Indian Geography MCQ Quiz - Objective Question with Answer for Indian Geography - Download Free PDF
Last updated on May 22, 2024
Latest Indian Geography MCQ Objective Questions
Indian Geography Question 1:
Konkan coast and Coromandel Coast in India are located
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 1 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is Along the Western and Eastern Ghats respectively.
 Key Points
Key Points
- India has a coastline of 7516.6 Km [6100 km of mainland coastline + coastline of 1197 Indian islands] touching 13 States and Union Territories (UTs).
- On the basis of the location and active geomorphological processes, it can be broadly divided into two:
- the western coastal plains;
- the eastern coastal plains.
- Extending from the Gujarat coast in the north to the Kerala coast in the south, the western coast may be divided into following divisions – the Kachchh and Kathiawar coast in Gujarat,
- Konkan coast in Maharashtra,
- Goan coast and in Karnataka,
- Malabar coast Kerala.
- The western coastal plains are narrow in the middle and get broader towards north and south.
- The rivers flowing through this coastal plain do not form any delta.
- The Malabar coast has got certain distinguishing features in the form of ‘Kayals’ (backwaters), which are used for fishing, inland navigation and also due to its special attraction for tourists.
- Every year the famous Nehru Trophy Vallamkali (boat race) is held in Punnamada Kayal in Kerala.
- Eastern coast extends from the Subarnarekha river along the West Bengal-Odisha border to Kanyakumari.
- This plain is known as the Northern Circars between the Mahanadi and the Krishna rivers and Carnatic/Coromandel between the Krishna and the Cauvery rivers.
- As compared to the western coastal plain, the eastern coastal plain is broader and is an example of an emergent coast.
- There are well developed deltas here, formed by the rivers flowing eastward in to the Bay of Bengal.
- These include the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri.
- Because of its emergent nature, it has less number of ports and harbours.
Indian Geography Question 2:
West Bengal shares boundaries with ________ countries.
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 2 Detailed Solution
- West Bengal shares boundaries with 3 countries.
- West Bengal shares its boundaries with Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- West Bengal, Mizoram, Assam, Tripura, and Meghalaya are the Indian states that share their borders with Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh is the country that India has the largest border with.
Indian Geography Question 3:
The water holding capacity is highest in-
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 3 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is Clayey soil.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Clayey soil has the highest water-holding capacity among the given options.
- This is because clay particles have a very small pore space that allows them to hold onto water for longer periods of time.
- In contrast, sandy soil has larger pore spaces and tends to drain water quickly, while loamy soil is a mixture of clay, sand, and silt and has an intermediate water-holding capacity.
- Soil water holding capacity is the amount of water that a given soil can hold for crop use.
- Soil texture and organic matter are the key components that determine soil water-holding capacity.
- In terms of soil texture, those made up of smaller particle sizes, such as in the case of silt and clay, have larger surface areas.
- The larger the surface area the easier it is for the soil to hold onto water so it has a higher water-holding capacity.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
- Mixture of sandy and loamy soil
- Sand that is mixed with the soil in sandy, loamy soils is very obvious to the naked eye. The sandy loamy soils will retain their shape when compressed together, but they will easily break apart. The high concentration of sand particles in these sandy loam soils gives them a grittiness.
- Sandy soil
- Sandy soils typically have a coarse texture up to a depth of 50 cm, retain few nutrients, and have a low capacity to hold water.
- Clayey soil
- There are a lot of clay particles and very little humus and silt in this kind of soil. Because it is so compact, this soil is unable to hold air.
Indian Geography Question 4:
Consider the following statement regarding Tropical Dry Deciduous forest.
1. It is found in that regions where rainfall is between 25 and 70 cm.
2. They occur in an irregular wide strip running from the foot of the Himalayas.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 4 Detailed Solution
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall is 100-150 cm.
Characteristics
- These are similar to moist deciduous forests and shed their leaves in the dry season.
- The major difference is that they can grow in areas of comparatively less rainfall.
- They represent a transitional type – moist deciduous on the wetter side and thorn forests on the drier side.
- They have a closed but uneven canopy.
- The forests are composed of a mixture of a few species of deciduous trees rising up to a height of 20 metres.
- Undergrowth: Enough light reaches the ground to permit the growth of grass and climbers.
Distribution
- They occur in an irregular wide strip running from the foot of the Himalayas to Kanyakumari except in Rajasthan, Western Ghats and West Bengal.
Indian Geography Question 5:
When environmental conditions are favorable, the the population growth curve will be
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 5 Detailed Solution
Concept:
Growth curves:
- The population growth curve represents the growth of the population over a while.
- Growth curves can be linear, exponential, or cubic depending on the fragments of the population given.
- Two types of population growth patterns may occur depending on specific environmental conditions:
- An exponential growth pattern (J curve) occurs in an ideal, unlimited environment.
- A logistic growth pattern (S curve) occurs when environmental pressures slow the rate of growth.
Explanation:
J-Shapes curve:
- A J-shaped growth curve occurs in a new environment where the population density of an organism increases rapidly in an exponential or logarithmic form.
- It then stops abruptly as environmental resistance (e.g. seasonality) or some other factor (e.g. the end of the breeding phase) suddenly becomes effective.
- Exponential population growth will occur in an ideal environment where resources are unlimited.
- In such an environment there will be no competition to place limits on a geometric rate of growth.
- Initially, population growth will be slow.
- As population numbers increase the rate of growth similarly increases, resulting in an exponential (J-shaped) curve.
- This maximal growth rate for a given population is known as its biotic potential.
- Exponential growth can be seen in very small populations or in regions that are newly colonized by a species.

Thus, when environmental conditions are favourable, the population growth curve will be J-Shaped
 Additional Information
Additional Information
Logistic growth:
- Logistic population growth will occur when population numbers begin to approach a finite carrying capacity.
- The carrying capacity is the maximum number of species that can be sustainably supported by the environment.
- As a population approaches the carrying capacity, environmental resistance occurs, slowing the rate of growth.
- This results in a sigmoidal (S-shaped) growth curve that plateaus at the carrying capacity (denoted by κ).
- Logistic growth will eventually be seen in any stable population occupying a fixed geographic space.

Top Indian Geography MCQ Objective Questions
Which state does not share its boundary with Myanmar ?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 6 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Sikkim.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Sikkim shares international boundaries with Bhutan, China, and Nepal.
- Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram share an international boundary with Myanmar.

Which of the following crops is an example of Kharif Crops ?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 7 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Cotton.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Cotton is a Kharif crop. It requires 6 to 8 months to mature.
- Cotton is a water-thirsty crop and around 6% of the water for irrigation in is used for its cultivation.
- It grows in the major parts of the country viz. Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and parts of Andhra Pradesh & Karnataka.
- The irrigated crop is sown from March-May and the rain fed crop in June-July with the commencement of the monsoon.
- Kharif Season:
- Kharif crops also are known as monsoon crops as they are cultivated in the monsoon season.
- These crops are sown at the beginning of the rainy season.
- Rice, maize, bajra, ragi, sorghum, soybean, groundnut, cotton, etc. are all Kharif types of crops.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
- Zaid Season:
- It is a short season between Kharif and Rabi season.
- The crops grown during this season are known as Zaid crops.
- Pumpkin, cucumber, watermelon, bitter gourd, etc. are all zaid types of crops.
- Rabi Season:
- These are the crops that are sown at the end of the monsoon season or at the beginning of the winter season.
- These crops also are known as winter crops.
- Wheat, Mustard, Peas, Pulses, Barley, etc. are all Rabi types of crops.
Maad soil is found in which part of Uttar pradesh?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 8 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFMaad soil is usually found in the Southern part of Uttar Pradesh.
- Maad soil contains silica(60%), Iron(15%), aluminum(25%).
- In this type of soil, agriculture is difficult.
- The Southern Plateau was made up in the Pre-Cambrian period also known as Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand regions.
The Zoji La Pass is in which mountain range?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 9 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is the Zanskar Range.
 Key Points:
Key Points:
Zoji La Pass:
- It is in the Zaskar range in the Indian union territory of Ladakh.
- The road route from Srinagar to Leh goes through this pass.
- It was formed by the Indus river.

Shortcut Trick
Himalayan Ranges from north to south-
- TRICK:- Kal Jana Padega Desh Se.
- K = Karakoram J= Zaskar D = Dhauladhar S = Shiwalik
Main Passes tricks-
- Sikkim
- Nathuram Sikkim Jail Gaya - Nathula, and Jelep La Pass
- Himachal Pradesh
- Rohit barah bje ship lene gaya
- Rohtang Pass, Barah Pass, Shipkila Pass
- Rohit barah bje ship lene gaya
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Dipu ne likha pyara patra
- Dipu La, Likhapani and Pangsan pass
- Dipu ne likha pyara patra
https://www.dangerousroads.org/asia/india/111-zoji-la-pass-india.html
Which of the following is known as the Diamond City of India?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 10 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe Correct Answer is Surat.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Surat is famous for its diamond cutting and polishing and is known as the Diamond City of India.
- 90% of all diamond cutting and polishing on the planet takes place in Surat.
 Important Points
Important Points
- Surat is a port city situated on the banks of the Tapi river.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
|
Name of Cities |
Nicknames of the Cities |
|---|---|
|
Bengaluru (Karnataka) |
1. Silicon Valley of India 2. Space City 3. Science city of India 4. Garden City of India |
|
Pochampalle (Telangana) |
Silk City |
|
Chennai (Tamil Nadu) |
1. Detroit of Asia 2. Automobile Capital of India 3. Gate Way Of South India 4. India's health capital 5. Electronic Manufacturing Hub in India 6. Banking Capital of India |
|
Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu) |
Manchester of South India |
|
Dibrugarh (Assam) |
Tea City of India |
|
Hyderabad (Telangana) |
City of Pearls |
|
Jaipur (Rajasthan) |
Pink City |
|
Jamshedpur (Jharkhand) |
Steel City of India |
|
Kolkata (West Bengal) |
City of Joy |
|
Kolhapur (Maharashtra) |
City of Wrestlers |
|
Kollam (Kerala) |
Cashew Capital of the World |
|
Kochi (Kerala) |
Queen of Arabian Sea |
|
Kurnool (Andhra Pradesh) |
The Gateway of Rayalaseems |
|
Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh) |
City of Nawab |
|
Madurai (Tamil Nadu) |
1. City of Festivals 2. Temple city 3. Athens of the East |
|
Mangalore (Karnataka) |
1. Cradle Of Indian Banking 2. Gateway Of Karnataka 3. Rome Of The East 4. Petrochemical capital of South India 5. Ice cream capital of India 6. Jewel of the West Coast 7. City of cuisines |
|
Mumbai (Maharashtra) |
1. City of Seven Islands 2. Gateway of India 3. Hollywood of India 4. Maximum City |
|
Mussoorie (Uttarakhand) |
Queen of the Mountains |
|
Muzaffarpur (Bihar) |
The Land of Leechi |
|
Nagpur (Maharashtra) |
1. Orange City 2. Tiger Capital |
|
Akola (Maharashtra) |
The Cotton City |
|
Patiala (Punjab) |
Royal City |
|
Panipat (Haryana) |
City of Weavers |
|
Pondicherry (Puducherry) |
Paris of the East |
|
Pune (Maharashtra) |
1. Oxford of the East 2. Queen of Deccan |
|
Siliguri (West Bengal) |
Gateway to the Dooars |
|
Surat (Gujarat) |
Diamond City |
|
Tezpur (Assam) |
City of Blood |
|
Tirunelveli (Tamil Nadu) |
1. Oxford city of south India 2. Halwa city of India 3. City of paddy fields |
|
Thoothukudi (Tamil Nadu) |
Pearl City |
|
Udaipur (Rajasthan) |
1. White City 2. City of Lakes |
|
Trivandrum (Kerala) |
Evergreen City of India |
|
Vadodara (Gujarat) |
1. Banyan City 2. Cultural Capital of Gujarat/ Sanskari Nagari 3. Power Equipment Manufacturing Hub of India 4. Pensioners' City |
Srisailam Hydroelectric Power Plant is built on which river?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 11 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Krishna River.
 Key Points
Key Points
- The Srisailam Dam is located in the Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh.
- Srisailam hydroelectric power project is constructed across the Krishna River.
- The Srisailam project is the 12th largest capacity hydroelectric project in the country.
- The 512 m long and 145 m high dam was constructed in a deep gorge.
- The left bank hydroelectric power station generates 6 X 150 MW of power and the right bank generates 7 X 110 MW of power.
- Srisailam dam forms the reservoir with a gross storage of 215 TMC ft.
- The Srisailam hydroelectric power station is the third-largest construction project in India.
 Important Points
Important Points
- The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is the largest completed hydroelectric plant in India.
- Its power capacity is 1920 megawatts.
- The first hydroelectric power station was the Shivanasamudra hydroelectric power station.
- Tehri Hydro Power Plant is the tallest hydropower project in the country, and Terry Dam is also the tallest hydropower plant in India.
- The Nathpa Jhakri Hydroelectric Power Plant is the largest underground hydroelectric project in the country.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
| Hydroelectric Power Plant | River | State |
|---|---|---|
| Bhakra Nangal Hydroelectric Power Plant | Sutlej River | Himachal Pradesh |
| Tehri Hydro Electric Power plant | Bhagirathi | Uttarakhand |
| Hirakud Hydro Electric Power plant | Mahanadi | Odisha |
| Nagarjunasagar Hydro-Electric Power Plant | Krishna River | Andhra Pradesh |
| Sardar Sarovar Hydro Electric Power plant | Narmada river | Gujarat |
| Koyna Hydroelectric Power plant | Koyna River | Maharashtra |
| Balimela Hydro Electric Power plant | Sileru | Odisha |
River Sutlej enters India through which pass?
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 12 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Shipki la.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Shipki La is a mountain pass and border post on the India-Tibet border.
- The river Sutlej enters India through this pass.
- It is located in the Kinnaur district in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India, and Tibet.
- This pass is India's third border post for trade with Tibet after Nathu La in Sikkim, and Lipulekh in Uttarakhand.
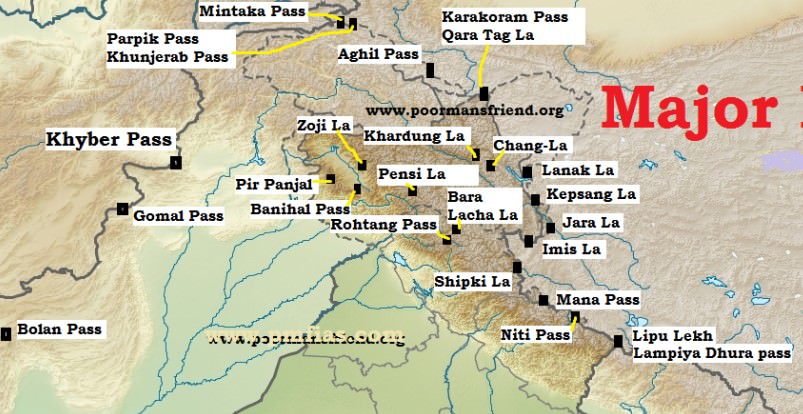
 Important Points
Important Points
| Zoji La |
|
| Nathula |
|
| Lipulekh |
|
The _________ is responsible for Earth's magnetic field.
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 13 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is outer core.
 Important Points
Important Points
- The interior of the earth is divided into three parts namely Crust, Mantle, and Core.
- The core is the innermost layer of the earth.
- The radius of the innermost layer(core) is about 3500 km.
- The core is made up of material constituted by nickel and iron.
- The temperature and pressure of the central core are very high.
 Key Points
Key Points
- The core is further subdivided into two layers called the outer core and inner core.
- The outer core of the earth is in a liquid state.
- The inner core is in solid-state
- The outer core is responsible for the earth's magnetic field.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
- The crust is the outermost of the earth.
- It is brittle in nature.
- it the thinnest layer of Earth.
- The thickness of the crust varies under the oceanic and continental areas.
- The mantle is the second layer in the interior of the earth.
- The mantle extends from Moho’s discontinuity to a depth of 2,900 km.
- The upper portion of the mantle is called the asthenosphere.

In Odisha, iron ores are located in _________.
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 14 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDF- Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar (Keonjhar) districts form a belt of Iron ore occurrence. The Badampahar Mines are located here.
- High-grade iron ore is exported from these sites via the Paradeep Port.
Pakyong Airport is located in -
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Indian Geography Question 15 Detailed Solution
Download Solution PDFThe correct answer is Sikkim.
- Pakyong Airport is in the state of Sikkim.
- It is the only airport in the state of Sikkim and the first greenfield airport in North-East India.

 Key Points
Key Points
|
Airport |
State |
|
Pakyong Airport |
Sikkim |
|
Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport |
Assam |
|
Pasighat airport |
Arunachal Pradesh |
|
Dimapur Airport |
Nagaland |


