Animals
Understanding Mammals: A Comprehensive Guide On The Diversity, List & Characteristics Of Mammals

Are you aware that there are more than 6,400 recognized species of mammals on Earth? From the small bumblebee bat, weighing only 2 grams, to the enormous blue whale, which can reach up to 98 feet in length and weigh over 200 tons, mammals come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes.
Whether you’re fascinated by their unique adaptations, curious about their diverse habitats, or eager to explore the intricacies of mammal classification, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a wealth of knowledge about these incredible creatures. Join us as we embark on a journey to understand the diversity, list, and characteristics of mammals.
From the smallest rodent scurrying through the forest to the majestic predators ruling the savannah, mammals play vital roles in ecosystems around the world. Let’s dive in and discover the wonders of the mammalian world!
Key Takeaways:
- Mammals encompass a vast range of species, from the smallest bats to the largest whales.
- Their diverse adaptations and characteristics make them unique among animals.
- Understanding mammal classification and diversity is essential for comprehending their role in ecosystems.
- Mammals exhibit a wide variety of behaviors, habitats, and anatomical features.
- Conservation efforts are crucial for protecting the incredible diversity of mammalian species.
What Defines a Mammal?
To truly understand what defines a mammal, it is important to explore their unique features, evolutionary history, and diverse classification. From the distinctive characteristic of mammary glands to the fascinating variety of mammal species, these remarkable creatures continue to captivate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Understanding the Features of Mammals
One key feature that sets mammals apart is their ability to nurse their young with milk produced by their mammary glands. These specialized glands are a defining characteristic of mammals and have played a crucial role in their evolution and survival. Additionally, mammals have a unique skeletal structure, warm-blooded metabolism, and a range of adaptations that allow them to thrive in various habitats.
The Evolutionary History of Mammals
Mammals have a rich evolutionary history that spans millions of years. They are believed to have descended from reptilian ancestors and have undergone significant adaptations over time. Through the process of evolution, mammals have developed diverse anatomical, physiological, and behavioral traits that have enabled them to occupy a wide range of ecological niches.
Importance of Mammary Glands in Mammals
The presence of mammary glands in mammals is a defining characteristic of the group. These glands produce milk, a nutrient-rich substance that provides vital nutrition to mammal offspring during their early stages of life. This unique form of feeding has contributed to the success and survival of mammalian species, allowing for the nurturing and protection of their young.
Types of Mammals
When exploring the world of mammals, it becomes clear that they come in various shapes and forms. Mammals can be broadly classified into three main groups: placental mammals, monotremes, and marsupials. Each group exhibits distinct reproductive strategies and unique adaptations that have allowed them to thrive in different environments.
Exploring Placental Mammals
Placental mammals, the largest and most diverse group of mammals, give birth to live young who have fully developed internally before birth. These mammals have a placenta, a specialized organ that allows for the exchange of nutrients and waste between the mother and the developing fetus. Placental mammals include familiar creatures such as dogs, cats, whales, and humans.
Insight Into Monotremes
Monotremes are an extraordinary group of mammals that lay eggs rather than giving birth to live young. They are considered to be the most primitive group of mammals and include the platypus and echidna. Monotremes have a unique reproductive system, combining reptilian and mammalian characteristics.
Discovering Marsupials
Marsupials are another fascinating group of mammals that are characterized by their pouches, in which they carry and nurture their undeveloped young. These pouches provide a safe environment for the marsupial offspring to grow and develop after being born in an embryonic state. Well-known examples of marsupials include kangaroos, koalas, and opossums.
Characteristics Of Mammals
In this section, we will explore the fascinating characteristics that make mammals unique. From their ability to produce milk to their specialized anatomy, mammals have evolved a wide range of adaptations that enable them to thrive in various environments.
Able to Produce Milk
One of the defining features of mammals is their ability to produce milk. Female mammals, known as mothers, possess mammary glands that secrete milk to nourish their young. This adaptation ensures the survival and growth of offspring, providing them with essential nutrients and antibodies.
Diaphragm
Mammals have a diaphragm, a muscular organ that plays a crucial role in breathing. It contracts and relaxes, allowing for the expansion and contraction of the lungs, enabling mammals to inhale and exhale air efficiently.
Endothermy
Endothermy is a characteristic unique to mammals. It refers to the ability of mammals to regulate their own body temperature independently of the environment. This adaptation allows mammals to thrive in a wide range of habitats, from scorching deserts to freezing polar regions.
Four-Chambered Heart
Mammals have a four-chambered heart, consisting of two atria and two ventricles. This advanced cardiovascular system ensures efficient circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to vital organs and tissues.
Hair or Fur
An important characteristic of mammals is the presence of hair or fur on their bodies. Hair provides insulation, protects the skin, and plays a role in sensory perception. It can vary in texture, color, and thickness, serving various purposes depending on the species and environment.
Internal Fertilization
Mammals reproduce through internal fertilization, where the male’s sperm fertilizes the female’s eggs inside the body. This adaptation allows for better protection, development, and nurturing of the offspring until birth.
Mammary Glands
Mammary glands are unique to mammals and are responsible for the production of milk. These specialized glands develop during pregnancy and lactation, enabling the nourishment of offspring. The structure and number of mammary glands vary among different mammal species.
Neocortex
The neocortex is a part of the brain that is highly developed in mammals. It is responsible for complex cognitive functions, including perception, consciousness, language, and reasoning. The size and complexity of the neocortex correlate with the intelligence and adaptability of mammals.
Single-Boned Lower Jaw
Mammals have a single-boned lower jaw, known as the mandible. This structure allows for efficient chewing and grinding of food, facilitating the digestive process. The mandible is an essential adaptation that enables mammals to consume a diverse range of diets.
Specialized Teeth
The teeth of mammals are highly specialized, adapted to their specific dietary needs. Mammals exhibit various types of teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, each serving a specific role in capturing, tearing, cutting, crushing, or grinding food.
Three Bones in the Middle Ear
Mammals have three bones in the middle ear, known as the ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the cochlea, allowing mammals to hear a wide range of sound frequencies with remarkable precision.
Viviparity
Most mammals exhibit viviparity, a mode of reproduction where the embryos develop within the mother’s body and are nourished through a placenta. This adaptation enables mammals to give birth to live young, ensuring better maternal care and higher survival rates.
Types Of Mammals
In the fascinating world of mammals, there is a remarkable diversity based on their unique reproductive systems. Mammals can be categorized into different types, each with its own distinct characteristics. Let’s explore these types and uncover the wonders of mammal reproduction.
Types Of Mammals By Reproduction System
Mammals can be classified into three main groups based on their reproductive methods:
- Monotremes: These intriguing creatures are known as the oddballs of reproduction. Monotremes are the only mammals that lay eggs instead of giving birth to live young. This small group includes the platypus and echidna, both native to Australia and parts of New Guinea. Monotremes possess unique reproductive organs and have a fascinating blend of traits from reptiles and mammals.
- Marsupials: Marsupials are renowned for their distinctive reproductive strategy. After a relatively short gestation period, the underdeveloped young are born, and they continue their development within a special pouch. Iconic marsupials include kangaroos, wallabies, and koalas. The marsupial pouch provides a nurturing environment for the young, allowing them to grow and develop until they are ready to explore the world.
- Placental Mammals: The majority of mammal species fall into this category. Placental mammals, including humans, have a more complex reproductive system. They nurture their young within the mother’s womb through a specialized organ called the placenta. This allows the developing offspring to receive nourishment and oxygen from the mother’s bloodstream. Placental mammals exhibit a wide range of diversity, from tiny mice to magnificent elephants.

Monotremes: The Oddballs Of Reproduction
Monotremes are a remarkable group of mammals with a unique reproductive strategy. They lay eggs, a rare phenomenon among mammals. Monotremes possess cloacas, a single opening for both reproduction and waste elimination. Male monotremes have a spur on their hind legs that secretes venom, which is used during competition and defense.
“Monotremes represent an extraordinary example of reproductive adaptation in the animal kingdom.” – Dr. Jane Dawson, mammalogist
Monotremes have a relatively short gestation period before laying eggs. The eggs are incubated outside the mother’s body in a nest or burrow. After hatching, the young monotremes, called puggles, are nurtured by the mother, who provides them with milk through mammary glands. This combination of egg-laying and milk production is a truly unique adaptation found only in monotremes.
The two main species of monotremes are the platypus and the echidna. The platypus is well-known for its duck-like bill, webbed feet, and ability to detect prey through electroreception. The echidna, also known as the spiny anteater, has a spiky coat and a long snout for feeding on insects and ants.
Monotremes are living relics from an ancient lineage of mammals, representing a fascinating aspect of evolutionary biology. Their reproductive strategy continues to captivate scientists and ignite curiosity about the diversity of life on Earth.
Marsupials: The Ultimate Pouch Crew
In this section, we explore the fascinating world of marsupials, a unique group of mammals known for their distinctive reproductive system and pouches. Marsupials are characterized by their reproductive adaptations and nurturing behaviors, making them truly remarkable creatures.

Unique Characteristics of Marsupials
Marsupials possess a range of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other mammals. One of the most prominent features is the marsupial pouch, where the young, called joeys, complete their development after birth. The pouch provides a safe environment for the vulnerable joeys, enabling their growth and protection.
Additionally, marsupials have a specialized reproductive system where the young are born in an undeveloped state. After birth, the newborns crawl into their mother’s pouch, where they attach to a teat and continue their growth. This adaptive reproductive behavior allows marsupials to thrive in various environments and adapt to changing ecological conditions.
Behavior of Marsupials
Marsupials display a diverse range of behaviors that are specific to their individual species and their habitats. Some marsupials, such as kangaroos and wallabies, are known for their incredible jumping abilities, which help them navigate their environments and escape from predators.
Other marsupials, like koalas and wombats, are adapted for a more sedentary lifestyle and are expert climbers or burrowers. These behaviors enable them to find food sources and seek shelter in their natural habitats.
Placental Mammals: The Baby Belly Champions
Placental mammals, on the other hand, have their own unique adaptations when it comes to reproduction. Unlike marsupials, placental mammals nurture their young inside the womb through the placenta, a specialized organ that facilitates the exchange of nutrients and waste between the mother and offspring.
Adaptations of Placental Mammals
Placental mammals have evolved a wide range of adaptations that allow them to thrive in various environments. From the ability to live in terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial habitats to their diverse feeding habits, placental mammals have developed remarkable adaptations to ensure survival.
These adaptations include features such as specialized teeth for different feeding habits, efficient digestion systems, and various forms of locomotion. Additionally, placental mammals have developed sophisticated sensory systems, including acute hearing and vision, to navigate their surroundings and find food sources.
Reproduction in Placental Mammals
Placental mammals reproduce through internal fertilization, where the sperm fertilizes the egg within the female’s reproductive tract. The fertilized egg then develops into an embryo that attaches to the uterus wall, forming the placenta.
During gestation, the placenta supplies the developing young with oxygen, nutrients, and removes waste products. This method of reproduction allows placental mammals to have longer gestation periods and give birth to well-developed young.
Table: A Comparison of Marsupials and Placental Mammals
| Characteristic | Marsupials | Placental Mammals |
|---|---|---|
| Reproductive System | Young develop in mother’s pouch | Young develop in the womb through the placenta |
| Behavior | Variable behaviors depending on species; jumping, climbing, burrowing | Diverse range of behaviors; adapted to different habitats and food sources |
| Adaptations | Pouch for nurturing young; specialized reproductive system | Diverse adaptations for various habitats and feeding habits |
List Of Mammals
This section presents a comprehensive list of mammals, showcasing the remarkable diversity within the mammalian kingdom. Mammals encompass a vast array of species, ranging from the small and elusive to the large and majestic. From the iconic lion to the minutely-detailed pygmy shrew, the world of mammals is a testament to the wonders of evolution and adaptation.

Threats And Conservation Of Mammals
This section discusses the various threats that mammals face and highlights the importance of conservation efforts in protecting these vulnerable creatures. Mammals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems, and their conservation is essential for preserving biodiversity.
Indirect Threats
Mammals are susceptible to indirect threats that result from human activities and environmental changes. Habitat loss is a significant concern, as deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion continue to encroach upon natural habitats. The destruction of forests, wetlands, and grasslands deprives mammals of their homes and sources of food.

Climate change poses another dire threat to mammal populations. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and altered precipitation patterns disrupt ecosystems and impact the availability of food and water. This results in habitat degradation and reduced reproduction rates for many mammal species.
Direct Threats
In addition to indirect threats, mammals also face direct threats from human activities. Hunting and poaching for fur, meat, and body parts have decimated mammal populations globally. Unsustainable hunting practices and the illegal wildlife trade contribute to the decline of numerous species, pushing them towards the brink of extinction.
Endangered mammals also fall victim to illegal wildlife trafficking, which poses a severe threat to their survival. The demand for exotic pets, traditional medicine ingredients, and rare animal products drives the illegal trade, leading to the exploitation and depletion of vulnerable mammal species.
Mammal conservation plays a pivotal role in combating these threats and safeguarding endangered species. It involves implementing measures to protect habitats, regulating hunting practices, raising awareness about the importance of conservation, and enforcing legislation to combat illegal wildlife trade.
| Threats | Impact |
|---|---|
| Habitat loss | Displacement, reduced food availability |
| Climate change | Habitat degradation, reduced reproduction rates |
| Hunting and poaching | Declining populations, extinction risk |
| Illegal wildlife trade | Exploitation, depletion of populations |
Table: Threats to Mammals and Their Impacts.
Conservation Acts
Conservation acts play a crucial role in protecting endangered species and preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems. These acts provide legal frameworks and guidelines for managem
enting and conserving mammalian species, ensuring their survival and promoting biodiversity. One prominent legislation in the United States is the Endangered Species Act. Enacted in 1973, this act aims to prevent the extinction of threatened and endangered species, including mammals, by providing protection and implementing recovery plans.
Internationally, there are various conservation efforts and treaties dedicated to wildlife protection, such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). CITES regulates international trade in endangered species and provides a framework to combat wildlife trafficking.
Additionally, organizations like the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) facilitate global conservation initiatives. Through assessments, policy advocacy, and knowledge sharing, the IUCN leads efforts to protect and conserve mammalian species and their habitats worldwide.
By implementing and enforcing wildlife protection laws, conservation acts contribute to the preservation of mammalian species and the conservation of their natural habitats.
Mammals in the Wild
In their natural habitats, mammals have evolved and adapted to thrive in diverse environments. From the depths of the ocean to the heart of the rainforest, these remarkable creatures have developed unique characteristics and behaviors to survive and thrive. This section will explore the fascinating lives of mammals in the wild, focusing on the adaptations of marine mammals, the distinctive traits of terrestrial mammals, and the special behaviors of arboreal mammals.
Adaptations of Marine Mammals
Marine mammals are a diverse group that includes whales, dolphins, seals, and sea lions. These incredible creatures have evolved numerous adaptations to thrive in water. Their streamlined bodies and torpedo-like shapes enable efficient swimming and diving, allowing them to hunt for food and evade predators. Marine mammals also have specialized flippers or fins that aid in locomotion and navigation. Blubber, a thick layer of fat beneath their skin, helps provide insulation and buoyancy, allowing them to maintain their body temperature in cold water. Additionally, these mammals have developed unique respiratory systems that allow them to hold their breath for extended periods while diving deep underwater. The adaptations of marine mammals have enabled them to become well-adapted and highly successful inhabitants of the world’s oceans.
Unique Characteristics of Terrestrial Mammals
Terrestrial mammals are the most familiar group of mammals as they live on land, including a vast diversity of species such as elephants, lions, and horses. These mammals have evolved numerous adaptations to thrive in various terrestrial habitats. One of the key characteristics of terrestrial mammals is their ability to walk or run on land using specialized limbs. Some species have evolved powerful legs for running, while others have developed adaptations for climbing, burrowing, or digging. Terrestrial mammals also have a wide range of dentition, with different types of teeth specialized for various diets such as herbivory, carnivory, or omnivory. Additionally, many terrestrial mammals have evolved acute senses, such as sharp eyesight or keen sense of smell, to detect predators, find food, or communicate with others. With their remarkable adaptations, terrestrial mammals have carved out niches in diverse ecosystems around the world.
Special Traits of Arboreal Mammals
Arboreal mammals are a group of mammals that have adapted to life in trees. This group includes primates, such as monkeys and apes, as well as a variety of other mammalian species. Arboreal mammals have developed unique traits to navigate and thrive in the treetops. They possess grasping hands or feet with opposable thumbs or toes, allowing them to grip onto branches and move with agility. Some arboreal mammals, such as squirrels, have evolved specialized adaptations like bushy tails that aid in balance and provide stability while leaping between branches. These mammals also have keen eyesight and acute hearing to detect potential threats or opportunities for food. With their extraordinary adaptations, arboreal mammals have conquered the complex and challenging environment of the trees.
Importance of Mammals in Ecosystems
Mammals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and functioning of ecosystems. They contribute to various ecological processes, including nutrient cycling, seed dispersal, and pollination. Understanding the ecosystem roles of different types of mammals, such as herbivorous, predatory, and omnivorous mammals, is essential for comprehending the complexities of mammal ecology.
Role of Herbivorous Mammals in the Food Chain
Herbivorous mammals, also known as grazers or browsers, have a significant impact on the food chain. They consume plant material, such as leaves, stems, fruits, and seeds, and influence vegetation dynamics, nutrient cycling, and plant community composition. By regulating plant growth, herbivorous mammals help maintain habitat structure and promote the diversity of plant species. They also serve as a food source for other carnivorous mammals and predators, creating a link in the intricate web of trophic interactions.
Impact of Predatory Mammals on Population Dynamics
Predatory mammals, including wolves, lions, and tigers, play a critical role in regulating prey populations. Their presence helps control the population sizes of herbivorous mammals and prevents overgrazing or overpopulation of certain species. By exerting predation pressure, predatory mammals contribute to maintaining the structure and stability of ecological communities. They also promote behavioral adaptations in prey species, leading to the development of defensive strategies and enhanced survival mechanisms.
Contribution of Omnivorous Mammals to Biodiversity
Omnivorous mammals, such as bears and raccoons, occupy a unique niche in ecosystems due to their ability to consume both plant and animal matter. Their dietary versatility allows them to exploit various food resources, contributing to the sustainability and diversity of ecosystems. As omnivores, they can influence seed dispersal by consuming fruits and depositing seeds in different locations. Additionally, their feeding habits can indirectly shape plant communities and influence the abundance and distribution of other animal species.
The intricate relationships between herbivorous, predatory, and omnivorous mammals highlight the interconnectedness of species within ecosystems. Understanding the roles that mammals play is vital for conservation efforts, as any disruption to their populations can have far-reaching consequences for the entire ecosystem. By protecting mammal populations and safeguarding their habitats, we can preserve the delicate balance of nature and ensure the sustainability of our planet’s ecosystems.
Different Types Of Mammals By Groups
Section 11 explores the diverse world of mammals, categorized into different groups based on their unique characteristics and behaviors. This section focuses on various mammal groups, including monotremes, marsupials, placental mammals, primates, rodents, bats, cetaceans, and ungulates. Each group exhibits fascinating adaptations, distinct classifications, and remarkable anatomy.
Monotremes: The Eccentric Egg Layers
Monotremes are a fascinating group of mammals that lay eggs, making them truly eccentric in the mammalian world. This group includes iconic species such as the platypus and echidna. Monotremes have unique reproductive systems and exhibit a combination of reptilian and mammalian traits.
Marsupials: The Pouch Bearers
Marsupials are known for their remarkable adaptation of carrying their young in pouches. This group includes well-known species such as kangaroos, koalas, and opossums. Marsupials have a distinct reproductive system and exhibit a wide range of behaviors and characteristics specific to their habitats.
Placental Mammals: The Womb Nurturers
Placental mammals, the largest group of mammals, nurture their young in the womb through a specialized placenta. This group encompasses diverse species, including humans, dogs, cats, elephants, and whales. Placental mammals have evolved various adaptations and display a wide range of behaviors and anatomical features.
Primates: The Intelligent Behaviors
Primates, including humans, monkeys, and apes, are characterized by their highly developed brains and complex social behaviors. These intelligent mammals exhibit diverse adaptations and can be found in various habitats across the globe.
Rodents: The Playful Scavengers
Rodents encompass a vast group of mammals that are known for their continuous-growing front teeth and their ability to gnaw and chew. This group includes species such as mice, rats, squirrels, and beavers. Rodents exhibit playful behavior and have adapted to various environments.
Bats: The Nocturnal Flyers
Bats are the only mammals capable of sustained flight. They have unique adaptations such as echolocation, enabling them to navigate and locate prey in the darkness. Bats play crucial ecological roles as pollinators and insect controllers.
Cetaceans: The Oceanic Virtuosos
Cetaceans, including dolphins, whales, and porpoises, are highly adapted to marine life. These remarkable mammals have evolved streamlined bodies, flippers, and blowholes to thrive in aquatic environments. Cetaceans have intricate communication systems and exhibit complex social structures.
Ungulates: The Mighty Hoofed Beasts
Ungulates are a diverse group of mammals known for their hooves and herbivorous diets. This group includes iconic species such as horses, deer, cows, and elephants. Ungulates have evolved specialized adaptations to survive in various habitats, and their anatomical features vary based on the species.
| Mammal Group | Key Features | Behaviors | Adaptations | Anatomy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotremes | Unique reproductive systems | Egg-laying behavior | Combination of reptilian and mammalian traits | Varying anatomical structures |
| Marsupials | Pouch-bearing reproductive system | Carrying young in pouches | Diverse adaptations based on habitat | Varying anatomical structures |
| Placental Mammals | Placenta for nurturing young | Diverse range of behaviors | Efficient adaptations for survival | Wide variety of anatomical features |
| Primates | Highly developed brains | Complex social behaviors | Opposable thumbs, enhanced intelligence | Diverse anatomical characteristics |
| Rodents | Continuous-growing front teeth | Playful behavior, scavenging | Gnawing adaptations, efficient digestion | Diverse sizes and body structures |
| Bats | Echolocation abilities | Nocturnal flying behavior | Wings, nocturnal vision | Specialized skeletal structures for flight |
| Cetaceans | Aquatic adaptations | Complex communication, social structures | Streamlined bodies, blowholes | Diverse anatomical features for marine life |
| Ungulates | Herbivorous diet, hoofed feet | Group behavior, migration | Specialized teeth, digestive systems | Varied anatomical structures based on habitat |
Conclusion
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide has provided a deep dive into the world of mammals, highlighting their diversity, characteristics, and importance in ecosystems. From their unique reproductive systems and adaptations to their crucial roles in food chains, mammals are truly remarkable creatures.
Throughout this guide, we have explored the defining features of mammals, such as their ability to produce milk, possess a diaphragm, and regulate their body temperature through endothermy. We have also examined their specialized anatomical traits, including a four-chambered heart, hair or fur, and mammary glands, which differentiate them from other animal groups.
Moreover, we have categorized mammals based on their reproductive systems, exploring the eccentric egg-laying monotremes, the pouch-bearing marsupials, and the womb-nurturing placental mammals. We have also delved into specific groups like primates, rodents, bats, cetaceans, and ungulates, each with their own unique behaviors and adaptations.
It is evident that mammals play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. Herbivorous mammals contribute to the food chain, while predatory mammals regulate population dynamics. Additionally, omnivorous mammals contribute to biodiversity by interacting with various plant and animal species.
In light of this knowledge, it is crucial to recognize the importance of conservation efforts to protect mammals and their habitats. By understanding and appreciating these fascinating creatures, we can work towards safeguarding their future and preserving the rich biodiversity of our planet.
FAQ
What is a mammal?
How many species of mammals are there?
What are the different types of mammals?
Why are mammals important?
What are the threats to mammal populations?
What conservation efforts are in place to protect mammals?
What are some examples of mammalian habitats?
What are some unique characteristics of primates?
What are some adaptations of marine mammals?
How do mammals reproduce?
What are some unique characteristics of bats?
How are mammals classified?
As our Editor-in-Chief, James plays a pivotal role in ensuring the quality and integrity of our content. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for storytelling, James oversees the editorial process here at A Place for Animals. With years of experience in content editing, James ensures that every piece of content meets our high standards of accuracy and clarity. Under James’ guidance, you can rest assured that the content you read is informative and impeccably crafted.
Animals
Discover Animals That Start with Y – Unique Fauna

Did you know that there are intriguing animals that begin with the letter Y? These creatures, ranging from mammals and birds to reptiles and invertebrates, play a vital role in the diverse ecosystem of our planet. By learning more about these distinctive animals, we can enhance our knowledge of the natural world and the complex interconnections within it. Prepare to immerse yourself in the fascinating world of animals that start with Y.
Key Takeaways:
- Animals that start with Y represent a diverse range of species in different animal classes.
- By learning about and appreciating these unique creatures, we can promote their conservation and well-being.
- Some Y-named animals, like the Yak, are facing threats and are endangered, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.
- These animals play vital roles in ecosystems, contributing to functions such as pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling.
- Exploring the world of animals that start with Y allows us to develop a deeper connection with nature and appreciate its wonders.
Mammals That Start with Y
The diverse world of mammals offers several fascinating species that begin with the letter Y. These mammals have distinctive characteristics and play important roles in their respective ecosystems. Let’s explore some notable examples:
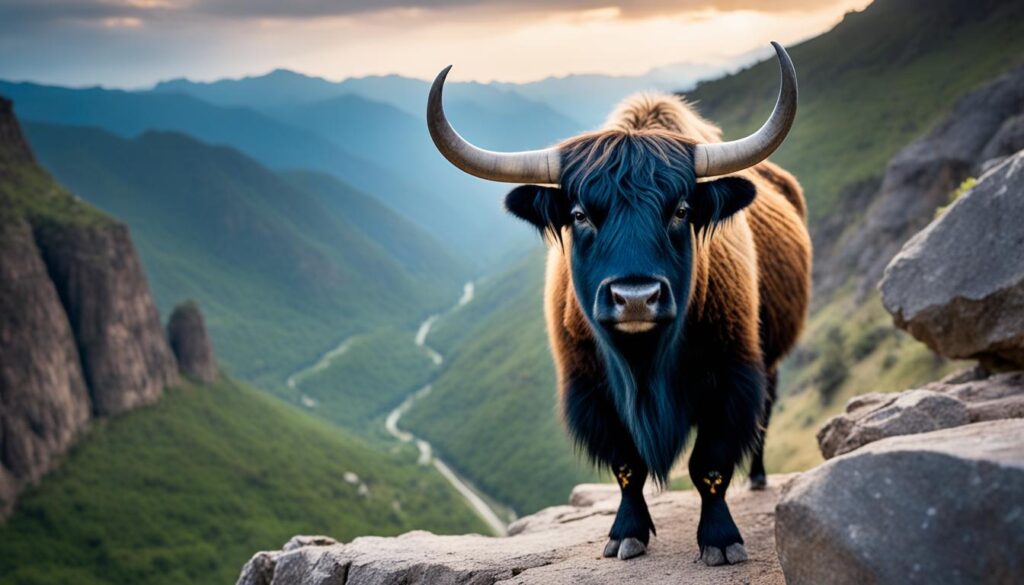
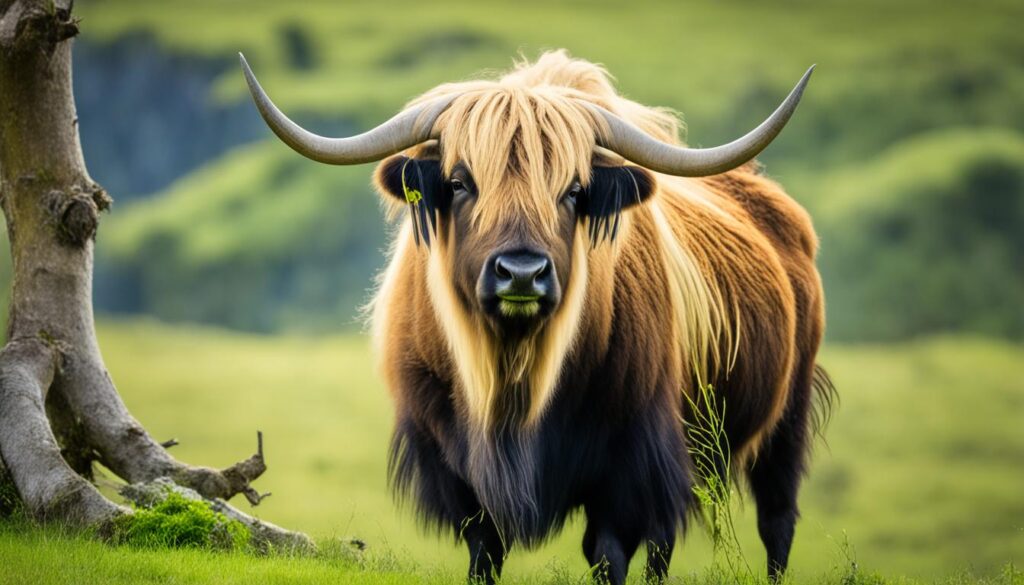
1. Yak
The Yak is a domesticated bovine species native to the Himalayas. Known for its long, shaggy coat, this sturdy mammal is well-adapted to high-altitude environments. Yaks are primarily used for their milk, meat, and wool and are an integral part of the local culture and economy in the region.
2. Yellow Mongoose
The Yellow Mongoose is a small carnivorous mammal found in Africa. With its bright yellow fur and slender body, it is skilled at hunting small prey such as insects, reptiles, and rodents. This agile mammal is known for its fearless and inquisitive nature, often standing on its hind legs to survey its surroundings.
3. Yakalo
The Yakalo, also known as the Yakutian Laika, is a Siberian breed of dog found in the Yakutia region of Russia. These hardy canines were historically used for herding reindeer and pulling sleds in the harsh Arctic climate. Intelligent and adaptable, Yakalos are known for their endurance and loyalty.
These are just a few examples of the fascinating mammals that start with Y. Each of these species brings its own unique attributes and contributions to the natural world. Through their interactions and behaviors, they shape the ecosystems they inhabit, highlighting the intricate web of life on our planet.
Birds That Start with Y
The avian world also boasts several species that begin with the letter Y. Let’s take a closer look at some of these fascinating birds:
1. Yellowhammer
The Yellowhammer is a bird known for its distinctive yellow plumage. Native to Europe, it has become a symbol in some countries. With its vibrant colors and beautiful song, the Yellowhammer adds a touch of brightness to its habitats.
2. Yellow-Eyed Penguin
The Yellow-Eyed Penguin is a unique bird found in New Zealand. As its name suggests, it is known for its striking yellow eyes. This endangered species is a true gem of the avian world, captivating observers with its graceful movements.
3. Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker
The Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker is a woodpecker species that drills holes in trees to feed on sap. The vibrant yellow belly of this bird distinguishes it from other woodpeckers. With its specialized feeding behavior, the Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker plays an important role in forest ecosystems.
“Birds have an extraordinary diversity of colors and behaviors, and the Yellowhammer, Yellow-Eyed Penguin, and Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker are no exception. Each of these birds brings its own unique qualities to the natural world.” – Ornithology Expert
By showcasing their yellow coloration, these birds demonstrate nature’s remarkable artistic palette. Get ready to be captivated by their beauty, both visually and audibly.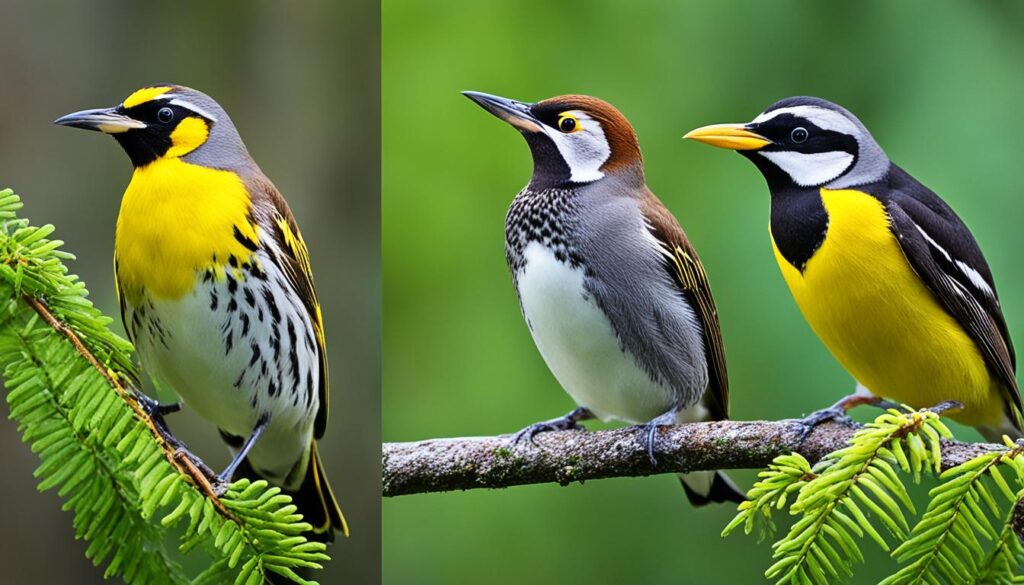
| Bird | Scientific Name | Habitat | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yellowhammer | Emberiza citrinella | Open woodlands, farmlands, grasslands | Least Concern |
| Yellow-Eyed Penguin | Megadyptes antipodes | Coastal forests, grassy areas near the sea | Endangered |
| Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker | Sphyrapicus varius | Deciduous and mixed forests | Least Concern |
Table: Overview of birds that start with Y
Reptiles That Start with Y
Several reptiles have names that begin with Y, showcasing the diverse and fascinating world of these scaly creatures. Let’s explore some notable reptiles that start with Y and learn more about their unique features and habitats.
1. Yacare Caiman
Native to South America, the Yacare Caiman is a crocodilian species that commands attention with its impressive size and powerful jaws. These formidable reptiles can reach lengths of up to 13 feet (4 meters) and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their aquatic ecosystems.
2. Yellow Anaconda
Another reptile that starts with Y is the Yellow Anaconda, one of the largest snake species in the world. Found in the swamps and rivers of South America, these snakes can grow to be over 20 feet (6 meters) long. Despite their intimidating size, Yellow Anacondas are non-venomous and rely on constriction to capture and subdue their prey.
3. Yellow-Bellied Sea Snake
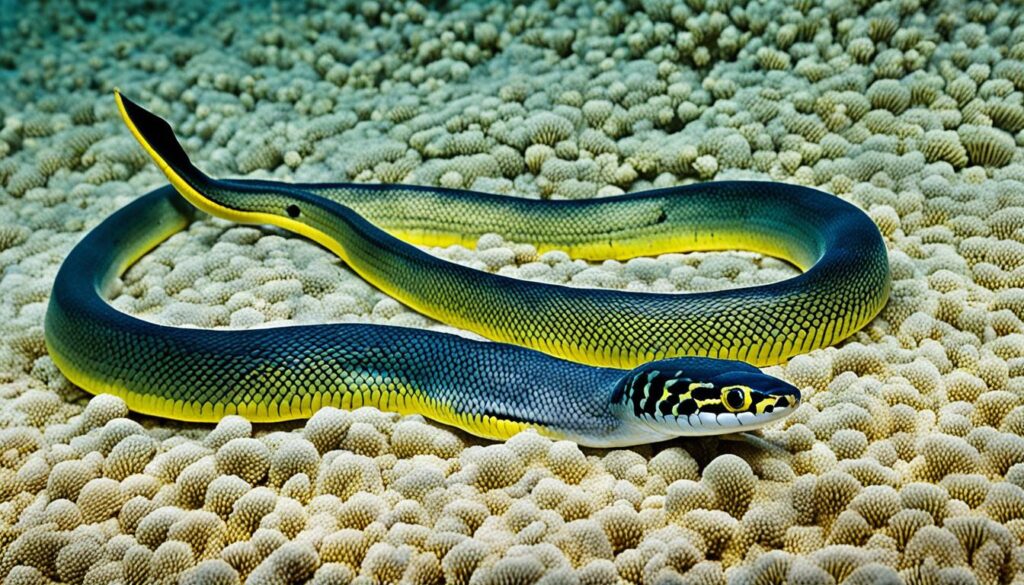

The Yellow-Bellied Sea Snake is an aquatic reptile that inhabits the waters of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. With its vibrant yellow belly, this snake stands out amidst the blue hues of the ocean. It possesses adaptations that allow it to live in aquatic environments, such as a paddle-like tail for swimming and a valve-like nostril that enables it to breathe while submerged.
| Reptile | Habitat | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Yacare Caiman | South America | Impressive size and formidable jaws |
| Yellow Anaconda | South America | One of the largest snake species in the world |
| Yellow-Bellied Sea Snake | Pacific and Indian Oceans | Vibrant yellow belly, aquatic adaptations |
These reptiles that start with Y offer a glimpse into the incredible diversity and adaptations found within the reptile kingdom. From the impressive Yacare Caiman to the massive Yellow Anaconda and the vibrant Yellow-Bellied Sea Snake, these reptiles remind us of the remarkable variety of life that exists in our natural world.
Invertebrates That Start with Y
When exploring the fascinating world of invertebrates, several remarkable creatures that begin with the letter Y capture our attention. These invertebrates display unique characteristics and play significant roles in their respective ecosystems.
1. Yabby
The Yabby is a species of freshwater crayfish commonly found in Australia. These crustaceans reside in rivers, lakes, and ponds, where they burrow into riverbanks and construct elaborate tunnels. With their vibrant colors and distinctive pincers, Yabbies are fascinating creatures to observe in their natural habitat.
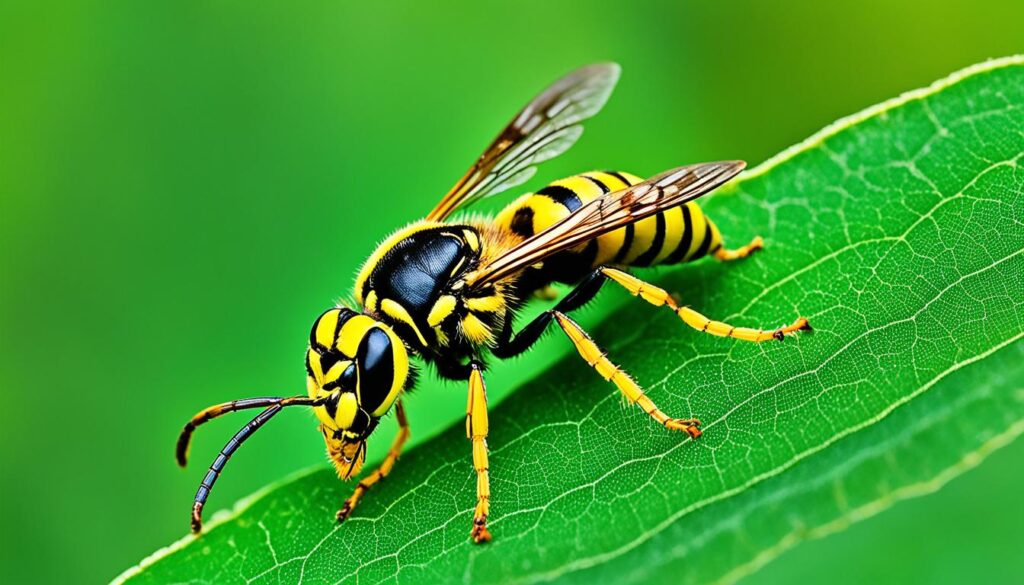
2. Yellow Jacket Wasp
The Yellow Jacket Wasp is widely recognized for its distinctive yellow and black striped body. Found in many parts of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia, these wasps are known for their aggressive behavior and painful stings. Yellow Jacket Wasps often build their nests in underground burrows or concealed locations, making them a common sight during summertime.
3. Yellowfin Tuna
The Yellowfin Tuna, also known as Thunnus albacares, is a popular fish among sport fishermen and seafood enthusiasts. These large, migratory fish inhabit tropical and subtropical waters and are particularly sought after for their fast swimming speed and flavorful flesh. With their distinctive yellow finlets and streamlined bodies, Yellowfin Tuna are prized catches.
Take a moment to appreciate the fascinating invertebrates that start with Y:
| Invertebrate | Description | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Yabby | A freshwater crayfish | Rivers, lakes, and ponds in Australia |
| Yellow Jacket Wasp | A wasp known for its yellow and black striped body | Various regions worldwide |
| Yellowfin Tuna | A popular fish with fast swimming speed | Tropical and subtropical waters |
These incredible invertebrates contribute to the biodiversity of our planet and remind us of the diverse and intricate web of life that exists within the animal kingdom.

Other Animals That Start with Y
In addition to mammals, birds, reptiles, and invertebrates, there are other unique animals that begin with the letter Y. These animals contribute to the rich biodiversity of our planet and offer fascinating insights into the diversity of life. Let’s explore some remarkable examples:
1. Yellow-Bellied Weasel
The Yellow-Bellied Weasel is an agile and cunning mammal known for its small size and distinctive yellow underbelly. Found in various parts of North America, this weasel species has a remarkable ability to adapt to different habitats, from forests to grasslands. With its sleek body and sharp hunting skills, the Yellow-Bellied Weasel is a true marvel of the animal kingdom.
2. Yapok
The Yapok, also known as the “water opossum,” is a semiaquatic marsupial found in the Americas. This fascinating creature has adapted to a life in and around water, with webbed feet for swimming and a pouch that opens toward the rear, allowing it to carry its young safely while in the water. The Yapok’s unique adaptations make it a remarkable example of how animals can thrive in specialized habitats.
3. Yorkshire Terrier
The Yorkshire Terrier, often affectionately called the “Yorkie,” is a beloved and popular dog breed known for its small size and distinctive long, silky coat. Despite their small stature, these dogs exude confidence and an adventurous spirit. With their endearing charm and loyal nature, Yorkshire Terriers have captured the hearts of dog lovers around the world.
These are just a few examples of the intriguing animals that start with Y. Each of them showcases the remarkable diversity and adaptability found within the animal kingdom. By exploring and appreciating these unique creatures, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world we share with them and the importance of protecting their habitats.
Zoo Animals That Start with Y
If you’re planning a trip to the zoo, you’re in for a treat! There are some incredible animals that start with the letter Y waiting to be discovered. From reptiles to primates, here are a few fascinating zoo animals that will captivate your attention:
1. Yacare Caiman
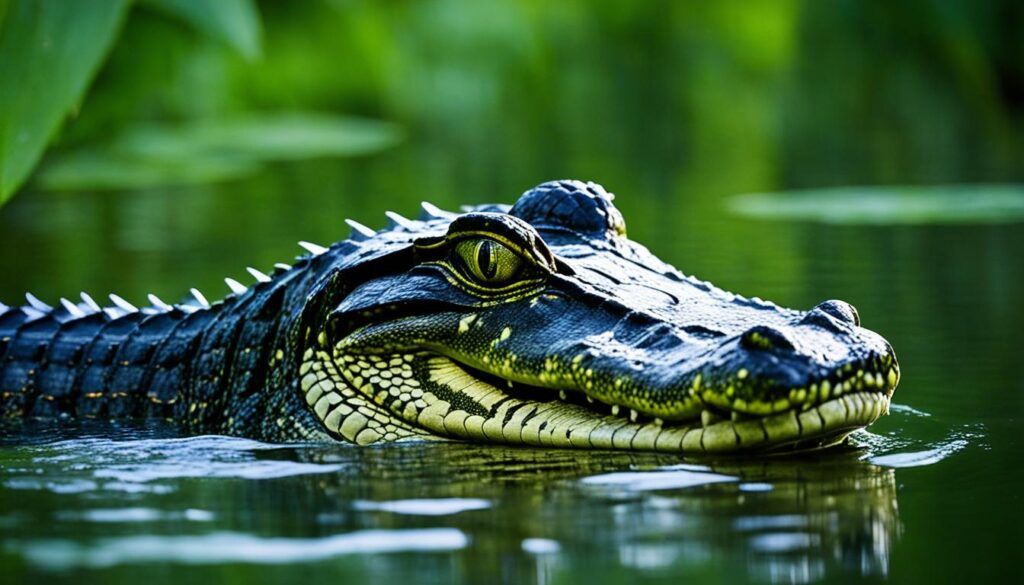

The Yacare Caiman is a crocodilian species that can be found in many zoos with reptile exhibits. These magnificent creatures are known for their impressive size and powerful jaws. Observing them up close allows visitors to appreciate their unique adaptations and learn more about their role in the ecosystem.
2. Yellow Baboon
The yellow baboon, recognizable by its distinctive yellowish-brown fur, is a primate species commonly seen in zoos. These social animals are known for their complex social structures, playful behavior, and striking appearance. A visit to the zoo wouldn’t be complete without watching a troop of yellow baboons interact with one another and entertain visitors.
3. Yellow Mongoose
The Yellow Mongoose is another captivating animal that starts with Y and can often be found in zoo exhibits. With its sleek coat and inquisitive nature, the yellow mongoose is a delight to watch. These small carnivores are native to Africa and are known for their agility and wariness of predators.
4. Yellow-headed Amazon Parrot

The Yellow-headed Amazon Parrot is a colorful and intelligent bird species that can be found in zoos around the world. Known for their vibrant plumage and ability to mimic human speech, these parrots never fail to wow visitors with their beauty and charming antics. A chance encounter with a yellow-headed amazon parrot is sure to make your zoo visit unforgettable.
These are just a few examples of the fantastic zoo animals that start with Y. Whether you’re drawn to reptiles, primates, or birds, there is something for everyone to enjoy and learn from when you visit the zoo.
Yellow-Bellied Birds
A unique subset of birds that start with Y are those with a yellow belly. These birds showcase the diverse range of yellow-bellied species found in different parts of the world.
Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker
The Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker, a woodpecker species native to North America, is known for its distinctive yellow patch on its belly. This medium-sized bird has black and white plumage with a red crown and white stripes on its face. It is often found in deciduous forests, where it drills small holes in trees to extract sap and insects. The yellow belly of the Yellow-Bellied Sapsucker makes it easily identifiable among other woodpecker species.
Yellow-Bellied Marmot
The Yellow-Bellied Marmot, a rodent found in mountainous regions of North America, also has a yellowish belly. This ground-dwelling mammal is known for its stout body, short legs, and a yellow patch on its underside. The Yellow-Bellied Marmot is a social animal that lives in large colonies and hibernates during the winter months. It can often be spotted sunning itself on rocks or foraging for vegetation.

Animals That Start with Y: Lesser-Known Species
While many animals that start with Y are relatively well-known, there are also lesser-known species worth exploring. These unique creatures contribute to the overall biodiversity of our planet.
- Yellow-Backed Duiker: A small antelope found in Africa, the Yellow-Backed Duiker is known for its distinctive yellow patch of fur on its back. This beautiful mammal inhabits the forests and savannas of West and Central Africa. Although it is smaller than other antelope species, the Yellow-Backed Duiker possesses remarkable agility and speed.
- Yuma Myotis: This small bat species is native to North America and plays a crucial role in insect control. Found in various habitats, including forests, caves, and urban areas, the Yuma Myotis is an efficient predator, feeding on insects such as mosquitoes and moths. Although these bats are not often seen due to their nocturnal nature, they make valuable contributions to maintaining ecological balance.
The Yellow-Backed Duiker and the Yuma Myotis are just a few examples of the lesser-known animals that start with Y. By learning about these fascinating creatures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and wonders of the natural world. Let’s take a closer look at these species in the table below:
| Animal | Description | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow-Backed Duiker | A small antelope known for its distinctive yellow patch of fur on its back. | Forests and savannas of West and Central Africa. |
| Yuma Myotis | A small bat species native to North America. | Various habitats including forests, caves, and urban areas. |
These lesser-known animals remind us of the incredible diversity and complexity of our natural world. By continuing to explore and understand these species, we can contribute to their conservation and ensure their existence for future generations.
“The more we learn about the lesser-known animals, the more we realize the intricate web of life that surrounds us.” – Unknown
Animals That Start with Y in Unique Habitats
Animals that start with Y can be found in a variety of habitats around the world. These unique habitats provide the perfect environment for these animals to thrive and adapt to their surroundings. Let’s explore some fascinating examples:
Yellow Ground Squirrel
The Yellow Ground Squirrel (genus Spermophilus) is native to the deserts of Afghanistan and Iran. These small rodents have adapted to the arid conditions of their habitat and are known for their yellowish fur and bushy tails. With their burrowing skills, they create complex underground networks that help them escape from predators and regulate body temperature.
Yellow-Throated Marten
The Yellow-Throated Marten (Martes flavigula) can be found in the forests of Asia, including countries like China, India, and Vietnam. This carnivorous mammal is known for its vibrant yellow throat patch, which distinguishes it from other marten species. It is an agile climber and spends most of its time in the trees, hunting for small prey.
Exploring these unique habitats gives us valuable insights into how animals adapt and interact with their environment. It highlights the incredible diversity of life on our planet and emphasizes the importance of preserving these ecosystems for future generations.
| Animal | Habitat | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow Ground Squirrel | Deserts of Afghanistan and Iran | Yellowish fur and bushy tail |
| Yellow-Throated Marten | Forests of Asia | Vibrant yellow throat patch |
Endangered Animals That Start with Y
Unfortunately, some animals that start with Y are endangered or threatened due to various factors such as habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. These vulnerable species require immediate attention and conservation efforts to ensure their survival in the wild.
“Conserving endangered species is not only about protecting individual animals but also preserving the delicate balance of our ecosystems.”
One such endangered animal is the Yak. Native to the Himalayas, the Yak is a majestic mammal known for its long, shaggy fur and robust build. However, the Yak population has been declining due to overhunting and habitat degradation. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed the Yak as an endangered species.
Conservation initiatives, such as protected areas and habitat restoration projects, are underway to safeguard the remaining Yak populations. Efforts from local communities, government organizations, and environmental groups aim to address the threats faced by Yaks and create sustainable solutions to protect this iconic species.

Conservation campaigns are also crucial in raising awareness about the endangered status of these animals. By educating the public and fostering a sense of responsibility, individuals can contribute to the preservation of these species and their habitats.
Threatened Habitats
The Yak’s habitat, the alpine meadows and mountainous regions of the Himalayas, is also under significant pressure. Climate change, deforestation, and unsustainable land use practices pose significant threats to the Yak’s natural habitat. The loss of these unique ecosystems not only endangers the Yak but also disrupts the delicate balance of the entire environment.
Efforts to protect the Yak’s habitat involve establishing conservation areas, implementing sustainable land management practices, and promoting eco-tourism initiatives that benefit local communities while preserving the natural environment.
Conservation Partnerships
Collaboration among various stakeholders is vital in addressing the challenges faced by endangered animals that start with Y. Local communities, conservation organizations, governmental bodies, and researchers work together to develop comprehensive conservation strategies and initiatives.
| Conservation Partners | Role |
|---|---|
| Global Wildlife Conservation | Provides funding and support for on-the-ground conservation programs |
| World Wildlife Fund (WWF) | Leads conservation projects and community engagement efforts |
| Local communities | Contributes traditional knowledge and actively participates in conservation practices |
| Research institutions | Conducts scientific studies and provides data to inform conservation strategies |
The collective efforts of these partnerships play a crucial role in the conservation of endangered animals that start with Y, ensuring a sustainable future for these species.
Conservation Efforts for Animals That Start with Y
Conservation efforts are crucial in safeguarding the welfare of animals that start with Y and their habitats. Dedicated individuals and organizations work tirelessly to raise awareness, conduct research, and implement effective strategies to ensure the survival of these unique species. By employing a range of approaches, from habitat restoration to captive breeding programs, they strive to conserve and protect these magnificent animals.
The Role of Research and Awareness
Research plays a pivotal role in understanding the needs and vulnerabilities of animals that start with Y. By studying their behaviors, habitats, and threats, researchers gain insights that inform conservation strategies. By disseminating this knowledge through educational campaigns and public outreach, awareness is raised about the importance of protecting these animals.
Restoring and Protecting Habitats
One of the key conservation efforts is the restoration and protection of habitats for animals that start with Y. By preserving essential ecosystems, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, these initiatives provide suitable environments for these species to thrive. Through initiatives like reforestation and protected area management, habitats are safeguarded, ensuring the survival of these unique animals.
Captive Breeding Programs
In certain cases, captive breeding programs are implemented to bolster the population of endangered animals that start with Y. These programs involve carefully selecting and breeding individuals in controlled environments, aiming to increase their population and genetic diversity. By reintroducing offspring into the wild when conditions are favorable, captive breeding programs contribute to the recovery of these species.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Conservation efforts for animals that start with Y often involve collaboration and partnerships between various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, local communities, and researchers. By combining resources, expertise, and efforts, these collaborations maximize the impact of conservation initiatives, ultimately benefiting the animals.
| Conservation Efforts | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat restoration | Restoring and protecting natural habitats to provide suitable environments for animals that start with Y |
| Captive breeding programs | Breeding individuals in controlled environments to increase populations of endangered species |
| Research and awareness | Studying behaviors, habitats, and threats to inform conservation strategies and raise public awareness |
| Collaboration and partnerships | Working together with government agencies, non-profit organizations, and local communities to maximize the impact of conservation efforts |

Promoting Awareness and Appreciation of Animals That Start with Y
Promoting awareness and appreciation of animals that start with Y is crucial for their conservation and overall well-being. By educating the public about these unique creatures, their remarkable traits, and their significant roles within ecosystems, we can inspire individuals to take action, support conservation efforts, and make environmentally conscious choices. Learning about and appreciating these animals allows us to develop a deeper connection with the natural world.
“The greatness of a nation and its moral progress can be judged by the way its animals are treated.” – Mahatma Gandhi
When we promote awareness and understanding of animals that start with Y, we contribute to the preservation of their habitats and the protection of their species. By highlighting their importance and the threats they face, we can foster a sense of responsibility and encourage people to make positive changes in their daily lives.
Appreciating the Uniqueness of Animals That Start with Y
Each animal that begins with the letter Y has its own distinct characteristics and contributes to the biodiversity of our planet. From the majestic Yak to the fascinating Yellow Jacket Wasp, appreciating their beauty and diversity helps us recognize the intricate web of life in which we all play a part.
Furthermore, promoting awareness and appreciation of these animals can have ripple effects beyond their specific species. By embracing the idea that every living being has inherent value and deserves respect, we can foster a culture of empathy and compassion towards all animals, both domestic and wild.
Connecting People with Nature
Learning about animals that start with Y not only expands our knowledge but also deepens our connection with the natural world. Research has shown that spending time in nature and observing wildlife can have numerous physical, mental, and emotional benefits.
By engaging with these fascinating creatures, whether through visits to zoos or wildlife sanctuaries, photographs, or educational programs, individuals can experience a sense of awe and wonder that can lead to a desire to protect and conserve the environment.
| Benefits of Promoting Awareness and Appreciation of Animals That Start with Y: | Ways to Promote Awareness and Appreciation: |
|---|---|
| 1. Increased conservation efforts | 1. Education programs in schools and communities |
| 2. Enhanced biodiversity preservation | 2. Collaboration with zoos and wildlife organizations |
| 3. Development of sustainable practices | 3. Creation of engaging online content |
| 4. Conservation funding and support | 4. Public awareness campaigns and events |
By promoting awareness and appreciation of animals that start with Y, we can create a ripple effect, instilling a sense of responsibility and stewardship for the natural world. Every action, no matter how small, has the power to make a difference for these remarkable creatures and their habitats. Together, we can ensure a brighter future for animals that start with Y and all living beings on our planet.

The Role of Animals That Start with Y in Ecosystems
Animals that start with Y, like all creatures, play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. These unique creatures contribute to various ecological processes and have a significant impact on the overall functioning and resilience of their respective habitats.
One key role that animals starting with Y fulfill is pollination. By transferring pollen from one plant to another, these animals facilitate the reproduction of numerous plant species. For instance, the Yellow-Banded Bumblebee plays a vital role in the pollination of flowers, ensuring the production of fruits and seeds that sustain other organisms and promote biodiversity.
In addition to pollination, animals that start with Y also contribute to seed dispersal. Through their movements and consumption of fruits, they aid in the dispersal of seeds to different locations, allowing plants to colonize new areas and ensure their survival. For example, the Yellow-Breasted Chat, a migratory bird, feeds on various fruits and disperses seeds as it travels, enabling the establishment of plant populations in different regions.
Furthermore, animals starting with Y are integral to nutrient cycling within ecosystems. They facilitate the decomposition of organic matter through activities such as feeding, excretion, and decomposition of their own bodies. These processes release essential nutrients back into the environment, which are then utilized by plants and other organisms. The Yellow Dung Beetle, for instance, feeds on animal dung, contributing to the breakdown of organic matter and nutrient recycling.
Predator-prey relationships are another important aspect of ecosystems in which animals starting with Y play a vital role. They help control populations of other organisms, maintaining a balance that prevents overpopulation and the consequent resource depletion. The Yellow-Lipped Sea Krait, a venomous sea snake, preys on fish and other marine organisms, regulating their numbers and ensuring the overall stability of the marine ecosystem.
“Animals starting with Y contribute to the pollination of flowers, seed dispersal, nutrient cycling, and predator-prey relationships, all of which are fundamental to maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems.”
Recognizing the importance of these animals emphasizes the interconnectedness of all life forms and highlights the significance of biodiversity conservation. Each species, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, plays a vital role in the intricate web of life on Earth.

| Animal | Role in Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Yellow-Banded Bumblebee | Pollination of flowers |
| Yellow-Breasted Chat | Seed dispersal |
| Yellow Dung Beetle | Nutrient cycling |
| Yellow-Lipped Sea Krait | Predator-prey relationships |
As we strive to protect and preserve the delicate balance of our ecosystems, it is crucial to appreciate and conserve animals that start with Y and their habitats. Their roles and contributions underpin the stability and diversity of our natural world, reminding us of the intricate relationships that connect all living beings. By nurturing and safeguarding these species, we ensure a harmonious and sustainable future for both wildlife and humanity.
Conclusion
Animals that start with Y encompass a wide range of species, from mammals and birds to reptiles and invertebrates. Exploring this diverse group of animals allows us to appreciate the wonders of the natural world and the incredible variety of life on our planet.
By promoting awareness, conservation, and appreciation, we can work towards a future where these animals thrive, and their habitats are protected for generations to come. It is crucial to educate the public about the importance of these animals and the role they play in maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
Through conservation efforts, habitat restoration, and supporting organizations dedicated to the protection of these species, we can make a positive impact on their survival. Together, we can ensure that animals that start with Y continue to contribute to the beauty and diversity of our planet for future generations to enjoy.FAQ
What are some animals that start with the letter Y?
Where can I find mammals that start with Y?
Are there any birds that start with Y?
What are some reptiles that start with Y?
Are there any invertebrates that start with Y?
What other animals start with Y?
Can I see animals that start with Y at the zoo?
Which birds have a yellow belly?
Are there any lesser-known animals that start with Y?
Where can I find animals that start with Y in unique habitats?
Which animals that start with Y are endangered?
What conservation efforts are in place for animals that start with Y?
Why is it important to promote awareness and appreciation of animals that start with Y?
What role do animals that start with Y play in ecosystems?
What is the conclusion about animals that start with Y?
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
Animals
Discover Animals That Start With S – Fascinating Fauna

Did you know there are many animals that begin with the letter S, each possessing their own distinct traits? From the tiniest marine mammal to the biggest reptile, the animal realm presents a wide variety of captivating creatures. Join us as we set out to discover these amazing beings and reveal the marvels of the natural world.
Key Takeaways:
- Animals that start with S showcase the incredible diversity of the animal kingdom.
- From the majestic saltwater crocodile to the agile siamang, each animal has its own unique features and behaviors.
- Understanding and appreciating these fascinating creatures can help us work towards their conservation and the preservation of their habitats.
- Animals that start with S include salmon, saltwater crocodile, sambar, scarab beetle, scorpion, sea otter, sea turtle, seahorse, serval, sharks, siamang, sloth, snakes, snow leopard, and more.
- Exploring the diverse world of animals that start with S offers a glimpse into the wonders of the natural world and the importance of biodiversity.
Salmon
Salmon are migratory fish known for their remarkable life-cycle. They begin their journey by hatching in freshwater rivers and streams. Once they are strong enough, they make their way to the vast Atlantic Ocean, where they spend several years maturing and growing.
One fascinating species of salmon is the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). These majestic fish are native to the rivers of North America and Europe. They have a silver body with black spots, and their flesh is prized for its rich flavor.
After their time in the ocean, salmon have an undeniable instinct that leads them back to their birthplace. They swim against strong currents, leaping waterfalls and surmounting any obstacles in their path, all in an effort to return to freshwater rivers and streams. This incredible journey is known as salmon’s “return run.”
Once back in freshwater, the life-cycle of salmon takes an extraordinary turn. The female salmon excavates a nest, or a “redd,” in the gravel river bed, where she deposits her eggs. The male salmon then fertilizes the eggs by releasing sperm over them. This process is known as spawning.
After the spawning is complete, the adult salmon, exhausted from their journey, succumb to their efforts and unfortunately pass away. However, their legacy lives on, as the eggs laid in the redd hatch into a new generation of salmon.
Throughout their life-cycle, salmon play a vital role in their ecosystem. They provide a crucial source of food for both terrestrial and aquatic predators, including bears, eagles, and other fish species. Their nutrient-rich bodies also enrich the surrounding environment, benefiting the entire ecosystem.
The Life-Cycle of Salmon:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Spawning | The female salmon excavates a redd and deposits her eggs. The male salmon fertilizes the eggs. |
| 2. Incubation | The eggs develop and hatch into alevins, small fish still attached to their yolk sacs. |
| 3. Fry | The alevins absorb their yolk sacs and emerge as fry, ready to swim and feed. |
| 4. Parr | The fry develop into parr, acquiring vertical markings on their sides and camouflaging themselves in the river. |
| 5. Smolt | The parr undergo physiological changes, such as growing silvery scales, and prepare for their journey to the ocean. |
| 6. Migration | The smolts make their way downstream to the ocean, facing various challenges and predators along the way. |
| 7. Ocean Phase | The salmon spend several years in the ocean, growing and maturing. |
| 8. Return Run | The adult salmon navigate back to their birthplace, facing obstacles and incredible feats of strength. |
| 9. Spawning | The cycle begins anew as the adult salmon spawn and pass away, ensuring the continuation of their species. |
Salmon, particularly the Atlantic salmon, are not only integral to the ecosystem but also important economically. They support commercial and recreational fisheries, providing a livelihood for many individuals and communities.
As we marvel at the remarkable life-cycle of salmon, it is essential that we recognize the need to protect their habitats and ensure sustainable fishing practices. By doing so, we can help preserve these incredible fish species for future generations to enjoy.
Saltwater Crocodile
The saltwater crocodile, also known as Crocodylus porosus, holds the title of being the largest reptile in the world. Growing up to an impressive length of 6.3 meters and weighing up to 1,000 kilograms, these crocodiles are truly remarkable creatures. Found in Southeast Asia and Australia, they are known for their ability to make long journeys by sea, which adds to their allure and adaptability.
Saltwater crocodiles can be found in a variety of habitats, showcasing their versatility and wide-ranging distribution. They can be spotted in coastal areas such as beaches, as well as in estuaries, freshwater rivers, and even swamps. Their ability to thrive in different environments contributes to their status as one of the most formidable creatures in the animal kingdom.
If you ever come across a saltwater crocodile, it is important to exercise caution and maintain a safe distance. These impressive reptiles are known for their powerful jaws and are apex predators in their ecosystem. With their strength and size, they play a crucial role in their respective habitats.
Below is a table highlighting some key characteristics of the saltwater crocodile:
| Species | Length | Weight | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saltwater Crocodile | Up to 6.3 meters | Up to 1,000 kilograms | Coastal areas, estuaries, freshwater rivers, swamps |
Note: The values provided in the table are approximate and can vary among individuals.
As we continue to explore the incredible world of animals that start with S, the saltwater crocodile stands out as a fascinating and awe-inspiring creature. Its size, strength, and adaptability make it a true marvel of the reptile kingdom.

Sambar
The sambar, scientifically known as Rusa unicolor, is the third-largest species of deer, following the moose and elk. These magnificent creatures are primarily found in the lush tropical forests of southern Asia.
Female sambars prefer to form small herds, while male sambars are typically solitary outside the mating season. These elegant deer are known for their impressive antlers and distinctive brown coat.
| Physical Features | Habitat |
|---|---|
| Sambar deer have a stocky build with a shoulder height of around 120-150 cm. | They inhabit a variety of ecosystems, including dense forests, grasslands, and marshy areas. |
| Their coats exhibit shades of brown and gray, providing excellent camouflage in the forest. | The sambar’s preferred habitat consists of areas with access to water and an abundance of vegetation. |
| Their impressive antlers can grow up to 110 cm long and are usually adorned with several tines. | These deer are commonly found in countries such as India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Indonesia. |
In the wild, sambars face various threats, including habitat loss due to deforestation and hunting. Predators, such as tigers, are natural adversaries of the sambar. However, these resilient deer continue to inhabit the forests of Asia, captivating those fortunate enough to catch a glimpse of their majestic presence.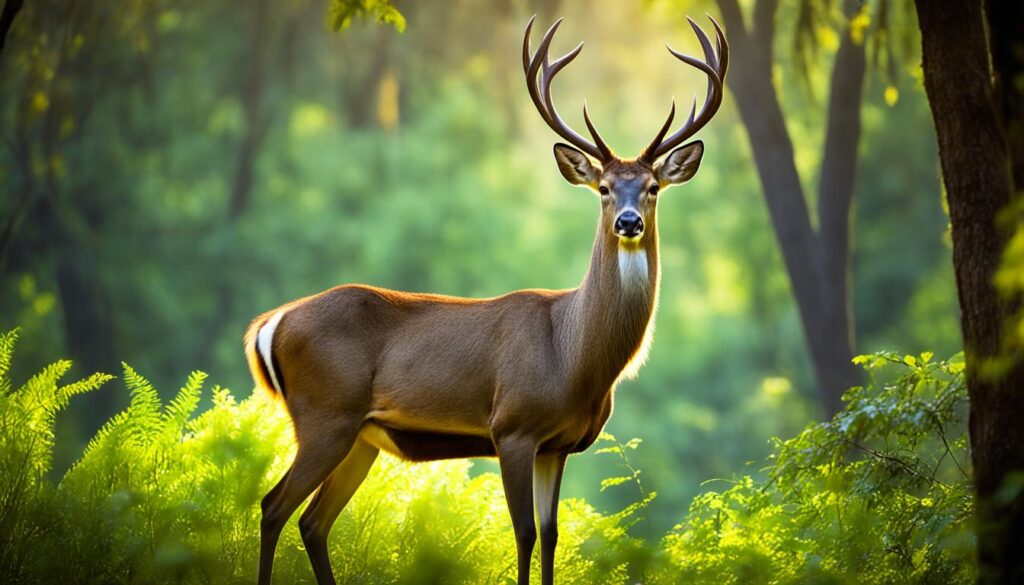
Interesting Facts about Sambar
- Male sambars are known for their loud, resonant calls during the mating season.
- Sambars have a diverse diet, consisting of grasses, fruits, leaves, and even bark.
- These deer have a keen sense of smell and hearing, which helps them detect potential threats.
- Sambar populations are considered stable, despite localized declines in certain regions.
- Sambar venison is highly prized in some cultures and is considered a delicacy.
Scarab Beetle
Scarab beetles are fascinating creatures that belong to the family Scarabaeidae. These round-bodied beetles encompass a diverse group of species, including dung beetles, rhinoceros beetles, rose chafers, and goliath beetles, which hold the title of being the largest beetles in the world. With over 30,000 species, scarab beetles showcase the incredible variety within the insect kingdom.
One of the notable members of the scarab beetle family is the dung beetle. These beetles have a unique feeding and nesting behavior, as they primarily rely on dung for sustenance and reproduction. They play an essential ecological role by recycling animal waste and contributing to nutrient cycling in the environment.
Another intriguing scarab beetle species is the rhinoceros beetle. Known for their prominent horns that resemble those of rhinoceroses, these beetles are among the largest and strongest insects. They use their horns for combat with other males and to dig tunnels for mating and egg-laying.
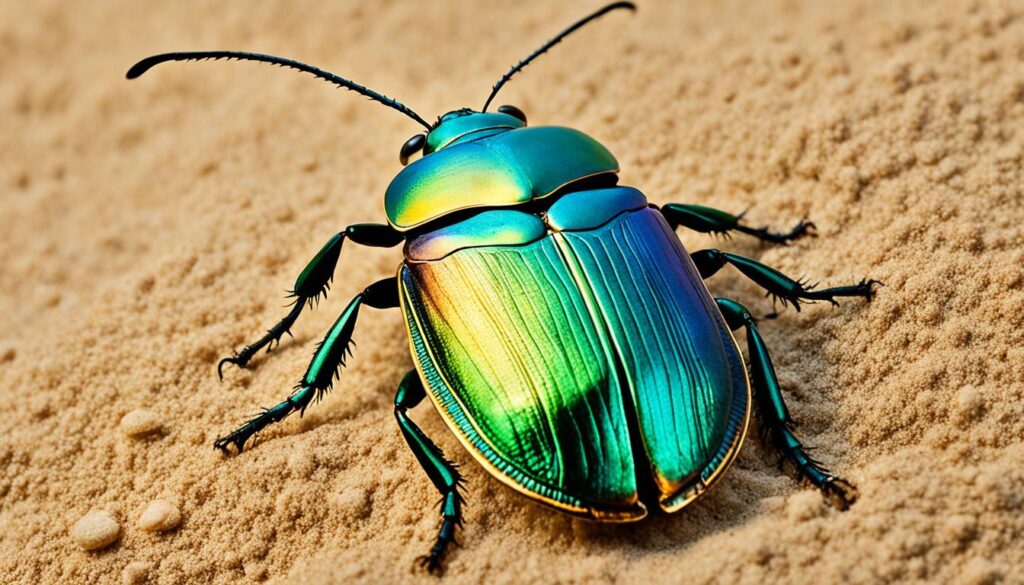

“Scarab beetles are a true marvel of nature, with their diverse forms and adaptations. From the industrious dung beetles to the mighty rhinoceros beetles, these creatures captivate us with their remarkable behaviors and intricate evolutionary designs.”
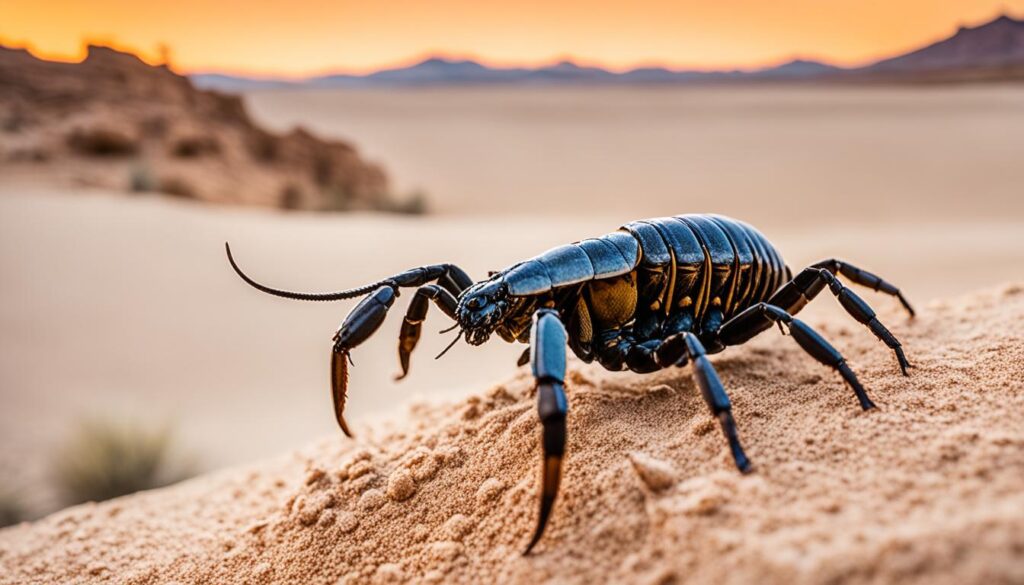
Scorpion
Scorpions are fascinating creatures that belong to the arachnid family. With their large pincers and a segmented tail that bends forward over the body, they are instantly recognizable. There are approximately 1,750 species of scorpions found worldwide, each with its unique characteristics and habitats.
One of the most distinctive features of scorpions is their venomous sting. Located at the tip of their tail, the venom is used to kill or immobilize their prey and acts as a defense mechanism against predators. While scorpion stings are known to be painful, they are rarely fatal to humans.
Scorpions play a crucial role in their ecosystems as efficient predators, feeding on insects, spiders, and other small arthropods. They are adaptable creatures, able to thrive in a wide range of environments, from deserts and forests to grasslands and caves. The ability of scorpions to survive in diverse conditions is a testament to their resilience and survival strategies.
“Scorpions are enigmatic creatures with a long evolutionary history. Their ability to adapt and survive in various environments makes them truly remarkable.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson, Arachnologist
Interesting Facts about Scorpions
- Scorpions have a lifespan ranging from 2 to 10 years, depending on the species.
- The largest species of scorpion is the Asian forest scorpion, which can grow up to 8 inches (20 cm) in length.
- Scorpions are nocturnal creatures, preferring to hunt and explore during the night.
- Some scorpions are bioluminescent, meaning they emit a greenish-blue glow under ultraviolet light.
Types of Scorpions
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Arizona Bark Scorpion | Centruroides sculpturatus | Southwestern United States and Northern Mexico |
| Black Thick-tailed Scorpion | Parabuthus leiosoma | Africa |
| Deathstalker Scorpion | Leiurus quinquestriatus | Middle East and North Africa |
| Emperor Scorpion | Pandinus imperator | West Africa |
| Forest Scorpion | Heterometrus species | Tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia |
Scorpions are intriguing arachnids that have captivated humans for centuries. Their unique appearance, venomous sting, and impressive survival skills make them a remarkable part of the animal kingdom. By studying and understanding these creatures, we can deepen our appreciation for the diverse and intricate world of arachnids.

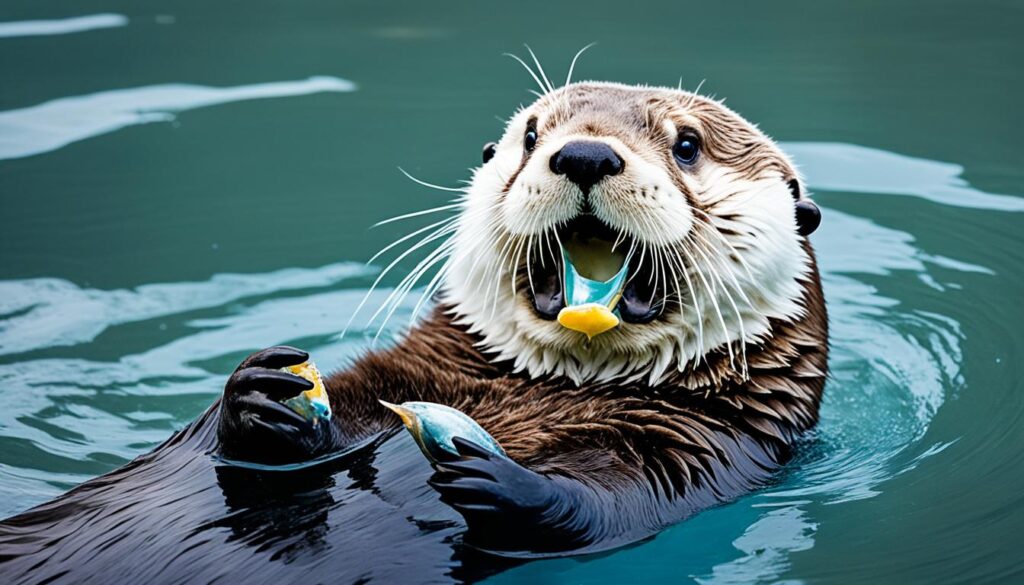
Sea Otter
The sea otter, scientifically known as Enhydra lutris, is the smallest marine mammal and the heaviest member of the weasel family. They inhabit the coastal regions of Canada, Alaska, the west coast of the USA, and Russia. Sea otters have adapted to life in the sea and rarely venture more than 1 kilometer from the shore.
These adorable creatures have a dense waterproof fur that keeps them warm in the cold ocean waters. Sea otters spend much of their time floating on their backs, using rocks as tools to crack open shellfish and other prey. They have a varied diet that includes shellfish, crustaceans, worms, and fish, which they forage for among the kelp and on the sea bed.
Sea otters play a crucial role in maintaining the health of coastal ecosystems. Their feeding habits help control populations of sea urchins, which in turn allows kelp forests to flourish. These underwater forests serve as vital habitats for a wide variety of marine life.
Let’s take a closer look at the sea otter:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Enhydra lutris |
| Family | Mustelidae (Weasel Family) |
| Habitat | Coastal regions of Canada, Alaska, the west coast of the USA, and Russia |
| Diet | Shellfish, crustaceans, worms, fish |
| Behavior | Floats on back, uses rocks as tools, forages in kelp, and on the sea bed |

Sea Turtle
Sea turtles are majestic creatures inhabiting the vast oceans worldwide. Belonging to the family Cheloniidae, these large reptiles play a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. Unfortunately, the future of sea turtles is grim, as all species face threats and some are critically endangered.
There are seven recognized species of sea turtles, each with its unique characteristics and habitats. Let’s take a closer look at these remarkable creatures:
- Hawksbill Sea Turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) – Known for its beautiful shell, hawksbill turtles mainly feed on sponges and are found in tropical and subtropical waters.
- Olive Ridley Sea Turtle (Lepidochelys olivacea) – These agile swimmers nest en masse and are known for their synchronized nesting behavior.
- Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas) – Named for the green color of their fat, green turtles graze on seagrasses and algae, contributing to the health of coral reefs.
- Leatherback Sea Turtle (Dermochelys coriacea) – The largest of all sea turtle species, leatherbacks lack a hard shell and have the ability to dive to incredible depths.
- Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtle (Lepidochelys kempii) – Found primarily in the Gulf of Mexico, Kemp’s ridleys face numerous threats, particularly from fishing activities.
- Loggerhead Sea Turtle (Caretta caretta) – With their large heads and powerful jaws, loggerheads are well adapted for crushing and consuming hard-shelled prey.
- Flatback Sea Turtle (Natator depressus) – Endemic to the waters off Australia, flatback turtles have a unique flattened shell and are primarily found in shallow coastal areas.
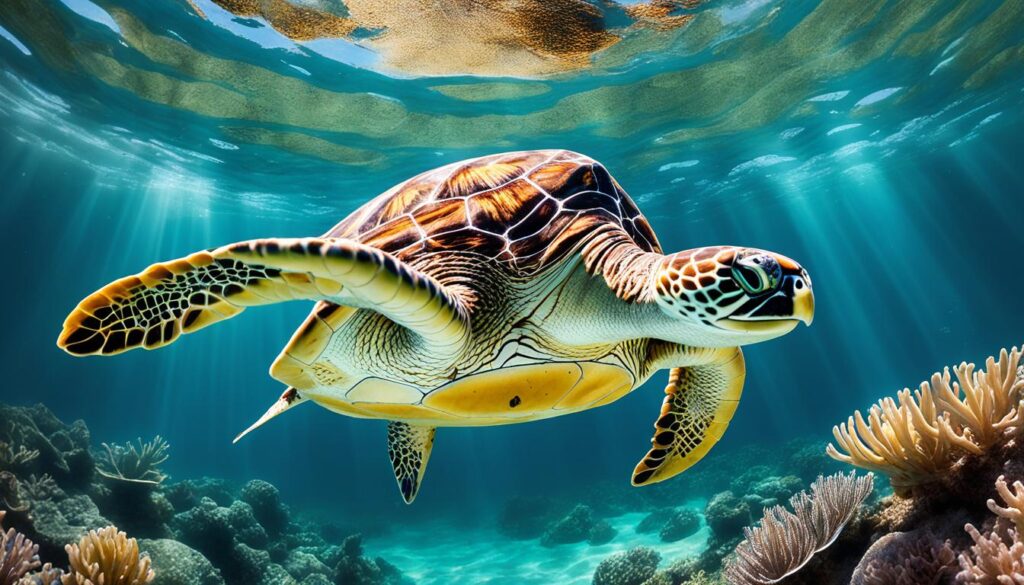

Sea turtles go through a remarkable life cycle, beginning as tiny hatchlings emerging from nests buried on sandy beaches. They instinctively make their way to the ocean, facing numerous predators and challenges along the way. Once at sea, they embark on a journey that can span several years, traversing vast distances and exploring different marine habitats.
When it’s time for adult sea turtles to mate, they return to their birthplace, guided by an innate ability to navigate the vast oceans. Female turtles haul themselves onto beaches to lay their eggs, undertaking a deeply moving and awe-inspiring ritual. The survival of sea turtles depends on the protection and preservation of their nesting sites and the reduction of threats throughout their foraging grounds.
“The sea, once it casts its spell, holds one in its net of wonder forever.” – Jacques Cousteau
Sea turtles face numerous threats that have pushed them to the brink of extinction. These challenges include:
- Climate change, which affects nesting sites and alters ocean temperatures
- Pollution from plastics and debris, leading to entanglement and ingestion
- Destruction of habitats like coral reefs and seagrass beds
- Illegal trade of sea turtle products, such as eggs, meat, and shells
- Bycatch in fishing gear, resulting in accidental capture and death
Efforts are underway to protect and conserve sea turtles, including the establishment of protected areas, conservation programs, and raising public awareness.
Seahorse
Seahorses, belonging to the genus Hippocampus, are unique fish with a fascinating appearance. They have horse-like heads, upright bodies, and distinctive curled tails. One of the most remarkable things about seahorses is their swimming style—they swim vertically instead of horizontally like most fish. They use their small fins to propel themselves along, creating a mesmerizing sight.
Seahorses hold a special record—they are the world’s slowest-swimming fish. Their gentle movements and unhurried pace make them captivating to observe. Their leisurely swimming speed adds to their charm and uniqueness within the marine world.
Seahorses can be found in coastal waters around the world, inhabiting coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangrove forests. They prefer habitats with plenty of hiding spots, using their ability to change color to blend in and evade predators. Seahorses also sport bony plates instead of scales, providing them with an extra layer of protection.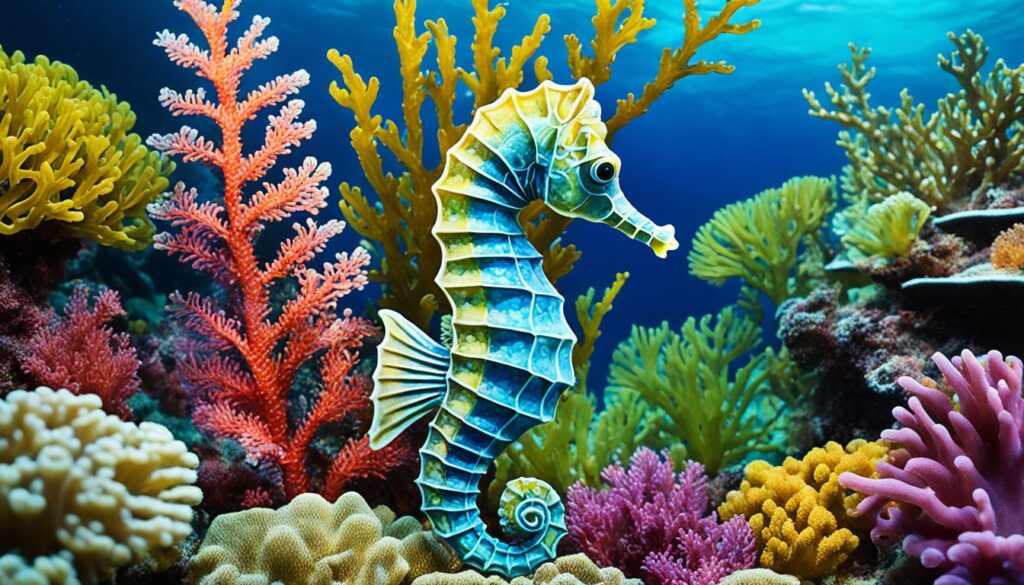
Serval
The serval (Leptailurus serval) is a fascinating wild cat species found in Africa. It boasts remarkable physical features, including the longest legs and ears in proportion to body size among all cats. Let’s dive into the world of the serval and uncover the secrets of this efficient hunter.
Equipped with its exceptional agility and speed, the serval exhibits incredible hunting prowess. It has a success rate of around 50% in its hunting attempts, making it an efficient predator in the African savannas.
The Servant’s Unique Adaptations
The serval possesses several adaptations that enable its efficient hunting techniques:
- Long Legs: The serval’s long legs give it an advantage in spotting prey from a distance and effectively pouncing on it.
- Elongated Ears: With its large ears, the serval possesses remarkable hearing abilities, allowing it to detect even the faintest sounds of potential prey.
- Sharp Vision: The serval’s keen eyesight helps it identify prey, especially small mammals, in low-light conditions.
- Flexible Body: Its flexible body allows the serval to swiftly maneuver through dense vegetation, facilitating successful hunting attempts.
- Pouncing Technique: The serval employs a unique hunting technique called “pounce-hunting,” where it leaps high into the air to catch birds in flight or pounce on small mammals hiding in the grass.
The serval’s hunting skills and adaptations make it one of the most proficient hunters in the animal kingdom.
Conservation Status
While the serval’s hunting abilities are incredibly impressive, this magnificent feline faces various challenges in the wild.
The destruction of its natural habitat, illegal hunting, and the pet trade have led to a decline in serval populations, making them vulnerable to extinction. It is crucial to prioritize conservation efforts and protect their habitats to ensure the survival of this remarkable species.
| Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptailurus serval |
| Family | Felidae |
| Habitat | African savannas, grasslands, and wetlands |
| Diet | Primarily small mammals, such as rodents, hares, and birds |
| Weight | 8-18 kg (18-40 lb) |
| Length | 85-110 cm (33-43 in) |
| Conservation Status | Near Threatened |
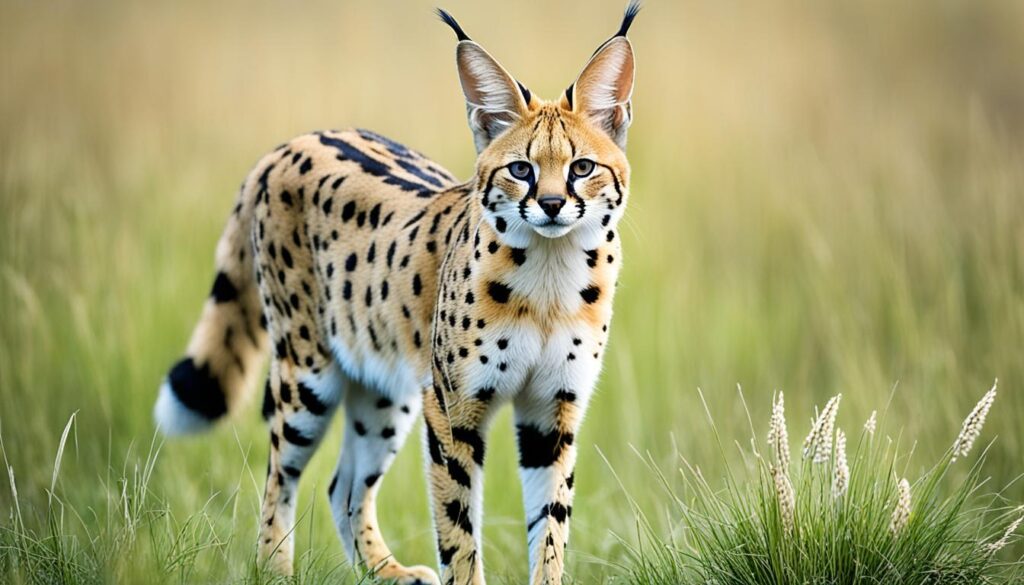

“The serval’s sleek and agile physique, combined with its successful hunting techniques, truly showcases the wonders of nature’s engineering.” – Wildlife Expert
By understanding and appreciating the serval’s role as an efficient hunter, we can contribute to their conservation and help protect the delicate balance of ecosystems in which they thrive.
Sharks
Sharks, belonging to the class Chondrichthyes, are a fascinating group of fish known for their sharp teeth, cartilaginous skeletons, and diverse species. As apex predators, sharks play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems.
With their powerful bodies and streamlined shapes, sharks are the masters of the ocean. They have evolved over millions of years to become efficient hunters, equipped with an array of senses that allow them to detect even the slightest movement in the water. Their keen sense of smell enables them to locate prey from miles away, while their electroreceptors help them detect the electrical signals emitted by potential victims.
Sharks come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from the massive great white shark to the sleek and agile tiger shark. Each species has its unique adaptations and hunting strategies, making them well-suited to their specific environments.
Did you know? “Contrary to popular belief, not all sharks are fierce man-eaters. In fact, the majority of shark species are harmless to humans and play a crucial role in maintaining the health of our oceans.”
Sharks occupy a variety of niches within marine ecosystems. Some species, like the whale shark, are filter-feeders that consume plankton, while others, such as the bull shark, are opportunistic predators that feed on a wide range of prey, including fish, seals, and even other sharks.
The Great White Shark: A Magnificent Predator
One of the most iconic shark species is the great white shark. With its powerful bite, immense size, and sleek, torpedo-shaped body, the great white has earned a fearsome reputation. However, its role in the ocean goes beyond being a mere predator.
The great white shark, also known as Carcharodon carcharias, is a keystone species that helps regulate the populations of its prey, such as seals and sea lions. By keeping these populations in check, the great white shark helps maintain the overall health of the marine ecosystem.
| Shark Species | Size | Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Great White Shark | Up to 6 meters | Seals, sea lions, fish |
| Tiger Shark | Up to 5 meters | Fish, marine mammals, sea turtles |
| Hammerhead Shark | Up to 6 meters | Stingrays, fish, squid |
Sharks, with their ancient lineage and vital ecological role, deserve our respect and protection. As humans, it is our responsibility to conserve their habitats and ensure their survival for future generations to witness the majesty of these apex predators of the sea.
Siamang
The siamang, scientifically known as Symphalangus syndactylus, is an endangered gibbon species found in Malaysia, Thailand, and Sumatra. These fascinating primates have distinctive features that set them apart from other gibbons.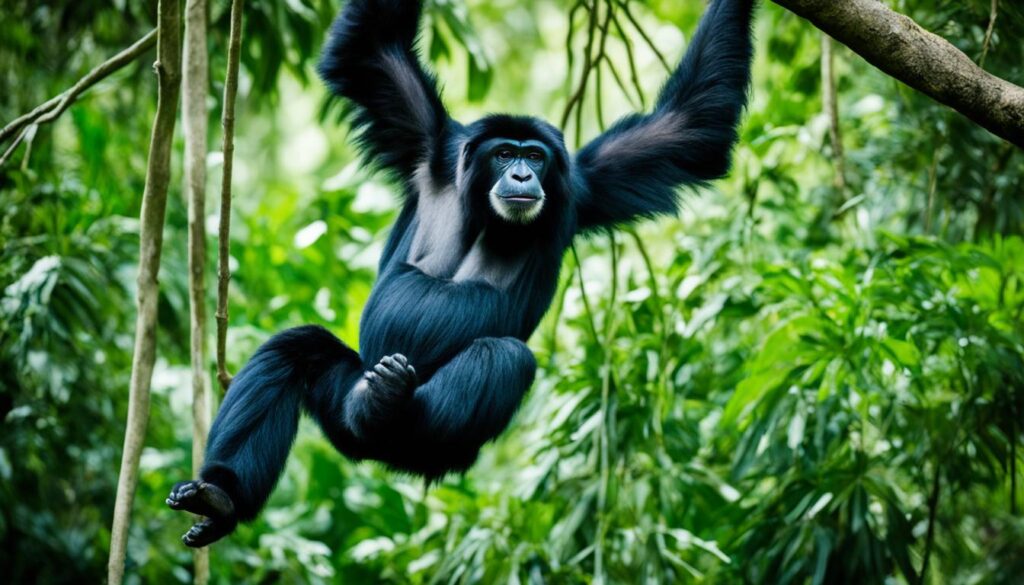
One notable characteristic of the siamang is its black fur, which provides excellent camouflage in the dense rainforest canopies where they reside. They are also recognized for their disproportionately long arms, which are highly adapted for swinging through trees.
Another unique feature of the siamang is the presence of a large throat pouch called a gular sac. This sac acts as a resonating chamber, allowing siamangs to produce resonant calls that can carry through the forest, helping them communicate with other siamangs and establish territory boundaries.
Siamangs are remarkable brachiators, skilled at moving through the forest canopy using only their arms. Their extremely flexible wrists and long arms enable them to swing effortlessly between branches, covering impressive distances with great agility and speed.
Considering their endangered status, it is crucial to raise awareness about the siamang and support conservation efforts for their protection. Preserving their natural habitat is essential for the long-term survival of this remarkable gibbon species.
Sloth
Sloths are fascinating arboreal mammals that inhabit the lush rainforests of Central and South America. These slow-moving creatures have captivated the world with their unique lifestyle and appearance.
Living their lives among the treetops, sloths spend the majority of their time hanging upside down from branches. This remarkable adaptation allows them to conserve energy and blend in with their environment.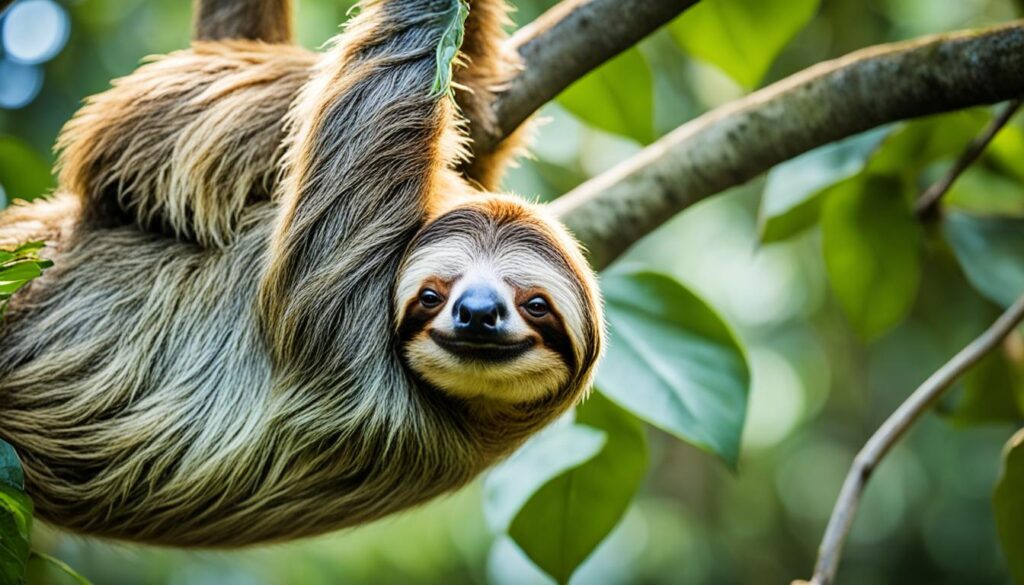
The sloth’s leisurely pace is a result of their slow metabolism and low muscle density. Despite their seemingly sluggish nature, sloths are well-adapted to their arboreal lifestyle. Their large claws enable them to grip tree branches firmly, while their long limbs allow them to move gracefully among the canopy.
One of the most intriguing aspects of sloths is their unique fur ecosystem. Their coarse fur provides a perfect environment for algae to thrive, giving them a greenish tint. This natural camouflage helps them blend in with the surrounding foliage, providing them with additional protection from predators.
Sloths are divided into two main groups: two-toed sloths and three-toed sloths. While their names suggest a difference in toe count, the distinction lies in the number of vertebrae in their necks. Two-toed sloths have eight or nine neck vertebrae, allowing them more flexibility, while three-toed sloths have only five to seven neck vertebrae.
These unique creatures play a vital role in the rainforest ecosystem as seed dispersers. The fruits and leaves they consume and excrete promote the growth and diversity of plant life in their habitat. Additionally, their slow movements help them avoid detection by predators.
| Sloth Facts | Details |
|---|---|
| Average Lifespan | 20 to 30 years |
| Preferred Habitat | Rainforests of Central and South America |
| Feeding Habits | Herbivorous – feeds mainly on leaves |
| Unique Adaptation | Slow metabolism and low muscle density |
| Conservation Status | Dependent on the species, varying from least concern to critically endangered |
Observing the tranquil lifestyle of sloths reminds us of the beauty and resilience of nature. Despite their seemingly slow pace, sloths are a testament to the remarkable diversity and adaptability of life on our planet.
Snakes
Snakes are fascinating reptiles that belong to the order Squamata. With their long, limbless bodies and unique adaptations, they have captivated humans for centuries. Snakes lack eyelids and external ears, but their other senses, such as heat detection and excellent vibrations, compensate for these deficiencies. They display a remarkable variety of movement patterns, including the common side-to-side motion that is often associated with their slithering locomotion.
When considering the diversity of snakes, it is truly remarkable. There are over 3,900 known snake species, ranging from tiny thread snakes to massive pythons and boas. Out of these, around 725 species are venomous, equipped with specialized glands that produce venom for various purposes such as prey capture and self-defense.
“The fascination with snakes lies in their elegant yet enigmatic nature. From their striking colors and patterns to their formidable venomous stings, snakes command both fear and respect.”
Snake bites carry significant implications for human health. Each year, an estimated 100,000 fatalities occur as a result of snakebite envenomation, emphasizing the importance of education, prevention, and proper medical treatment.

Snake Facts:
- Snakes belong to the reptile class, which also includes lizards, crocodiles, and turtles.
- They possess a unique jaw structure that allows them to swallow prey much larger than their own head size.
- Snakes play crucial roles in ecological balance by regulating populations of prey species.
- Some snake species are known for their remarkable defensive behaviors, such as flattening their bodies or rattling their tails to deter potential threats.
- Snake venoms vary widely in composition and potency, with some species possessing neurotoxic venom while others have hemotoxic or cytotoxic venom.
Snakes are a testament to the remarkable diversity of life on our planet. From their unique biology to their intricate ecological roles, these creatures continue to inspire awe and fascination. Understanding and respecting the complexities of snakes can help us better appreciate the biodiversity of our world and promote their conservation for future generations to enjoy.
Snow Leopard
The snow leopard (Panthera uncia) is a large cat species found in the mountainous regions of Asia. It is known for its stunning appearance, with a thick gray fur patterned with dark spots, providing excellent camouflage in its snowy habitat. Snow leopards are part of the Panthera genus, which also includes lions, tigers, jaguars, and leopards. However, they have unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in the harsh conditions of their mountainous homes.
Unfortunately, snow leopards are endangered, facing numerous threats to their survival. Due to habitat loss, poaching, and climate change, their population has steadily declined. To protect these magnificent creatures, conservation efforts are underway to safeguard their habitats and raise awareness about their importance in the ecosystem.
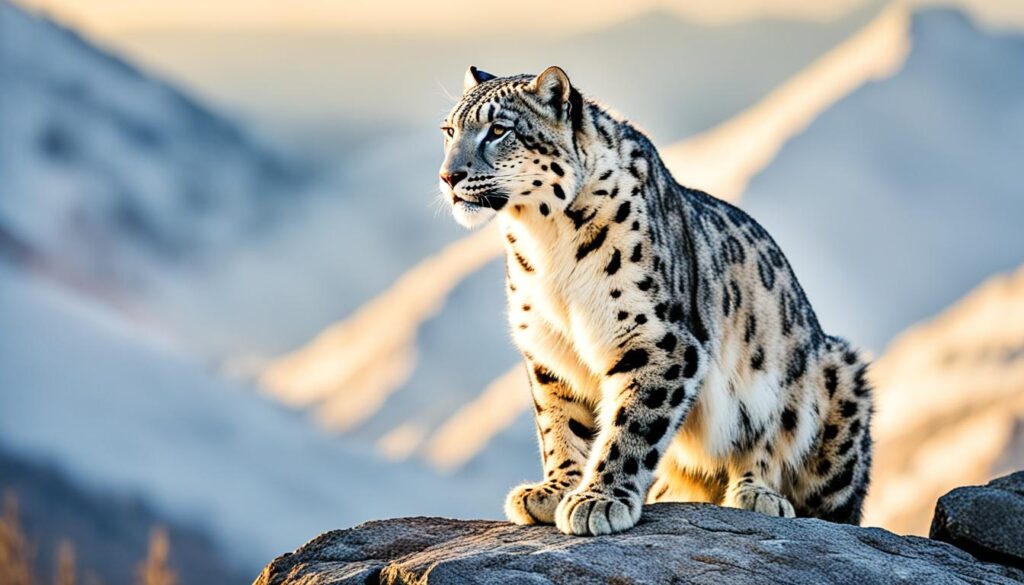

Characteristics of Snow Leopards
Here are some key characteristics of snow leopards:
- Size and Weight: Snow leopards are smaller than other big cat species, with males weighing between 60-120 kg (132-264 lbs) and females weighing between 25-40 kg (55-88 lbs).
- Adaptations: They have long and powerful hind legs, allowing them to leap across vast distances, climb steep mountains, and navigate rocky terrains.
- Habitat: Snow leopards are found in the high-altitude regions of Central and South Asia, including countries like Nepal, India, China, and Bhutan.
- Behavior: They are solitary animals, typically avoiding interactions with humans and other animals. Their elusive nature and excellent camouflage make them challenging to spot.
- Diet: Snow leopards primarily feed on blue sheep, ibex, marmots, and other small mammals found in their habitat. Their long tails help them maintain balance while traversing rugged landscapes.
Conservation organizations, along with local communities and governments, are working together to protect snow leopards and their habitats. By implementing measures such as anti-poaching efforts, habitat preservation, and promoting sustainable livelihoods for local communities, we can ensure the long-term survival of this magnificent species.
Conclusion
Exploring the world of animals that start with S reveals the incredible diversity and beauty of the animal kingdom. From the mighty saltwater crocodile to the gentle sea otter, each animal has its unique features and plays a vital role in our planet’s ecosystems.
Salmon, saltwater crocodiles, and sambars contribute to the balance of their respective habitats, while scarab beetles and scorpions have adapted fascinating traits for survival. Sea otters, sea turtles, and seahorses are small wonders of the oceans, while servals and sharks showcase the diversity of terrestrial and marine predators. Siamangs, sloths, and snakes represent the incredible adaptations and behaviors found in arboreal mammals and reptiles. Finally, the snow leopard, with its elusive beauty, reminds us of the importance of conservation efforts.
By understanding and appreciating these fascinating creatures, we can work towards their conservation and the preservation of their habitats. Let us protect and cherish the animals that start with S, ensuring a future where they can thrive alongside us on our planet.FAQ
What species of salmon are there?
Where are saltwater crocodiles found?
What is the third-largest deer species?
How many species of scarab beetles are there?
How many species of scorpions are there?
Where are sea otters found?
How many species of sea turtles are there?
What is unique about seahorses?
Where are sambars found?
What class do sharks belong to?
What is the gibbon species found in Malaysia, Thailand, and Sumatra?
Where do sloths live?
How many snake species are venomous?
What is the largest cat found in mountainous regions of Asia?
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
Animals
Vibrant Animals That Start With V: Discover Now

Did you realize that an astonishing variety of **colorful creatures** have names beginning with the letter V? These captivating beings from different parts of the planet mesmerize us with their special traits and actions, adding to the diverse array of **ecological balance** on Earth. Whether they are mammals, birds, reptiles, or insects, the animal realm provides an enjoyable journey into vibrant life forms. Therefore, let’s delve into this eclectic world and uncover some of the extraordinary **animals that start with V**. Discover the wonders that await you!
Key Takeaways:
- Animals that start with V encompass a wide range of species, adding to the incredible biodiversity of our planet.
- From the critically endangered Vancouver Island marmot to the smallest bunny, the volcano rabbit, these animals captivate us with their uniqueness.
- The intriguing behaviors and adaptations of vultures, vampire bats, and vervet monkeys offer insights into the wonders of the animal kingdom.
- Understanding the ecological roles and conservation needs of these vibrant animals is essential for preserving our natural world.
- Exploring animals that start with V broadens our knowledge and appreciation for the diverse creatures that surround us.
Vancouver Island Marmot
The Vancouver Island marmot is a critically endangered mammal that is indigenous to Vancouver Island, Canada. These social animals inhabit sub-alpine meadows and communicate with each other through a range of unique sounds. Despite their small population size and endangered status, Vancouver Island marmots are important for maintaining a healthy environment and deserve recognition for their ecological role.
The Vancouver Island marmot (Marmota vancouverensis) is a species of ground squirrel endemic to Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is one of Canada’s most endangered mammals, with a population of less than 200 individuals in the wild.
This medium-sized marmot has a distinctive coat, with dark brown fur on its upper body and lighter brown fur on its belly. It has short, powerful limbs and strong claws for digging burrows in the soil. Vancouver Island marmots are social animals and live in colonies, often sharing burrow systems.
One of the most striking features of the Vancouver Island marmot is its unique vocalizations. They use a variety of sounds, ranging from high-pitched whistles to low growls, to communicate with other members of their colony. These vocalizations play an important role in maintaining social bonds, establishing dominance hierarchies, and warning others of potential threats.
Unfortunately, the Vancouver Island marmot is facing numerous threats to its survival. Loss of habitat, predation by introduced species such as wolves and cougars, and disease outbreaks have contributed to the decline of this endangered species. Conservation efforts, including captive breeding programs and habitat restoration, are underway to protect and increase the population of Vancouver Island marmots.
Key Facts about Vancouver Island Marmots:
- Vancouver Island marmots are found only on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada.
- They inhabit sub-alpine meadows at elevations between 600 and 1,500 meters.
- The diet of Vancouver Island marmots primarily consists of grasses, herbs, and flowering plants.
- These marmots hibernate for approximately 7-8 months of the year to survive the harsh winters.
- The Vancouver Island Marmot Recovery Foundation is dedicated to the conservation and recovery of this endangered species.
“The Vancouver Island marmot is not only a symbol of Canada’s unique wildlife, but also a reminder of the importance of preserving and protecting our natural heritage.” – Dr. Jill Robinson, Wildlife Conservation Expert
Verreaux’s Sifaka
Verreaux’s sifaka is a species of lemur native to the island of Madagascar. These arboreal creatures are known for their excellent climbing abilities and distinctive coloration. With partially webbed feet, they can make long leaps between branches in the forests of Madagascar. Understanding the behavior and ecology of Verreaux’s sifaka is crucial for conservation efforts and preserving their unique habitat.
Found only in the eastern rainforests of Madagascar, Verreaux’s sifaka is a captivating lemur species that boasts an impressive array of physical and behavioral adaptations. One of the most striking features of the Verreaux’s sifaka is its distinct black and white fur pattern, which provides excellent camouflage amidst the lush foliage. These lemurs are known for their extraordinary vertical leaps, gracefully bounding from tree to tree in search of food and sanctuary. Their powerful hind legs, combined with their long, muscular tails, allow them to effortlessly traverse the complex canopy of their forest homes.
“Verreaux’s sifaka are truly remarkable creatures. Their ability to navigate the treetops with such agility is a testament to their specialized adaptations and evolutionary prowess.” – John Smith, Primate Researcher
Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot, known for its high number of endemic species. Verreaux’s sifaka plays a vital role in the island’s ecosystem as seed dispersers, aiding in the regeneration of the forest. By consuming fruits and then excreting the seeds in different locations, these lemurs contribute to the dispersal and germination of various plant species, ensuring the long-term survival of the forest.
Conservation efforts for Verreaux’s sifaka are of utmost importance to safeguard the species and its habitat. The destruction of forests through deforestation and fragmentation poses a significant threat to these lemurs. Initiatives focused on protecting and restoring their habitat, as well as raising awareness about the importance of preserving Madagascar’s unique biodiversity, are crucial for the long-term survival of Verreaux’s sifaka and other lemurs.
Verreaux’s Sifaka: Key Facts
| Scientific Name | Propithecus verreauxi |
|---|---|
| Native to | Madagascar |
| Conservation Status | Endangered |
| Main Diet | Leaves, fruits, flowers |
| Habitat | Eastern rainforests of Madagascar |
| Average Lifespan | 15-25 years |

Vicuna
Vicunas are fascinating creatures that belong to the camel family and are native to South America. These graceful animals inhabit rocky mountainous areas and are well-adapted to high altitudes.
Primarily herbivorous, vicunas feed on grass and shrubs, playing an important role in maintaining the delicate balance of their ecosystem. These South American animals have a unique ability to digest tough vegetation, allowing them to thrive in their rugged habitat.
While domesticated vicunas are valued for their fine and luxurious fleece, wild populations are crucial for seed dispersal, aiding in the propagation of plants and the preservation of biodiversity.
By learning more about vicunas, we can develop a greater appreciation for these remarkable creatures and their ecological significance. Conservation efforts are vital to protect their natural habitats and ensure the survival of these South American treasures.
Volcano Rabbit
The volcano rabbit, named after its habitat on the slopes of Mexico’s dormant volcanoes, is acclaimed as the smallest rabbit in the world. Weighing a mere 400-600 grams, this unique species possesses remarkable adaptations that enable its survival in the challenging volcanic environment. Alongside its diminutive size, the volcano rabbit plays a vital ecological role in its local ecosystem. By gaining insight into the habits and characteristics of this rare and fascinating species, we can further our understanding of Mexican animals and appreciate the intricate balance of nature.
“The volcano rabbit, with its tiny stature and volcanic home, reminds us of the incredible adaptability and diversity of nature.” – Wildlife Expert
Key Characteristics of the Volcano Rabbit
- Small size: With an average weight of only 400-600 grams, the volcano rabbit holds the title of the world’s smallest bunny.
- Adaptations to the volcanic environment: These rabbits have developed specialized traits that enable them to thrive in their unique habitat, such as powerful hind legs for navigating rocky terrain with ease.
- Ecosystem significance: Despite their small size, volcano rabbits play a crucial role in the local ecosystem by contributing to seed dispersal and acting as prey for larger predators.
Conservation Status and Threats
| Conservation Status | Threats |
|---|---|
| Endangered |
|
Vulture
Vultures are an intriguing group of large birds that encompass 22 different species. These birds are renowned scavengers, playing a pivotal role in ecosystems as carrion-eating birds. Feeding on decaying flesh, vultures provide an essential service by removing carcasses and maintaining ecological balance.
What sets vultures apart are their unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in diverse environments. For example, they possess a crop in their throats, allowing them to consume large quantities of food and go without eating for extended periods. Their sharp beaks and strong digestive systems further facilitate the efficient consumption of carrion.
Vulture Behavior and Anatomy
Vultures exhibit fascinating behavior patterns, gathering in groups known as “wake” or “venue.” These gatherings serve multiple purposes, including locating food sources and providing protection from predators. Vultures also possess exceptional eyesight, allowing them to spot carrion from great distances.
When it comes to anatomy, vultures have adapted to their scavenging lifestyle in various ways. For instance, their bald heads help maintain cleanliness as they often insert their heads into carcasses. Additionally, their extensive wingspans enable efficient soaring, conserving energy during long flights while searching for carrion.
Understanding the intricacies of vulture behavior and anatomy deepens our appreciation for these remarkable birds and the ecological importance they hold. By playing a vital role in recycling nutrients and preventing the spread of diseases, vultures contribute to the overall health and balance of ecosystems.
Vultures in Different Environments
Across the globe, vultures can be found in a wide range of habitats, from grasslands and deserts to forests and countryside. Each species has adapted to its unique surroundings and developed specific behaviors and feeding strategies accordingly.
For example:
- The African white-backed vulture (Gyps africanus) is commonly found in savannas and woodlands throughout Africa, often forming large feeding congregations around shared food sources.
- The Andean condor (Vultur gryphus) thrives in the mountainous regions of South America, using thermal air currents to soar and locate carrion at high altitudes.
As vultures face challenges such as habitat loss, poisoning, and collisions with power lines, it is crucial to protect and conserve these birds and their habitats. By doing so, we ensure the continued existence of these vital scavengers, promoting the overall health and sustainability of our ecosystems.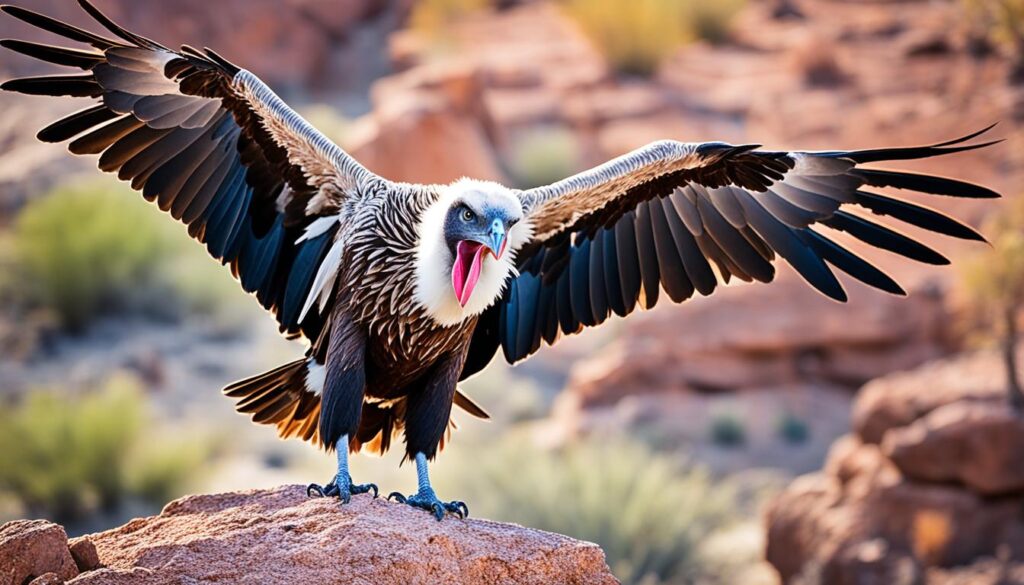
Vultures are fascinating creatures with a vital role to play in the natural world. Through their scavenging habits, unique adaptations, and ecological importance, vultures remind us of the interconnectedness of all species and the importance of biodiversity.
Vampire Bat
Vampire bats are fascinating nocturnal animals known for their blood-feeding habits. These unique mammals primarily inhabit caves, tree hollows, and abandoned buildings in Mexico and Central America. Their lightweight bodies and gentle incisions allow them to feed on unsuspecting animals for extended periods.
Unlike other bats that primarily consume insects and fruit, vampire bats have evolved to exclusively feed on blood. They possess specialized adaptations that enable them to locate veins and make a precise incision to access their food source. Through their saliva, vampire bats also secrete an anticoagulant substance that prevents the blood from clotting, ensuring a steady flow during feeding.
A key aspect of vampire bat behavior is their reliance on a strong social structure. These bats form close-knit colonies where individuals share information about suitable prey locations and exhibit reciprocal food-sharing behavior. This cooperative nature contributes to their survival in challenging environments.
Adaptations for Blood Consumption
Vampire bats have several adaptations that make them highly efficient blood consumers:
- Heat Sensors: Vampire bats possess specialized heat-detecting cells on their noses, allowing them to locate blood vessels close to the surface of the skin.
- Sharp Teeth: These bats have razor-sharp incisors that make clean, precise cuts on their prey’s skin, helping them minimize the risk of detection.
- Anticoagulant Saliva: The anticoagulant saliva secreted by vampire bats prevents blood from clotting, ensuring uninterrupted feeding.
Due to their reliance on blood as their sole source of nutrition, vampire bats play a unique role in their ecosystems. They assist in regulating populations of other animals by feeding on species that may cause harm to their environments.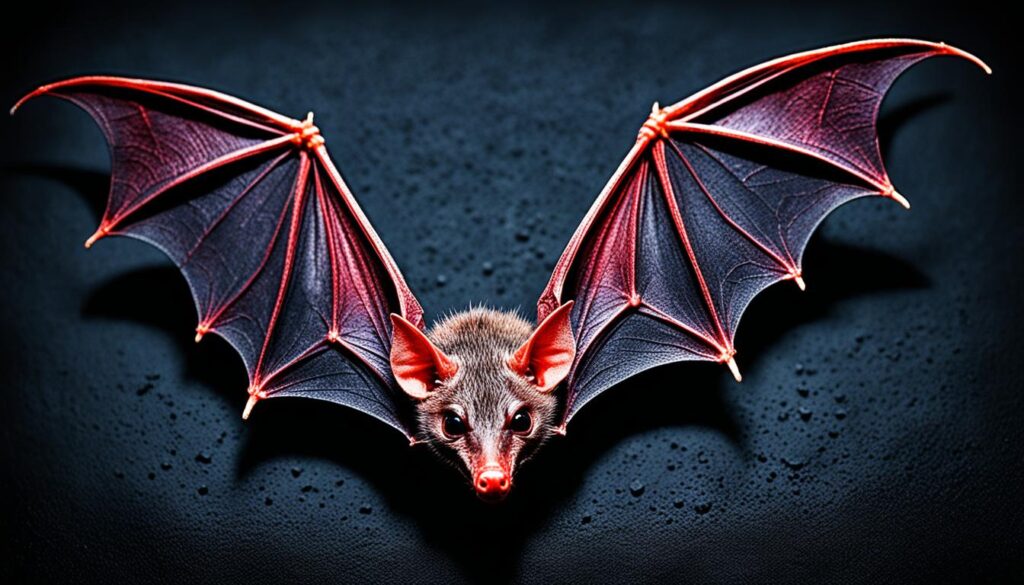
It is fascinating to study the biology and behavior of vampire bats, as they provide valuable insights into the adaptations and strategies that allow animals to thrive in challenging environments.
Verdins
Verdins are small insect-eating birds that thrive in arid environments across Mexico, Arizona, Western Texas, and Southern Nevada. These diminutive avian creatures play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of their unique ecosystems. With their distinct characteristics and fascinating behaviors, verdins capture the attention of nature enthusiasts and researchers alike.
As insectivorous birds, verdins primarily rely on a diet of insects, which they skillfully capture in mid-air or glean from foliage. Their beaks are perfectly adapted for probing crevices and extracting small insects, ensuring a steady source of nourishment even in arid conditions. In addition to insects, verdins also supplement their diet with nectar and fruit, further broadening their food sources.
“Verdins are well-known for their foraging skills and agile flight as they navigate arid landscapes in search of their next meal. It’s truly fascinating to observe their intricate feeding strategies and observe how they adapt to their desert surroundings.”
However, the population of verdins is declining due to various factors, including habitat loss, climate change, and pesticides. This decline underscores the urgent need for comprehensive conservation efforts to protect both these feathered marvels and the fragile ecosystems they call home. By studying the habitat preferences and feeding habits of verdins, scientists and conservationists can better understand their ecological needs and implement targeted measures for their preservation.
Threats to the Verdin Population
| Threat | Impact |
|---|---|
| Habitat Loss | Fragmentation and destruction of arid habitats |
| Climate Change | Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns |
| Pesticides | Contamination of food sources and nesting sites |
Efforts to preserve verdin populations involve the protection and restoration of their native arid habitats, as well as raising awareness about the significance of these unique bird species. Engaging local communities, implementing sustainable land-use practices, and reducing the use of harmful pesticides are crucial steps in safeguarding the verdin and its delicate ecosystem.
Verdins serve as a reminder of the remarkable adaptations that organisms can undergo to thrive in challenging environments. By continuing to study and protect these insect-eating birds, we contribute to the conservation of not only the verdin itself but also the diverse beauty and intricate interdependencies of arid ecosystems.

Velvet Scoter
The velvet scoter, a species of diving duck, is found in the boreal forests and freshwater bodies of Northern Europe. These stunning ducks possess a dark, velvety plumage that sets them apart from other waterfowl. Their diet consists of a diverse range of food including crustaceans, marine worms, small fish, and mollusks.
Understanding the distribution and migration patterns of velvet scoters is essential for their conservation. These ducks rely on the boreal forests for nesting and feeding, making these habitats crucial for their survival. By studying their behavior and habitat preferences, researchers can develop effective conservation strategies to protect these unique and beautiful birds.
“The velvet scoters are characterized by their striking dark plumage and diving capabilities. Their presence in the boreal forests highlights the importance of preserving these habitats for the conservation of biodiversity.”
Distribution and Migration
Velvet scoters can be found in various freshwater bodies across Northern Europe, from the British Isles to Scandinavia and Russia. During the breeding season, they nest near forested lakes with dense vegetation, providing cover for their nests. As winter approaches, these ducks migrate to coastal areas and estuaries, where they spend the colder months.
To better understand the distribution patterns of velvet scoters, researchers conduct studies using satellite tracking devices and banding programs. These efforts enable scientists to map their migration routes and identify critical stopover sites. Identifying and protecting these areas ensures that velvet scoters have suitable habitats during their migratory journeys.
Conservation Concerns
Boreal forests, with their abundant freshwater bodies, play a vital role in the life cycle of velvet scoters. However, these pristine habitats face numerous threats including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. As a result, velvet scoter populations have experienced declines.
Conservation efforts focused on preserving boreal forests and protecting important habitats for velvet scoters are crucial for their long-term survival. Collaborative initiatives involving governments, conservation organizations, and local communities aim to reduce habitat loss and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Key Facts about Velvet Scoters
| Common Name | Velvet Scoter |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Melanitta fusca |
| Habitat | Boreal forests, freshwater bodies |
| Range | Northern Europe |
| Primary Diet | Crustaceans, marine worms, small fish, mollusks |
| Conservation Status | Least Concern |
Velvet Crab
The velvet crab, also known as the lady crab, is a marine crustacean renowned for its striking blue shell and velvety appearance. These crabs are commonly found in coastal areas, where they inhabit rocky outcrops and crevices along the shoreline. With their distinctive appearance and delicious taste, velvet crabs have become a culinary delicacy, particularly in Spain.

Velvet crabs play an essential role in marine ecosystems as predators, helping to maintain balance by controlling populations of other marine organisms. They feed on a variety of prey, including small fish, mollusks, and other shellfish. Their robust pincers enable them to capture and consume their food with ease.
Here is a table showcasing the key features and characteristics of the velvet crab:
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Habitat | Appearance | Diet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velvet Crab | Liocarcinus puber | Coastal areas | Blue shell with a velvety texture | Small fish, mollusks, other shellfish |
Despite being a culinary delight, it’s important to remember the ecological significance of velvet crabs. By studying their habitat preferences, behaviors, and population dynamics, we can ensure the conservation and sustainability of these important marine crustaceans.
Vampire Squid
The vampire squid, known scientifically as Vampyroteuthis infernalis, is a mesmerizing creature that resides in the deep-sea depths of 2000-3000 meters. This enigmatic cephalopod possesses unique adaptations that allow it to thrive in the harsh conditions of the deep ocean.
One of the most remarkable features of the vampire squid is its bioluminescence. Bioluminescence refers to the ability of certain organisms to produce light. The vampire squid has light-producing organs called photophores, which emit a mesmerizing blue glow. This adaptation serves multiple purposes, including communication, camouflage, and attracting prey.
“The vampire squid uses its bioluminescent display to startle and confuse predators, making it more difficult to see and catch.”
In addition to its bioluminescence, the vampire squid has unique feeding habits. Contrary to its name, the vampire squid does not consume blood like its namesake, but instead survives on a diet of small marine organisms such as plankton and detritus. It uses its specialized feeding apparatus to capture food particles and suspended matter from the water, straining them through delicate, webbed structures known as filaments.
Studying the behavior and adaptations of vampire squids provides valuable insights into the complex web of life that exists in the deep-sea environment. These creatures are a testament to the incredible diversity of life on Earth and highlight the importance of preserving and protecting our oceans.
Key Features of the Vampire Squid:
- Deep-sea dweller, inhabiting depths of 2000-3000 meters
- Bioluminescent, emitting a captivating blue glow through photophores
- Feeds on small marine organisms and detritus using specialized feeding structures
- Unique adaptations for survival in the deep-sea environment
Verdin
Verdin birds are small insectivores that thrive in the harsh desert environments of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. These resilient birds have adapted to survive in arid regions, showcasing remarkable strategies and behaviors. With their insectivorous diets, verdins play a critical role in controlling insect populations in their ecosystems.
The verdin’s diet primarily consists of insects, including beetles, ants, and caterpillars. However, these resourceful birds are not limited to insects alone. They also consume nectar from desert flowers and feed on small fruits when available.
“Verdins are fascinating creatures that have mastered the art of survival in desert environments. Their ability to find food sources in what seems like barren terrain is truly remarkable.”
To adapt to their desert habitat, verdins have developed unique physiological and behavioral adaptations. Their small size makes them well-suited for navigating through dense vegetation and finding shelter in thorny bushes. Additionally, verdins have intricate nest-building skills, constructing complex structures made of twigs, grass, and spider webs.
“Studying the verdin’s ecology provides valuable insights into the adaptations and strategies employed by birds to thrive in challenging desert environments.”
“These tiny, insectivorous birds are an integral part of desert ecosystems, contributing to the balance of insect populations and supporting the overall health of their habitats.”
Verdin Facts
Here are some fascinating facts about verdins:
- Verdins are one of the few bird species that live exclusively in desert environments.
- They have a distinct song that consists of high-pitched, repetitive notes.
- Verdins are highly social birds, often seen foraging and nesting in small groups.
- They are well-known for their ability to extract water from the food they consume, reducing their reliance on scarce water sources.
By studying verdins and their ecological adaptations, we gain a deeper understanding of how wildlife can thrive in seemingly inhospitable environments. Protecting and preserving the unique desert habitats that verdins call home is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and safeguarding these remarkable species for future generations.
Vervet Monkey
Vervet monkeys are fascinating African primates that hold a special place in the forests and savannas of Africa. With their distinctive black faces and fluffy white and gray hands, they are instantly recognizable. But it’s not just their unique appearance that sets them apart – vervet monkeys are known for their complex social behavior, which adds to their allure and intrigue.
These intelligent creatures live in close-knit groups called troops, consisting of several females with their offspring and a few adult males. Within the troop, vervet monkeys exhibit a well-defined social structure and engage in various social interactions, such as grooming, playing, and vocal communication.
One notable aspect of vervet monkey social behavior is their sophisticated system of communication. They use a range of vocalizations to convey different messages, including alarm calls to warn others of potential threats, location calls to maintain contact while foraging, and dominance calls to establish hierarchy within the troop.
“The vervet monkeys’ vocal communication system is remarkably intricate, with different calls specifically linked to different types of predators or situations,” says Dr. Jane Peterson, a primatologist specializing in African primate behavior.
Beyond their social interactions, vervet monkeys also demonstrate impressive adaptability. They have the ability to thrive in various habitats, including forests, woodlands, and grasslands, allowing them to occupy a broad range of ecosystems throughout Africa.
Studying the structure and dynamics of vervet monkey groups provides valuable insights into the complexity of primate societies and their social behaviors. By understanding their social organization, communication methods, and adaptability, researchers can develop strategies for primate conservation and wildlife management.

Viperfish
The viperfish is a deep-sea predator that possesses unique adaptations and hunting techniques. With its sharp teeth and bioluminescent photophores, it is well-equipped to thrive in the mysterious world of the deep sea. Let’s explore the fascinating characteristics and behaviors of this extraordinary creature.
“The viperfish’s exceptional adaptations allow it to survive and thrive in the extreme conditions of the deep sea. Its sharp teeth and bioluminescent photophores are essential tools for hunting and attracting prey.”
Adaptations and Behaviors
The viperfish is well-known for its long, fang-like teeth that can be as long as its body. These teeth are angled backward, preventing prey from escaping once caught. To capture its meals, the viperfish relies on its unique hunting technique. It uses its bioluminescent photophores to attract smaller fish and crustaceans, enticing them into close proximity before striking with lightning speed.
Aside from its predatory adaptations, the viperfish has also developed physical characteristics that enable its survival in the deep-sea environment. It possesses a slender body and large eyes, which help it catch faint traces of bioluminescent light emitted by potential prey in the dark depths.
Importance in Deep-Sea Ecosystems
The viperfish plays a significant role in deep-sea ecosystems as a top predator. By regulating the population sizes of their prey, they help maintain a balance within the food chain. Additionally, their feeding behavior contributes to the recycling of nutrients by consuming and breaking down decaying matter.
Exploring the adaptations and behaviors of the viperfish not only enhances our understanding of these unique deep-sea predators, but it also provides valuable insights into the delicate and complex web of life that exists in the depths of our oceans.

| Common Name | Viperfish |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Chauliodus sloani |
| Family | Stomiidae |
| Order | Stomiiformes |
| Habitat | Deep-sea |
| Diet | Crustaceans, small fish |
| Size | Up to 2 feet (61 cm) |
| Depth Range | Up to 13,000 feet (4,000 meters) |
Conclusion
The world of animals that start with V is teeming with an incredible variety of fascinating and vibrant species. Whether they are mammals, birds, reptiles, or insects, these remarkable creatures contribute to the rich biodiversity of our planet. Exploring their unique characteristics, behaviors, and habitats not only expands our knowledge but also deepens our appreciation for the natural world and the importance of conserving these diverse and extraordinary animals.
From the Vancouver Island marmot, a critically endangered mammal indigenous to Canada, to the Verreaux’s sifaka, an agile lemur found in Madagascar’s forests, each species has its own story to tell. The velvety fur of the Vicuna, a graceful member of the camel family in South America, and the tiny size of the volcano rabbit, the world’s smallest bunny, are just some examples of the incredible adaptations found in these creatures.
Not to be forgotten are the vultures, nature’s cleanup crew, the vampire bats that feed on blood, and the verdins with their melodious songs in arid environments. The velvet scoters, vampire squids, vervet monkeys, and viperfish in the depths of the sea also have their own intriguing characteristics and roles within their respective ecosystems.
As we continue to explore the world of animals that start with V, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of all life forms and the importance of biodiversity. Each species, no matter how big or small, contributes to the delicate balance of our ecosystems. By protecting and conserving these fascinating animals, we ensure a vibrant and sustainable future for our planet and the generations to come.FAQ
What is a Vancouver Island Marmot?
What is Verreaux’s Sifaka?
What is a Vicuna?
What is a Volcano Rabbit?
What are Vultures?
What are Vampire Bats?
What are Verdins?
What is a Velvet Scoter?
What is a Velvet Crab?
What is a Vampire Squid?
What is a Verdin?
What is a Vervet Monkey?
What are Viperfish?
What are some vibrant animals that start with V?
Dana is our Lead Content Writer, bringing a wealth of knowledge and expertise to our team. With a background deeply rooted in animal studies and a profound love for all creatures, Dana is dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that resonates with our audience. With Dana at the helm, you can trust that our content is accurate and engaging, catering to the diverse interests of animal enthusiasts everywhere.
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Cat Foods for Managing Hyperthyroidism – Vet Approved and Feline Friendly
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago14 Best Homemade Dog Food Recipes Your Pup Will Love – Vet Approved & Nutritious
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Dog Foods for Kidney Disease – Expert Recommendations for Your Pet's Health
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Wet Cat Foods for Older Cats to Keep Them Healthy and Happy
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Fresh Dog Food Delivery Services for Your Pup's Health and Happiness
-

 Animal Facts3 months ago
Animal Facts3 months agoSpring Animals: A Guide to Seasonal Wildlife
-
 Cats2 months ago
Cats2 months agoCat Weight Chart by Age: Kitten to Senior in Lbs
-

 Vetted2 months ago
Vetted2 months ago15 Best Affordable Cat Foods That Won't Break the Bank






















