in stories such as "The Pearls of Parlay" and "The Heathen". London was part of the radical literary group "The Crowd" in San Francisco and a passionate advocate of unionization, socialism, and the rights of workers. He wrote several powerful works dealing with these topics, such as his dystopian novel The Iron Heel, his non-fiction exposé The People of the Abyss, and The War of the Classes.More Jack London
- #97 of 508 onThe 500+ Best Writers of All Time
- #49 of 296 onThe Best Novelists of All Time
- #19 of 66 onThe Best Short Story Writers of All Time
- Dec. at 66 (1913-1980)Robert Hayden (August 4, 1913 – February 25, 1980) was an American poet, essayist, and educator. He served as Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress from 1976 to 1978, a role today known as US Poet Laureate. He was the first African-American writer to hold the office.More Robert Hayden
- #39 of 63 onThe Best American Poets
- #261 of 342 onThe Greatest Poets of All Time
- #10 of 32 onThe Best African American Poets of All Time
- Dec. at 89 (1915-2005)Arthur Asher Miller (October 17, 1915 – February 10, 2005) was an American playwright, essayist, and a controversial figure in the twentieth-century American theater. Among his most popular plays are All My Sons (1947), Death of a Salesman (1949), The Crucible (1953) and A View from the Bridge (1955, revised 1956). He wrote several screenplays and was most noted for his work on The Misfits (1961). The drama Death of a Salesman has been numbered on the short list of finest American plays in the 20th century. Miller was often in the public eye, particularly during the late 1940s, 1950s and early 1960s. During this time, he was awarded a Pulitzer Prize for Drama, testified before the House Un-American Activities Committee and was married to Marilyn Monroe. In 1980, Miller received the St. Louis Literary Award from the Saint Louis University Library Associates. He received the Prince of Asturias Award, the Praemium Imperiale prize in 2002 and the Jerusalem Prize in 2003, as well as the Dorothy and Lillian Gish Prize in 1999.
- Dec. at 32 (1902-1934)Wallace Henry Thurman (August 16, 1902 - December 22, 1934) was an American novelist active during the Harlem Renaissance. He also wrote essays, worked as an editor, and was a publisher of short-lived newspapers and literary journals. He is best known for his novel The Blacker the Berry: A Novel of Negro Life (1929), which explores discrimination within the black community based on skin color, with lighter skin being more highly valued.
- Dec. at 39 (1925-1964)Mary Flannery O'Connor (March 25, 1925 – August 3, 1964) was an American novelist, short story writer and essayist. She wrote two novels and thirty-two short stories, as well as a number of reviews and commentaries. She was a Southern writer who often wrote in a sardonic Southern Gothic style and relied heavily on regional settings and supposedly grotesque characters, often in violent situations. The unsentimental acceptance or rejection of the limitations or imperfection or difference of these characters (whether attributed to disability, race, crime, religion or sanity) typically underpins the drama.Her writing reflected her Roman Catholic religion and frequently examined questions of morality and ethics. Her posthumously compiled Complete Stories won the 1972 U.S. National Book Award for Fiction and has been the subject of enduring praise.
- Age: 105Lawrence Monsanto Ferlinghetti (March 24, 1919 – February 22, 2021) was an American poet, painter, socialist activist, and the co-founder of City Lights Booksellers & Publishers. He was the author of poetry, translations, fiction, theatre, art criticism, and film narration. Ferlinghetti was best known for his first collection of poems, A Coney Island of the Mind (1958), which has been translated into nine languages, with sales of more than one million copies. Ferlinghetti turned 100 in March 2019, leading the city of San Francisco to proclaim his birthday, March 24, "Lawrence Ferlinghetti Day".
- #203 of 342 onThe Greatest Poets of All Time
- #33 of 34 onThe Most Unbearably Pretentious Authors In Literary History
- #23 of 71 onWho Is The Most Famous Lawrence Or Laurence In The World?
- Age: 77Bruce Benderson (born August 6, 1946) is an American author, born to Jewish parents of Russian descent, who lives in New York. He attended William Nottingham High School (1964) in Syracuse, New York and then Binghamton University (1969). He is today a novelist, essayist, journalist and translator, widely published in France, less so in the United States. In 2004, Benderson's lengthy erotic memoir Autobiographie érotique, about a nine-month sojourn in Romania, won the prestigious French literary prize, the Prix de Flore. The book was published in the United States (Tarcher/Penguin) and the United Kingdom (Snow Books) in 2006 under the title The Romanian: Story of an Obsession. Benderson's book-length essay, Toward the New Degeneracy (1997), looks at New York’s Times Square, where rich and poor once mixed in a lively atmosphere of drugs, sex, and commerce. Benderson argues that this kind of mingling of classes has been the source of many modern avant-garde movements, and he laments the disappearance of that particular milieu. His novel User (1994) is a lyrical descent into the world of junkies and male hustlers. He is also the author of James Bidgood (Taschen, 1999), about the maker of the cult film Pink Narcissus. A book-length essay by Benderson, Sexe et Solitude, about the extinction of urban space and the rise of the Internet, was published in French in 1999. A collection of his essays, published under the title Attitudes, appeared in French in 2006. These essays, along with 'Sexe et Solitude' and 'Toward the New Degeneracy,' were printed in America in a nonfiction anthology of Benderson's writings entitled Sex and Isolation (University of Wisconsin Press, 2007), which was cited as one of the 10 best university press books of the year by the magazine Foreword. The year 2007 also saw the publication in French (Editions Payot & Rivages) of a new novel by Benderson called "Pacific Agony," a caustic satire of life in America's Pacific Northwest, as well as Benderson's personal illustrated encyclopedia of the 60s and 70s, Concentré de contreculture (Editions Scali), published in French only. The novel Pacific Agony was published in English by Semiotext(e)/MIT Press in fall 2009. In 2014, Semiotext(e))/MIT Press also published Benderson's controversial 60-page essay, Against Marriage, as part of a collection exhibited at the 2014 Whitney Museum Biennial. A French edition of the book has been planned. Benderson's shorter literary efforts have been published in Between C & D, 3:AM Magazine, American Letters and Commentary, Men on Men and Flesh and the Word.As a journalist, he has written on squatters for the New York Times Magazine, boxing for the Village Voice, unusual shelters for nest, the art of translation for The Wall Street Journal, and film, books, and culture for various other publications, including "Paris Vogue," "Vogue Hommes," French "GQ," "Libération," Out, The Stranger, New York Press, BlackBook magazine, and Paper. He has translated numerous books of French origin, including Virginie Despentes' novel Baise Moi (which was later adapted into a controversial film); the writers Robbe-Grillet, Pierre Guyotat, Sollers, Benoît Duteurtre, Grégoire Bouillier, Philippe Djian, Martin Page and Nelly Arcan; and, though it is quite far away from his usual subject matter, the autobiography of Céline Dion. In 2007, his translation of Tony Duvert's Le bon sexe illustré (Good Sex Illustrated) was published by Semiotext(e)/MIT Press. A second book by Duvert he has translated, entitled Diary of An Innocent, was released by the same publisher in 2009. His translation of David Foenkinos's novel, Delicacy, was released in December 2011 by Harper Perennial. In 2014, Benderson began working on the translation of a 1,000-page biography of the filmmaker Jean Renoir by Pascal Mérigeau. Benderson is the literary executor of the deceased novelist, Ursule Molinaro. He is mentioned in Frédéric Beigbeder's most recent book, Windows on the World. In 2006, he became a publishing associate at Virgin Books USA and later worked developing projects and editing proposals for the literary agent David Vigliano. He has taught at the maverick ranch college, Deep Springs, on three separate occasions. From 2008 to 2013, he wrote a monthly column, in French, for the magazine, Têtu. For his French publisher he completed a book about the future interfacing of biology and technology and the notion of The Singularity, as developed by Ray Kurzweil. The book is called Transhumain and was published by Editions Payot & Rivages in late October 2010.
- Dec. at 81 (1913-1994)Ralph Waldo Ellison (March 1, 1914 – April 16, 1994) was an American novelist, literary critic, and scholar best known for his novel Invisible Man, which won the National Book Award in 1953. He also wrote Shadow and Act (1964), a collection of political, social and critical essays, and Going to the Territory (1986). For The New York Times, the best of these essays in addition to the novel put him "among the gods of America's literary Parnassus." A posthumous novel, Juneteenth, was published after being assembled from voluminous notes he left upon his death.More Ralph Ellison
- #49 of 141 onThe Greatest American Writers Of All Time
- #10 of 72 onThe Hottest Dead Writers
- #31 of 78 onHistory's Greatest Essayists
- Age: 79Richard Rodriguez (born July 31, 1944) is an American writer who became famous as the author of Hunger of Memory: The Education of Richard Rodriguez (1982), a narrative about his intellectual development.
- Age: 68Robert Rodi (born 1956 in Chicago, Illinois) is an American novelist, playwright, comic book writer, essayist, and performance artist.
- Age: 76John Perry Barlow (October 3, 1947 – February 7, 2018) was an American poet and essayist, a cattle rancher, and a cyberlibertarian political activist who had been associated with both the Democratic and Republican parties. He was also a lyricist for the Grateful Dead and a founding member of the Electronic Frontier Foundation and the Freedom of the Press Foundation. He was Fellow Emeritus at Harvard University's Berkman Klein Center for Internet & Society, where he had maintained an affiliation since 1998.
Jonathan Franzen
Age: 64Jonathan Earl Franzen (born August 17, 1959) is an American novelist and essayist. His 2001 novel The Corrections, a sprawling, satirical family drama, drew widespread critical acclaim, earned Franzen a National Book Award, was a Pulitzer Prize for Fiction finalist, earned a James Tait Black Memorial Prize and was shortlisted for the International Dublin Literary Award. His novel Freedom (2010) garnered similar praise and led to an appearance on the cover of Time magazine alongside the headline "Great American Novelist".Franzen has contributed to The New Yorker magazine since 1994. His 1996 Harper's essay Perchance to Dream bemoaned the state of contemporary literature. Oprah Winfrey's book club selection in 2001 of The Corrections led to a much publicized feud with the talk show host. In recent years, Franzen has become recognized for his opinions on everything from social networking services such as Twitter ("What happens to the people who want to communicate in depth, individual to individual, in the quiet and permanence of the printed word?"; "the actual substance of our daily lives is total electronic distraction") to the impermanence of e-books ("All the real things, the authentic things, the honest things, are dying off.") and the self-destruction of America.More Jonathan Franzen- #47 of 108 onThe Greatest Living Writers & Most Famous Authors Today
- #15 of 19 onThe Most Notorious Public Breakdowns Ever Caught on Social Media
- #29 of 31 onThe Most Powerful Time Covers
- Age: 55Darren A. Drozdov (born April 7, 1969) is an American essayist, former football player and retired professional wrestler who competed in the World Wrestling Federation (WWF) from 1998-99 under the ring names Puke and Droz. Drozdov is quadriplegic due to a neck injury sustained from a botched wrestling maneuver, but has regained most of the use of his upper body and arms. Drozdov was born in the Mays Landing section of Hamilton Township, Atlantic County, New Jersey.
- Dec. at 71 (1933-2004)Susan Sontag (; January 16, 1933 – December 28, 2004) was an American writer, filmmaker, philosopher, teacher, and political activist. She mostly wrote essays, but also published novels; she published her first major work, the essay "Notes on 'Camp'", in 1964. Her best-known works include On Photography, Against Interpretation, Styles of Radical Will, The Way We Live Now, Illness as Metaphor, Regarding the Pain of Others, The Volcano Lover, and In America. Sontag was active in writing and speaking about, or travelling to, areas of conflict, including during the Vietnam War and the Siege of Sarajevo. She wrote extensively about photography, culture and media, AIDS and illness, human rights, and communism and leftist ideology. Although her essays and speeches sometimes drew controversy, she has been described as "one of the most influential critics of her generation."More Susan Sontag
- Dig Deeper...Famous People Buried in Montparnasse Cemetery
- #70 of 123 onThe Best Gay Authors
- #21 of 78 onHistory's Greatest Essayists
- Dec. at 89 (1892-1982)Archibald MacLeish (May 7, 1892 – April 20, 1982) was an American poet and writer who was associated with the modernist school of poetry. MacLeish studied English at Yale University and law at Harvard University. He enlisted in and saw action during the First World War and lived in Paris in the 1920s. On returning to the US, he contributed to Henry Luce's magazine Fortune from 1929 to 1938. For five years MacLeish was Librarian of Congress, a post he accepted at the urging of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. From 1949 to 1962, MacLeish was Boylston Professor of Rhetoric and Oratory at Harvard University. MacLeish was awarded three Pulitzer Prizes for his work.
- Age: 69Barbara Kingsolver (born April 8, 1955) is an American novelist, essayist and poet. She was raised in rural Kentucky and lived briefly in the Congo in her early childhood. Kingsolver earned degrees in biology at DePauw University and the University of Arizona and worked as a freelance writer before she began writing novels. Her widely known works include The Poisonwood Bible, the tale of a missionary family in the Congo, and Animal, Vegetable, Miracle, a non-fiction account of her family's attempts to eat locally. Her work often focuses on topics such as social justice, biodiversity and the interaction between humans and their communities and environments. Each of her books published since 1993 has been on the New York Times Best Seller list. Kingsolver has received numerous awards, including the Dayton Literary Peace Prize's Richard C. Holbrooke Distinguished Achievement Award 2011, UK's Orange Prize for Fiction 2010, for The Lacuna, and the National Humanities Medal. She has been nominated for the PEN/Faulkner Award and the Pulitzer Prize. In 2000, Kingsolver established the Bellwether Prize to support "literature of social change".
- Dec. at 82 (1929-2012)Adrienne Cecile Rich (; May 16, 1929 – March 27, 2012) was an American poet, essayist and feminist. She was called "one of the most widely read and influential poets of the second half of the 20th century", and was credited with bringing "the oppression of women and lesbians to the forefront of poetic discourse." Rich criticized rigid forms of feminist identities, and valorized what she coined the "lesbian continuum"; which is a female continuum of solidarity and creativity which has impacted and even filled women's lives.Her first collection of poetry, A Change of World, was selected by renowned poet W. H. Auden for the Yale Series of Younger Poets Award. Auden went on to write the introduction to the published volume. She famously declined the National Medal of Arts, protesting the vote by House Speaker Newt Gingrich to end funding for the National Endowment for the Arts.
- Dec. at 56 (1954-2011)Victor L. Martinez (February 21, 1954 – February 18, 2011) was a Mexican American poet and author. He won the 1996 U.S. National Book Award for Young People's Literature for his first novel, Parrot in the Oven: Mi Vida.
- Dec. at 49 (1933-1982)Not to be confused with John Gardner (British writer)John Champlin Gardner Jr. (July 21, 1933 – September 14, 1982) was an American novelist, essayist, literary critic and university professor. He is best known for his 1971 novel Grendel, a retelling of the Beowulf myth from the monster's point of view.
- Dec. at 84 (1889-1973)Conrad Potter Aiken (August 5, 1889 – August 17, 1973) was an American writer, whose work includes poetry, short stories, novels, a play, and an autobiography.