Get to know How to Improve Your Memory?
Memory plays a fundamental role in our daily lives, The human mind is a remarkable thing, capable of storing and recalling a vast amount of information. But how exactly does this process work? Memory is the foundation of our experiences, shaping who we are and influencing everything we do.
 |
| Memory - What is memory and its types?. |
In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of memory, exploring its different types and how it functions within us.
What is Memory?
Memory is the remarkable ability of the human mind to acquire, store, and retrieve information. It is the foundation of our experiences, shaping our thoughts, actions, and sense of self. Without memory, we would be unable to learn, form relationships, or navigate the world around us.
Memory is not a single process but rather a complex system involving various stages and mechanisms. It begins with encoding, where we convert sensory information into a form our brains can process. This encoded information is then transferred to short-term memory for temporary storage, allowing us to hold onto it for immediate use.
Over time, through a process called consolidation, some of this short-term information is transferred to long-term memory, where it becomes a permanent part of our knowledge and experiences. Long-term memory is further divided into explicit memory, which allows us to recall specific events and facts, and implicit memory, which involves unconscious skills and habits.
Factors Influencing Memory
Our ability to remember is influenced by a surprising number of factors, both internal and external. Here are some key influences to consider:
- Age📌Memory function can decline naturally with age, but this varies from person to person.
- Stress📌Chronic stress can hinder memory formation and retrieval.
- Sleep📌Adequate sleep is crucial for memory consolidation.
- Health📌Overall health, including diet and exercise, impacts memory function.
- Learning Strategies📌Effective encoding techniques like active learning can strengthen memory.
- Emotional State📌Emotional experiences can leave a stronger memory imprint.
Exploring these influencing factors can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain and improve memory capabilities throughout life.
What Is Memory Disorders?
Memory disorders disrupt our ability to store, retrieve, and use information. Here are some common signs:
- Increased forgetfulness of recent events.
- Difficulty learning new things.
- Confusion and disorientation.
- Problems with language and communication.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional. Memory disorders can't be cured, but treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
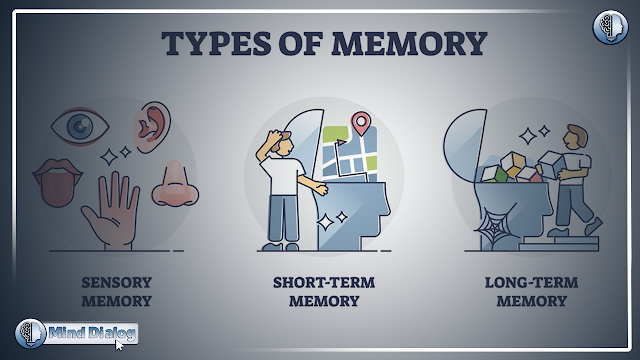
Unveiling the Different Types of Memory
Our memory system isn't a single entity, but rather a collection of specialized systems working together. Each type of memory plays a specific role in how we process and retain information. Here's a closer look at the main types of memory:
Sensory Memory
Sensory memory is the most basic form of memory, responsible for registering information we take in through our senses (sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch). It acts like a fleeting snapshot, holding onto sensory details for a fraction of a second before fading away.
Short-Term Memory - STM
Short-term memory, also known as working memory, serves as a temporary storage space. It allows us to hold onto a small amount of information for a brief period, typically around 20-30 seconds. This memory is crucial for performing everyday tasks like remembering a phone number while dialing it or following a list of instructions enhance STM and facilitate the retention of information.
Long-Term Memory - LTM
Long-term memory is the powerhouse of our memory system, responsible for storing information for extended periods, ranging from hours to a lifetime. It LTM allows us to recall facts, events, and experiences that shape who we are. Long-term memory can be further categorized into two main types:
Explicit Memory - Recalling Facts and Experiences
- Episodic Memory✅ This type of memory allows us to recall specific events from our personal lives, like a childhood birthday party or a recent vacation.
- Semantic Memory✅ This type of memory stores general knowledge and facts about the world, such as historical events, geographical locations, or mathematical formulas.
Implicit Memory - Unconscious Recollection
Implicit memory, also known as procedural memory, allows us to perform skills and tasks without conscious thought. It's how we remember how to ride a bike, tie our shoes, or play a musical instrument.
Working Memory
Working memory is more than just passive storage. It's the active workspace where we manipulate and process information held in short-term memory. We use working memory for reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Tips for Improved Memory Retrieval
Struggling to recall information? Here are some practical strategies to boost your memory retrieval:
- Create Retrieval Cues establish effective retrieval cues, such as visual imagery or emotional associations, to trigger the recall of specific memories.
- Vary Retrieval Methods practice retrieving information in different ways, such as writing it down, drawing it out, or discussing it with others.
- Reduce Stress stress can impair memory retrieval. Manage stress levels through relaxation techniques, exercise, or mindfulness practices.
By incorporating these tips, you can enhance your ability to access stored information and keep your memory sharp.
Techniques to Enhance Memory Consolidation
Consolidate those memories Here's how to solidify information and transfer it to long-term storage:
- Get Enough Sleep⚡ Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Space Out Learning⚡ Instead of cramming information all at once, space out your learning sessions over time. This allows for repeated exposure and better consolidation.
- Practice and Apply⚡ Actively use and apply the information you're trying to remember. Teaching others or engaging in practice exercises can strengthen memory retention.
Incorporating these techniques into your routine can optimize memory consolidation and promote better memory retention over time.
In conclusion, memory is a fundamental aspect of human cognition, allowing us to navigate the world and interact with our surroundings. Understanding the different types of memory, along with the factors that influence memory functioning, is essential for optimizing cognitive performance and promoting overall well-being. By learning more about memory and its complexities, we can enhance our learning abilities, improve decision-making skills, and maintain cognitive health throughout life.

