Heads up! 6 planets in a line from late May into early June
From late this month into early June, six of the eight major planets in our solar system will grace the eastern sky before sunup. Read more here or watch a video below.
May 30: Last quarter moon
The instant of last quarter moon will fall at 17:13 UTC on May 30, 2024 (12:13 p.m. CDT). It’ll rise after midnight your local time and will set around noon. Look for it high in the sky before dawn.
May 31 morning: Moon visits Saturn
In the early morning hours of May 31, 2024, the moon will hang very close to Saturn. Also, sky watchers in parts of Argentina, Chile, Brazil and Uruguay among others will see the moon pass in front of – or occult – Saturn near 8 UTC on May 31.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.

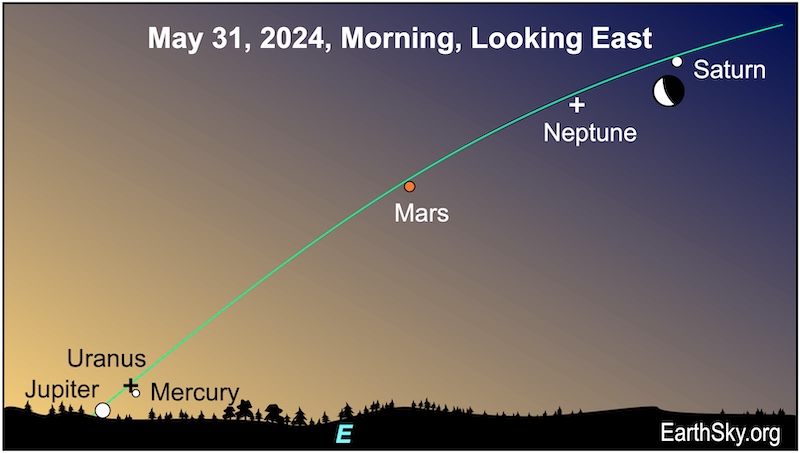
May 31 morning: Sneak peak of the lineup of 6 planets
Start watching for the lineup of six planets on May 31, 2024. The thick waning crescent moon will lie near golden Saturn. You can see the moon and Saturn in dark skies before dawn. The moon will visit five more planets (Neptune, Mars, Uranus, Mercury and Jupiter) over the next few days. The moon and Saturn will rise about three hours before sunrise, but to catch all six planets look about 30 minutes before sunrise.

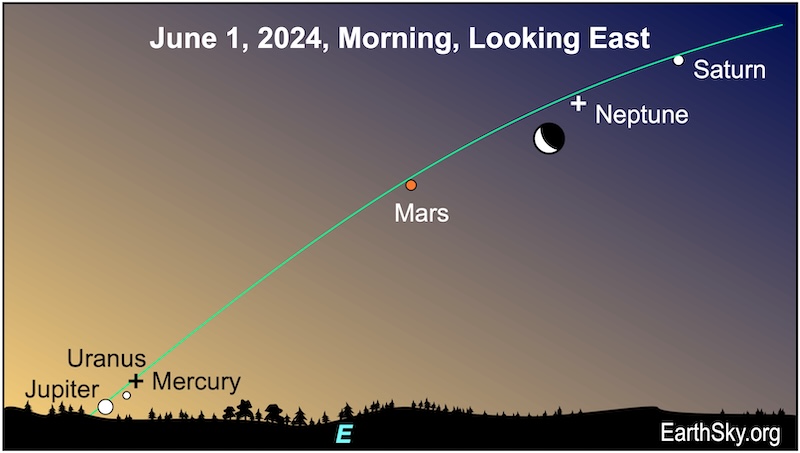
June 1 morning: Moon between Saturn and Mars
On June 1, 2024, the lineup of six planets will find the waning crescent moon hanging between Saturn and Mars, and it’ll be close to the spot where Neptune lies. Just remember, Neptune will require optical aid and dark skies to spot. Look for them before dawn, Saturn and Mars will rise several hours before sunrise. If you look later during morning twilight, Saturn and Mars might be difficult to see, but you might also glimpse Mercury, Jupiter and the spot where Uranus lies low on the horizon.
June 2: Moon reaches perigee
The moon will reach perigee – its closest point in its elliptical orbit around Earth – at 7 UTC (2 a.m. CDT) on June 2, 2024, when it’s 228,727 miles (368,102 kilometers) away.
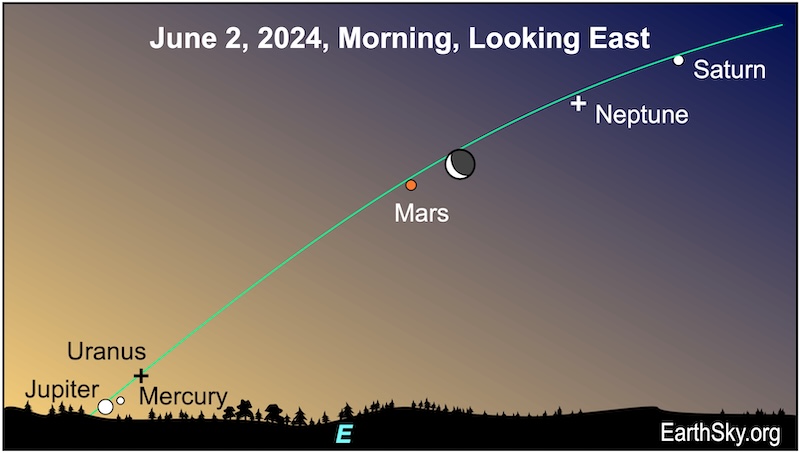
June 2 morning: Moon near Mars
The lineup of six planets continues on June 2, 2024, when the lit portion of the waning crescent moon will point to reddish Mars. At the same time, Mercury is dropping down toward the horizon and Jupiter, in anticipation of their upcoming conjunction. And Saturn will be higher in the eastern pre-dawn sky. The moon and Mars will rise about two hours before sunrise. The spots where Neptune and Uranus lie are marked with plus signs. If you want to try and catch all six planets, look about 30 minutes before sunrise.
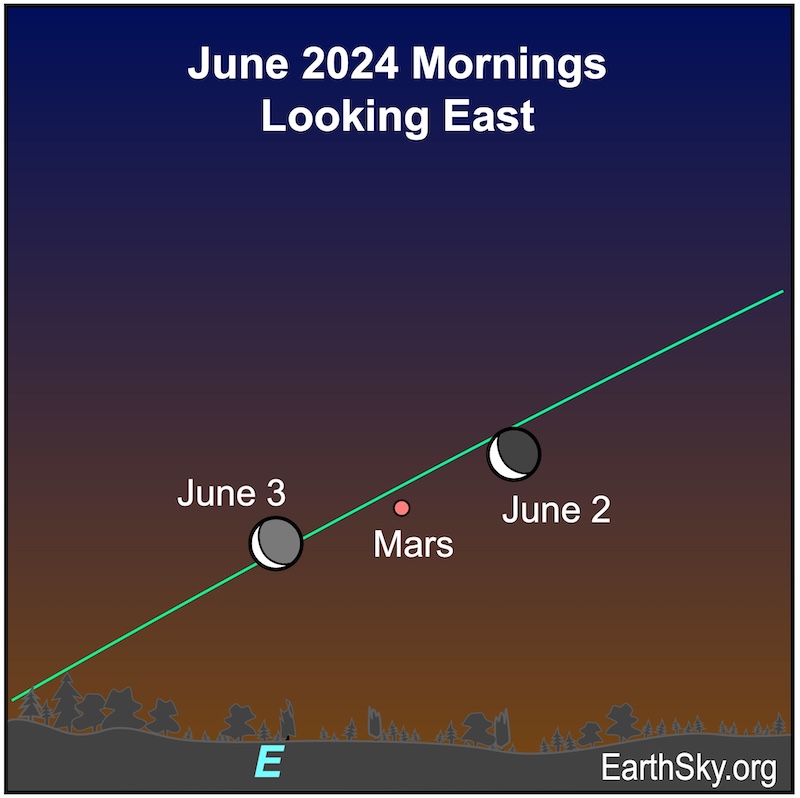
June 2 and 3 mornings: Moon near Mars
On the mornings of June 2 and 3, 2024, the waning crescent moon will lie close to the reddish planet Mars. They will rise a few hours before dawn.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
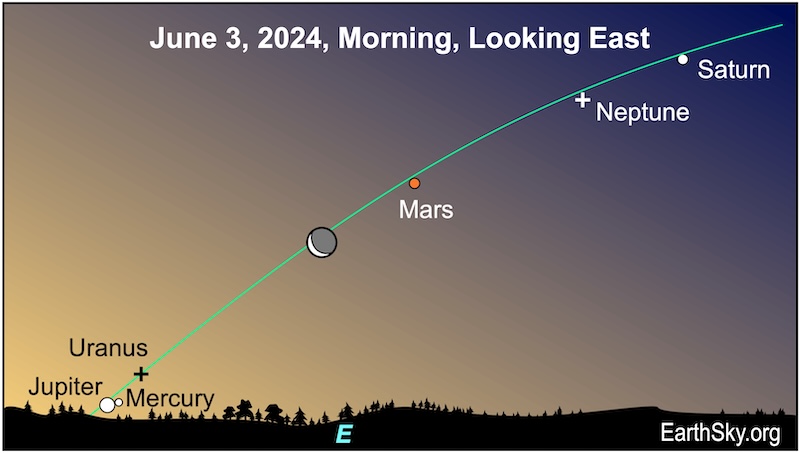
June 3 morning: Moon hangs near Mars
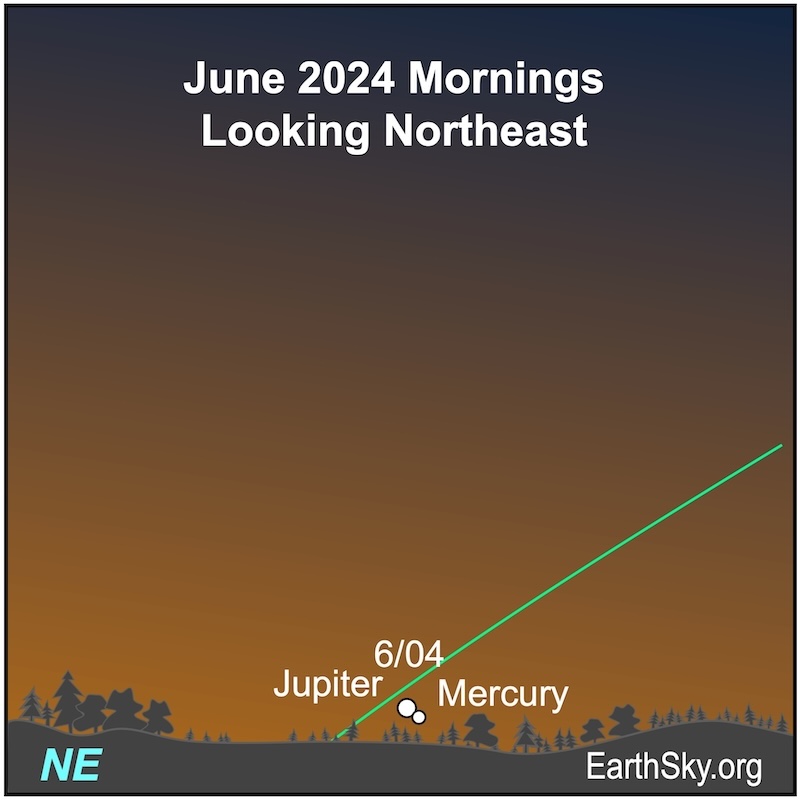
The mornings of June 3 and 4, 2024, will probably be the best time to try to catch all six planets at once. Start looking about 40 minutes before sunrise. On June 3, the waning crescent moon will be pointing to Mercury and Jupiter (and the spot where Uranus lies) near the sunrise point. And Mercury and Jupiter will be just a day away from being closest to each other. Meanwhile, Mars, Saturn and Neptune will be higher in the eastern predawn sky.
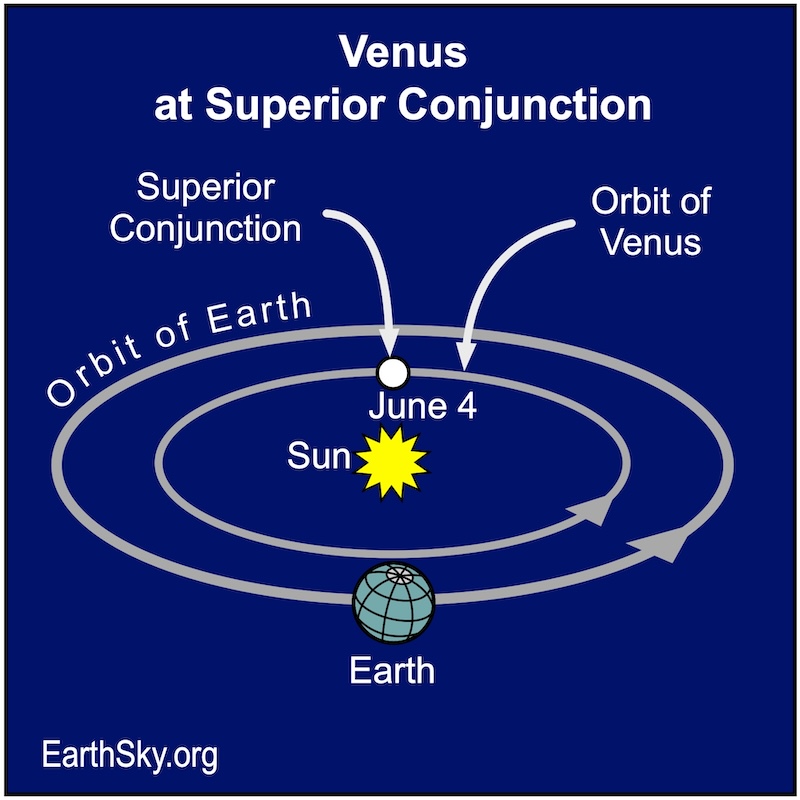
June 4: Venus at superior conjunction
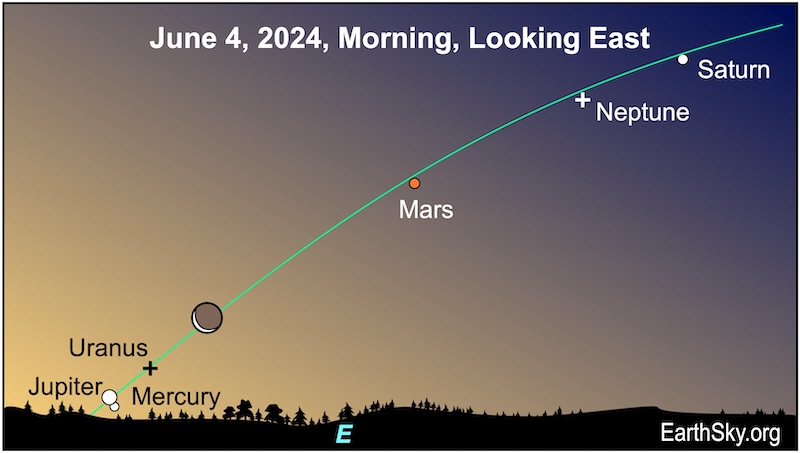
June 4 morning: Moon moving toward Jupiter and Mercury
On June 4, 2024, the waning crescent moon will be floating above the planets low on the horizon. Mercury and Jupiter will appear closest together in the morning sky when they will be less than a degree apart. And that’s if you can find them in the bright morning twilight! Even though the planets are shining brightly, they’ll be competing with the rising sun’s glow. Look in the morning twilight about 40 minutes before sunrise. Also, look for Mars and Saturn higher in the sky.
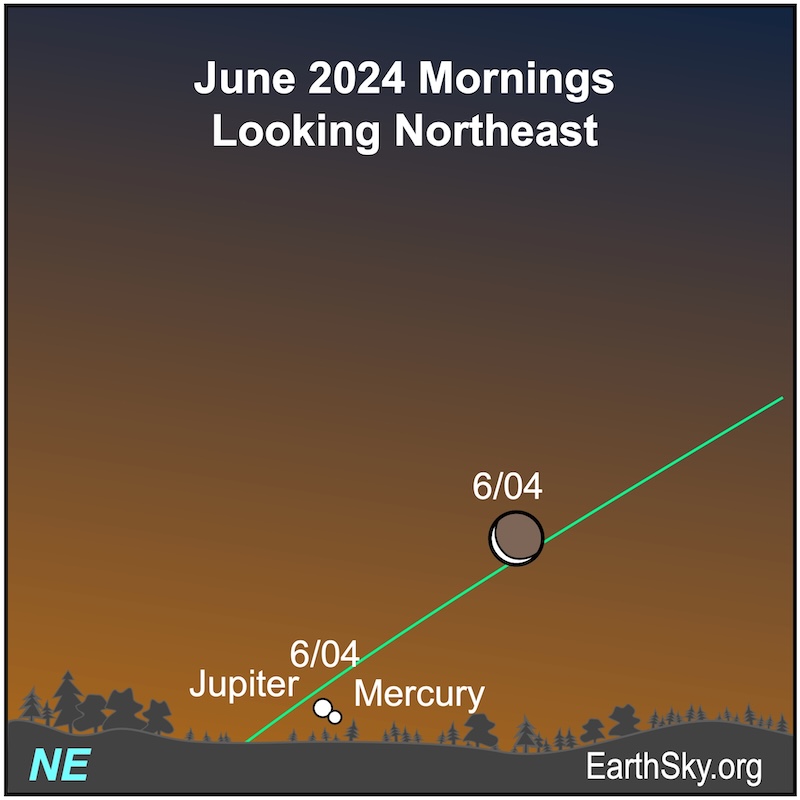
June 4 morning: The moon, Jupiter and Mercury
On the morning of June 4, 2024, the lit portion of the waning crescent moon will point to a close pairing of the bright planets Jupiter and Mercury. The largest and smallest planets of our solar system will lie low on the horizon in the bright morning twilight and be 0.1 degrees apart. Binoculars may help spot them about 30 minutes before sunrise.
June 5 morning twilight: Last chance to see all 6 planets
Your last chance to snag all six planets before sunrise is probably on June 5, 2024. Mercury will be descending fast toward the horizon. Jupiter will be ascending, and the whisper-thin waning crescent moon (at just 1.7% lit!) will hover above the planetary pair. Look for them in the morning twilight about 40 minutes before sunrise. Soon, Mercury will be too close to the sun to see. However, Jupiter will be moving higher out of the sunrise’s glow. Mars and Saturn lie higher in the sky and are easier to spot before dawn.
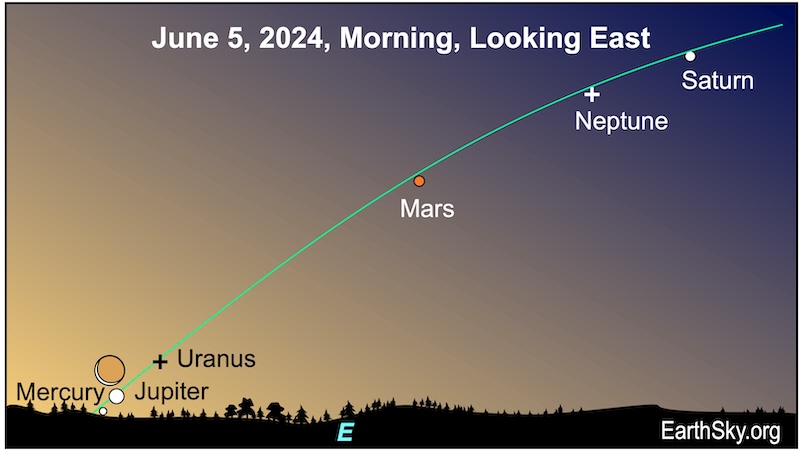
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
June 6: New moon
The instant of new moon will fall at 12:38 UTC on June 6, 2024 (7:38 a.m. CDT). That night is a perfect time to enjoy stargazing under dark skies.
Before dawn June 7: Arietids meteor shower
Watch for the Arietids in the dark hours before dawn breaks. There won’t be any moonlight to hinder meteor watching in the morning sky. The Arietids are sometimes said to be the most active daytime meteor shower.
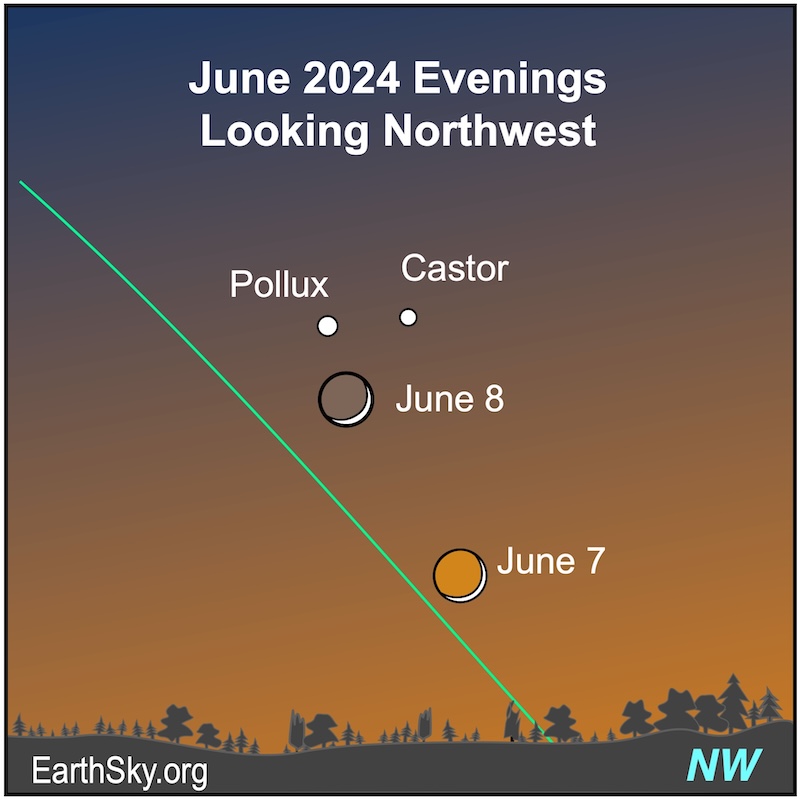
June 7 and 8 evenings: Moon near Gemini’s twin stars
On the evenings of June 7 and 8, 2024, the waxing crescent moon will shine near Pollux and Castor, the twin stars of Gemini. Even though they are called twins, they don’t look alike. Pollux is a bit brighter and shines with a golden light, while Castor is a white star. On both evenings, the unlit portion of the moon will exhibit the lovely glow of earthshine, which is reflected light from Earth. They’ll rise before sunset, travel across the sky’s dome and set before midnight.
June 11 evening: Moon near Regulus
On the evening of June 11, 2024, the waxing crescent moon will hang near the bright star Regulus, the brightest star in Leo the Lion. They’ll be visible until around midnight.

June 14: 1st quarter moon
The instant of 1st quarter moon will fall at 5:18 UTC on June 14 15, 2024 (12:18 a.m. CDT). A 1st quarter moon rises around noon your local time and sets around midnight. Watch for it high in the sky at sundown.
June 14: Moon reaches apogee
The moon will reach apogee – its farthest distance from Earth in its elliptical orbit around Earth – at 14 UTC (9 a.m. CDT) on June 14, 2024, when it’s 251,081 miles (404,076 kilometers) away.
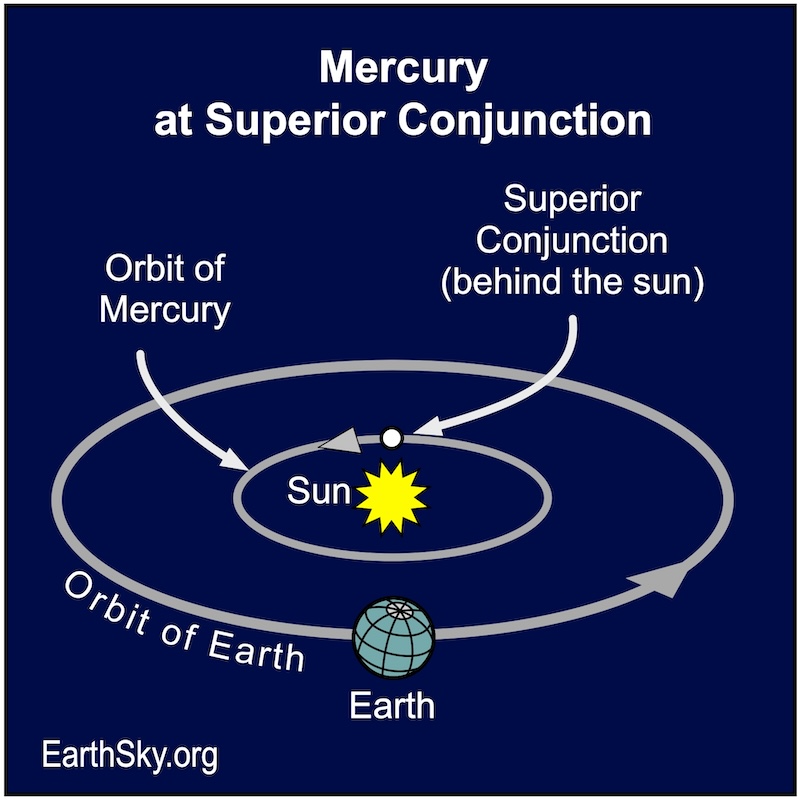
June 14: Mercury at superior conjunction
Mercury moves behind the sun on June 14, 2024. This point in its orbit is called superior conjunction. It’ll emerge in the evening sky the last few days of June.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
June 15 and 16 evenings: Moon near Spica
On the evenings of June 15 and 16, 2024, the fat waxing gibbous moon will hang near the bright star Spica in Virgo the Maiden. They’ll rise before sunset and be visible through several hours after midnight. Locations including Kazakhstan, western Russia, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan will see the moon pass in front of – or occult – Spica around 18 UTC on June 16. Others may see Spica close to the limb of the moon.

June 19 evening: Moon near Antares
On June 19, 2024, the bright red star Antares in Scorpius the Scorpion will lie close to the fat waxing gibbous. Also, sky watchers in locations including Papua New Guinea, eastern Indonesia, Solomon Islands and Fiji will see the moon pass in front of – or occult – Antares near 11 UTC on June 20. Other locations may see Antares very close to the limb of the moon.

June 20: Solstice
In 2024, the June solstice will fall at 20:51 UTC (3:51 p.m. CDT) on Thursday, June 20.
June 21 evening: Moon near the Teapot
The full moon will lie near the Teapot – an asterism in Sagittarius the Archer – on the evening of June 21, 2024. You can catch the moon and the Teapot until dawn.

June 22: Full moon
The full moon will occur at 1:08 UTC on June 22, 2024, (8:08 p.m. CDT on June 21). It’ll be visible all night.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
June 27: Moon reaches perigee
The moon will reach perigee – its closest point in its elliptical orbit around Earth – at 12 UTC (7 a.m. CDT) on June 27, 2024, when it’s 229,463 miles (369,286 kilometers) away.
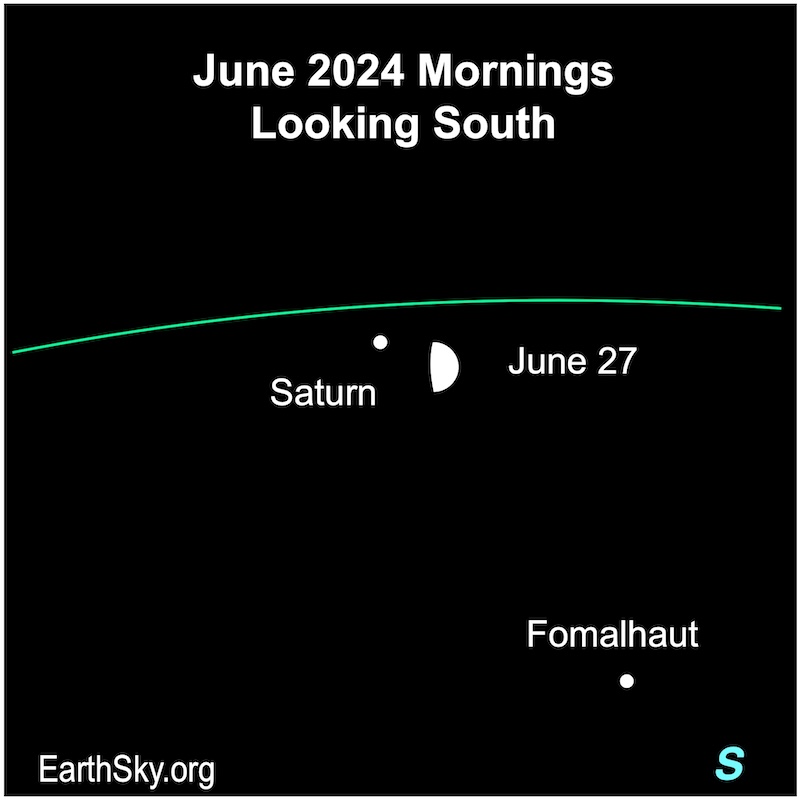
June 27 morning: Moon visits Saturn
In the early morning hours of June 27, 2024, the waning gibbous moon will hang close to Saturn. The bright star Fomalhaut will shine nearby. Also, sky watchers in locations including eastern Australia, northeastern New Zealand, Fiji and New Caledonia will see the moon pass in front of – or occult – Saturn near 15 UTC on June 27.
June 28: Last quarter moon
The instant of last quarter moon will fall at 21:53 UTC (4:53 p.m. CDT) on June 28, 2024. It’ll rise after midnight your local time and will set around noon. Look for it high in the sky before dawn.
June 30 mornings: Moon near Mars
On June 30, 2024, the waning crescent moon will lie close to the reddish planet Mars. The lit portion of the moon will point to the reddish planet. Also nearby will be the bright planet Jupiter and the Pleiades star cluster. The moon and Mars will rise about four hours before sunrise.
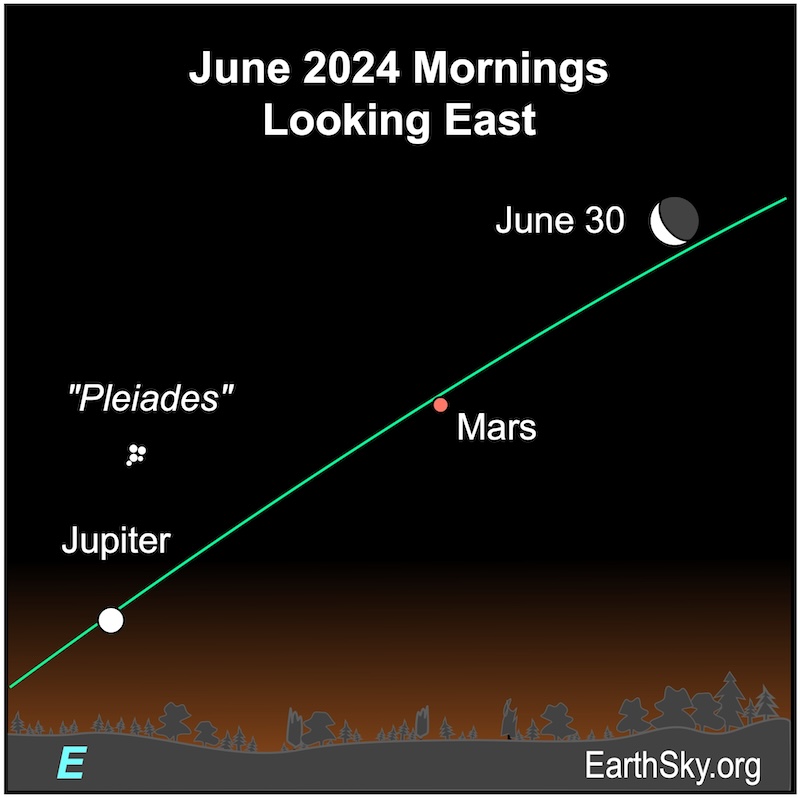
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
Stars and constellations overhead now
If you’re out stargazing on any evening, look for these stars and constellations overhead in the sky.
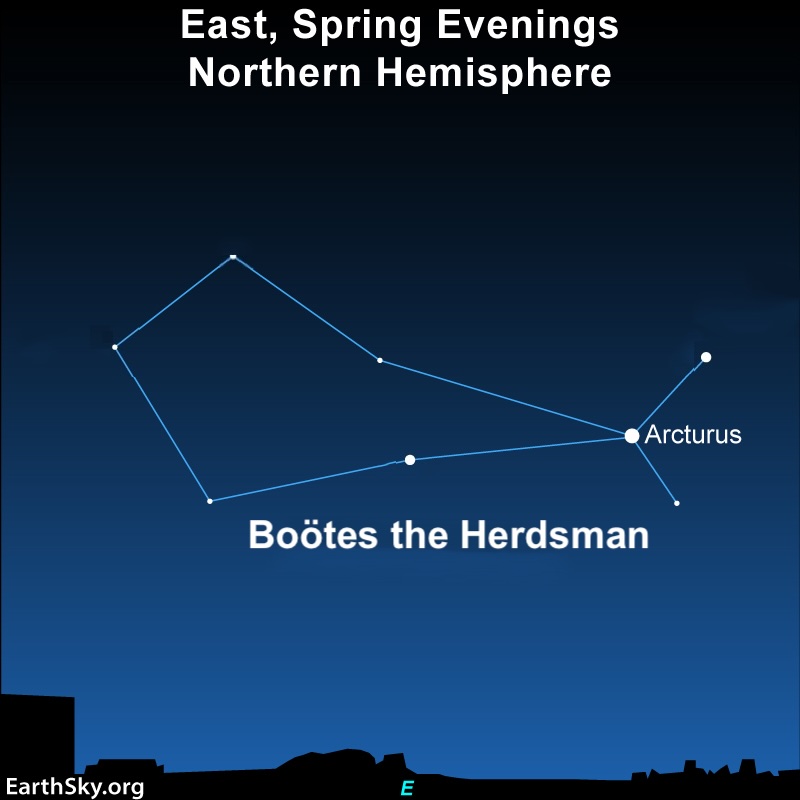
Boötes the Herdsman
Almost overhead on June evenings is bright orange Arcturus. It’s in the constellation Boötes the Herdsman. Boötes has the shape of a kite, and Arcturus is at the point where you’d attach a tail. You can’t miss its distinctive shape.
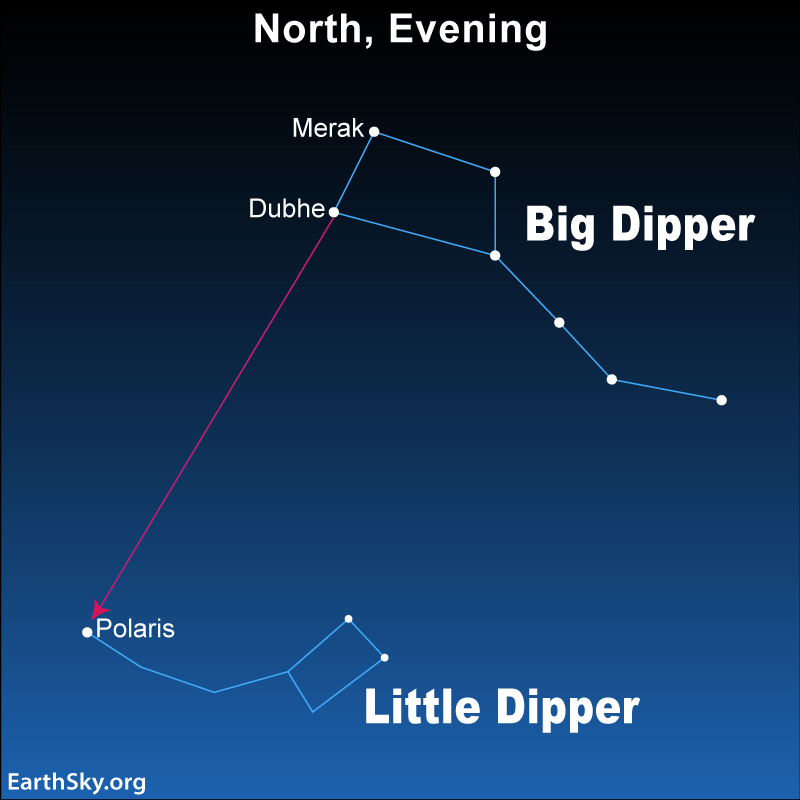
The Big Dipper
Ursa Major the Great Bear is home to the Big Dipper. The Big Dipper is an asterism – a well-known group of stars – not an official constellation. You’ll find the Big Dipper high overhead from mid-northern latitudes in the June evening skies. You can use the two outer stars in the Big Dipper’s bowl – sometimes called the Pointers – to find Polaris, the North Star.
Hercules the Hero and the Hercules Cluster
Hercules is a faint constellation. But its midsection contains the easy-to-see Keystone asterism. You can find Hercules between the bright stars Vega in Lyra the Harp and Arcturus in Boötes the Herdsman. And once you find the Keystone, you can easily locate M13, the Hercules cluster.

Have fun exploring the sky!
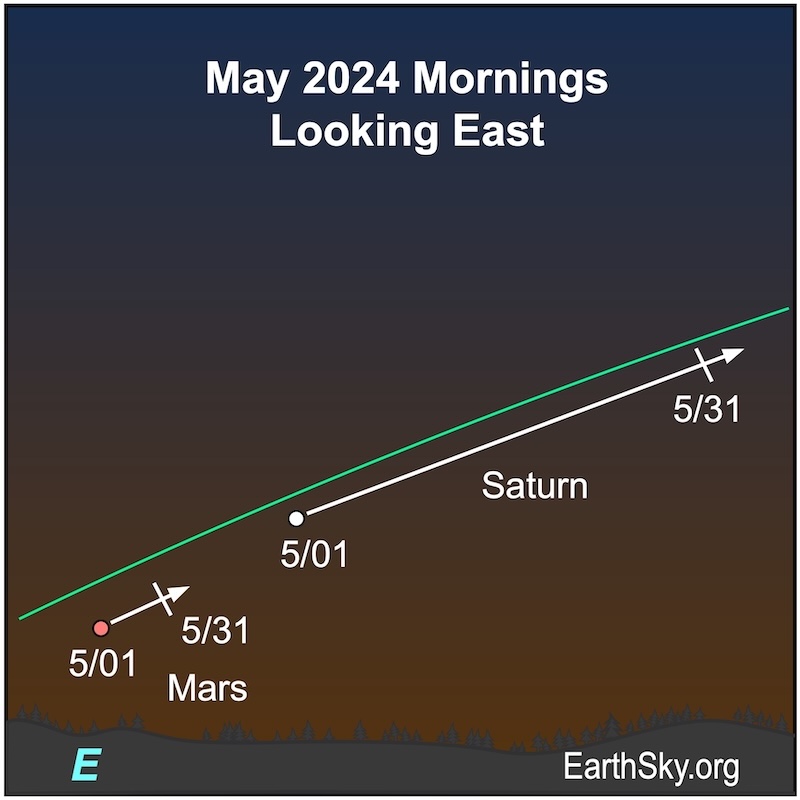
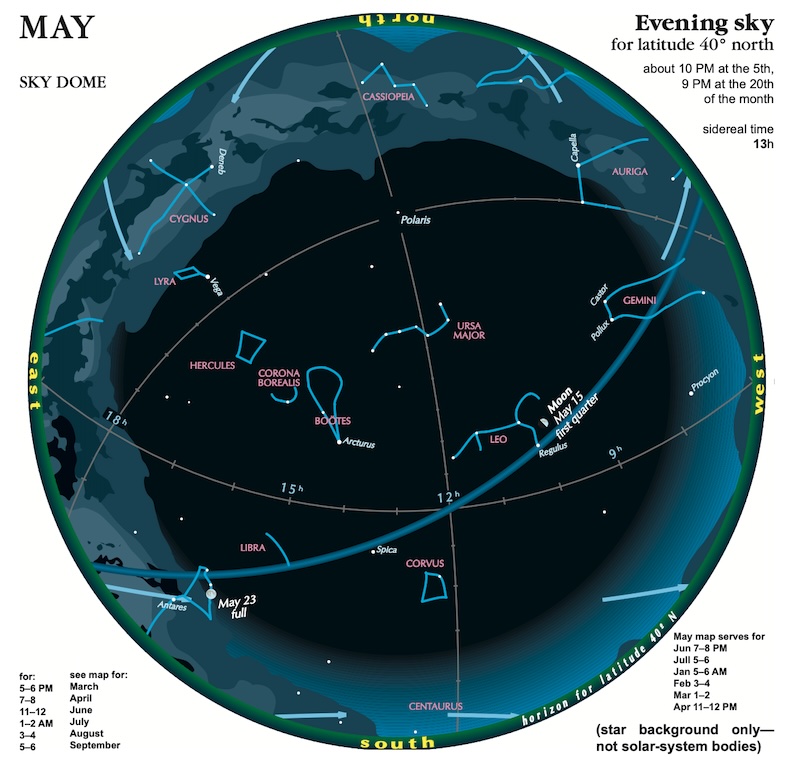
Visible planets in the May morning sky
In May 2024, look for this trio of planets in the morning sky. Mercury lies low in the morning twilight with Mars and Saturn lined up across the sky dome.

Mars and Saturn
You can see Mars and Saturn before dawn in the morning sky in May. They’ll climb higher each day and drift apart as the month goes by. Both are shining around 1st magnitude. Notice they are different colors, Mars is reddish and Saturn is golden.
In May 2024, Mars will shine at magnitude 1.1, and its disk will reach 5 arc minutes diameter by month’s end. It’ll have a close visit from the waning crescent moon on May 4 and 5, 2024. An occultation on May 4 will be visible in areas including Madagascar, Mauritius, Reunion and Seychelles, among others. Mars spends the month in the dim constellation of Pisces the Fish. It’ll rise about 90 minutes before the sun on May 1 and will rise about two hours before the sun by month’s end.
Saturn begins and ends the month of May with close passes from the moon. They’ll pair up on May 3 and 31. And occultations are visible in the Southern Hemisphere on both May 3 and May 31. Saturn will be dimming slightly in May because its ring system is closing – they’ll be edge-on in 2025 – and it’s getting farther from Earth. You can still notice an interesting comparison – in color and brightness – between Saturn and Mars throughout May. However, the two planets will grow farther apart as the month passes. Saturn spends the month in the faint constellation of Aquarius the Water Bearer. It’ll rise about two hours before the sun on May 1 and will rise about three hours before the sun by month’s end.
Mercury
Mercury climbs higher further from the morning sun through May 9, 2024, when it reaches its greatest morning elongation and is 26 degrees from the sun. It’ll be shining at magnitude 0.6. It’ll continue to brighten a bit for the rest of the month until it slips from view. This will be the best morning apparition of 2024 for Southern Hemisphere observers. Mercury spends most of its time this month in the dim constellation of Pisces the Fish. It’ll rise about 45 minutes before the sun on May 1 and will rise about 30 minutes before the sun by month’s end. You might also spot Mars higher in the sky in the morning twilight.
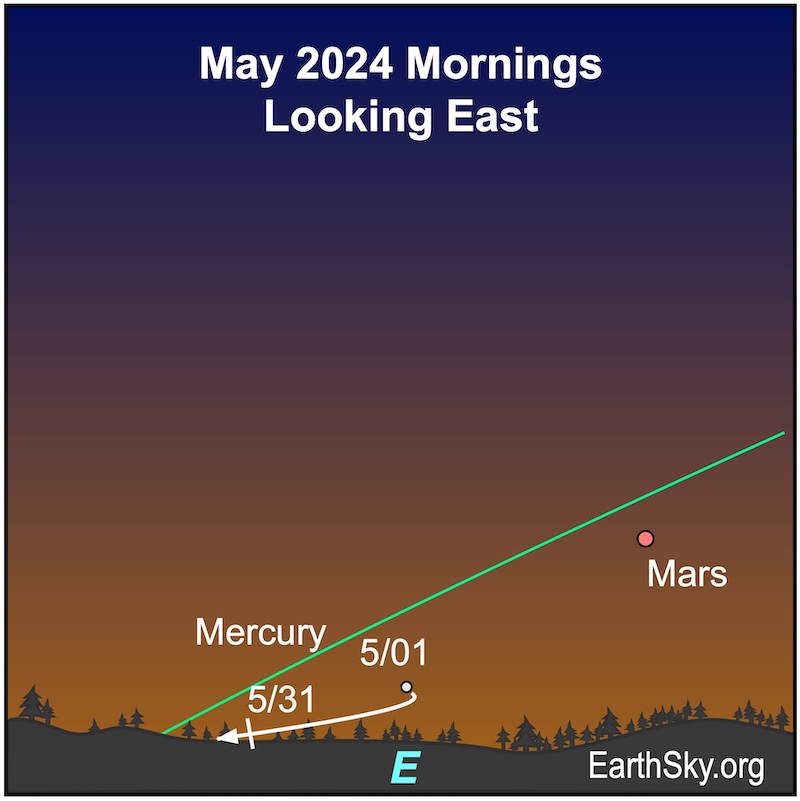
Where are Venus and Jupiter?
Both Venus and Jupiter are too close to the sun to be visible this month. Venus will emerge in the evening sky around the beginning of August. And Jupiter will emerge in the morning sky by early August.
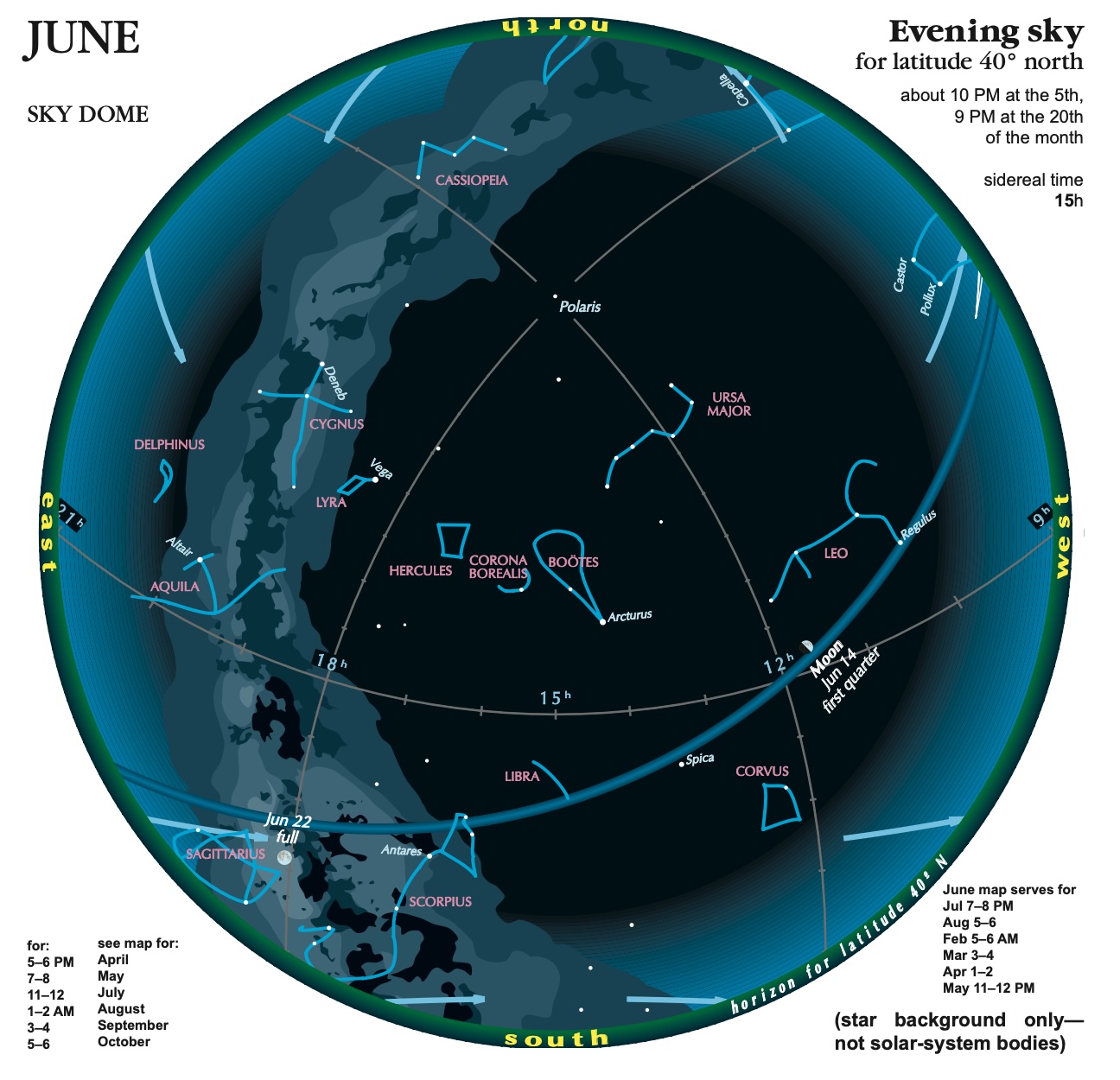
June morning planets
In June 2024, Mars will shine at 1st magnitude, and its disk will grow from 5 arcminutes in diameter to 5.4 arcminutes by the end of the month. The waning crescent moon will be near Mars on the mornings of June 2 and 3, 2024. Mars begins the month in the dim constellation of Pisces the Fish. And then it’ll move to the faint constellation Aries the Ram. It’ll rise about 2 hours before sunrise on June 1 and around 3 hours before sunrise by the end of June.
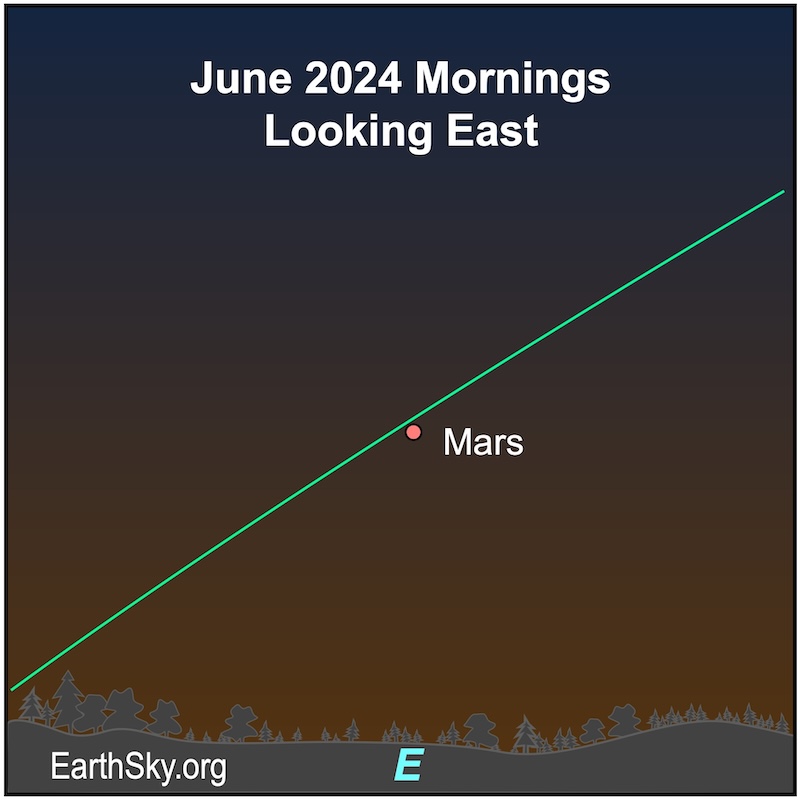
Chart via EarthSky.
Saturn will shine around 1st magnitude in June 2024. Its ring system is closing – they’ll be edge-on in 2025 – and it’s getting farther from Earth. The bright star Fomalhaut shines nearby. Saturn spends the month in the faint constellation of Aquarius the Water Bearer. Saturn ends the month of June with a close pass from the moon. They’ll pair up on June 27. Observers in eastern Australia, northeastern New Zealand, Fiji and New Caledonia will see the moon pass in front of – or occult – Saturn near 15 UTC on June 27. Saturn will rise about three hours before the sun on June 1 and will rise around midnight by month’s end.
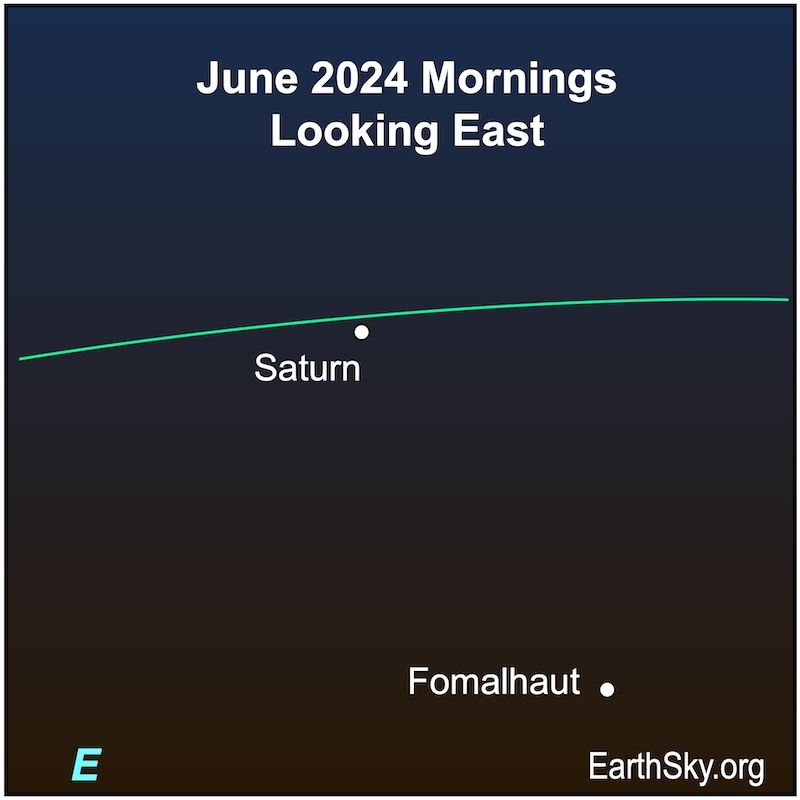
Chart via EarthSky.
Jupiter becomes easier to see as the month progresses. It spends the month in the constellation Taurus the Bull. It’s shining at -1.8 magnitude most of the month, but that bright light is washed out in the morning twilight. Jupiter will rise about 30 minutes before the sun on June 1 and will rise about two hours before sunrise by month’s end. It has a close pairing with Mercury on the morning of June 4, however they’ll be challenging to spot in the morning twilight. And, the delicate Pleiades star cluster is nearby. Mars will lie higher in the sky.
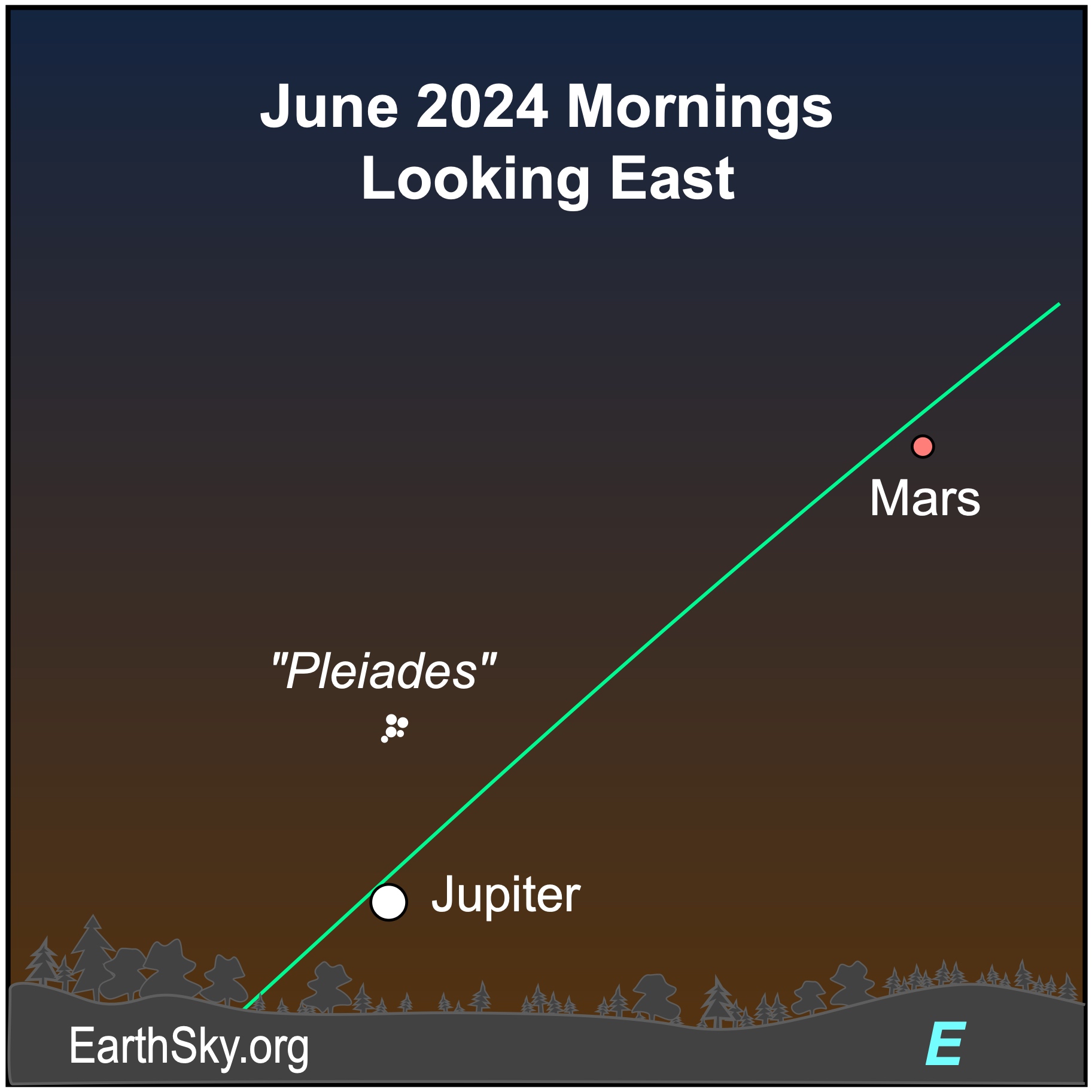
Mercury slips away in the glare of the morning sun at the beginning of June. It’ll be shining at magnitude -0.8. It will rise about 40 minutes before the sun. Before Mercury disappears from the morning sky, it’ll have a close pairing with Jupiter in the morning twilight on June 4, 2024. The pair will lie low on the horizon. Mercury will then emerge in the evening twilight by month’s end.
June evening planet
Mercury emerges in the evening sky at the end of June. Binoculars will help spot this little world. It’ll reach its greatest evening elongation on July 22, 2024, when it’s 27 degrees from the sun. It’ll be shining at magnitude 0.6. This will be the best evening apparition of 2024 for Southern Hemisphere observers. Mercury will be in the constellation Gemini the Twins. It’ll set about an hour after the sun by the end of June.

Where is Venus?
Venus is too close to the sun to be visible this month. It’ll emerge in the evening sky by the end of July.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
Our charts are mostly set for the northern half of Earth. To see a precise view – and time – from your location, try Stellarium Online.
Thank you to all who submit images to EarthSky Community Photos! View community photos here. We love you all. Submit your photo here.
Looking for a dark sky? Check out EarthSky’s Best Places to Stargaze.
Sky dome maps for visible planets and night sky
The sky dome maps come from master astronomy chart-maker Guy Ottewell. You’ll find charts like these for every month of 2024 in his Astronomical Calendar.
Guy Ottewell explains sky dome maps
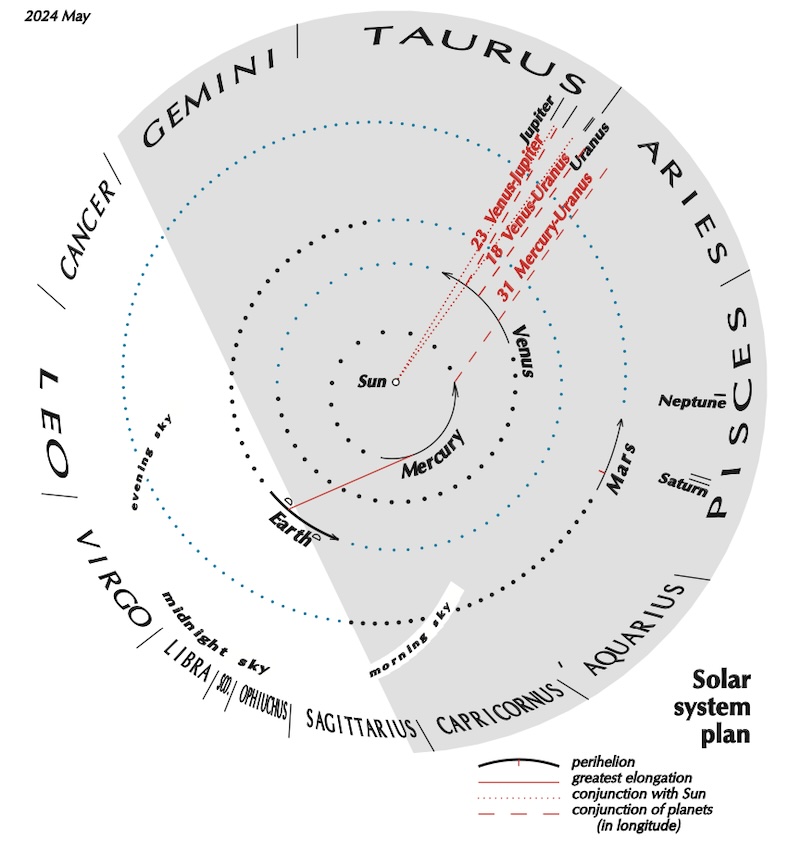
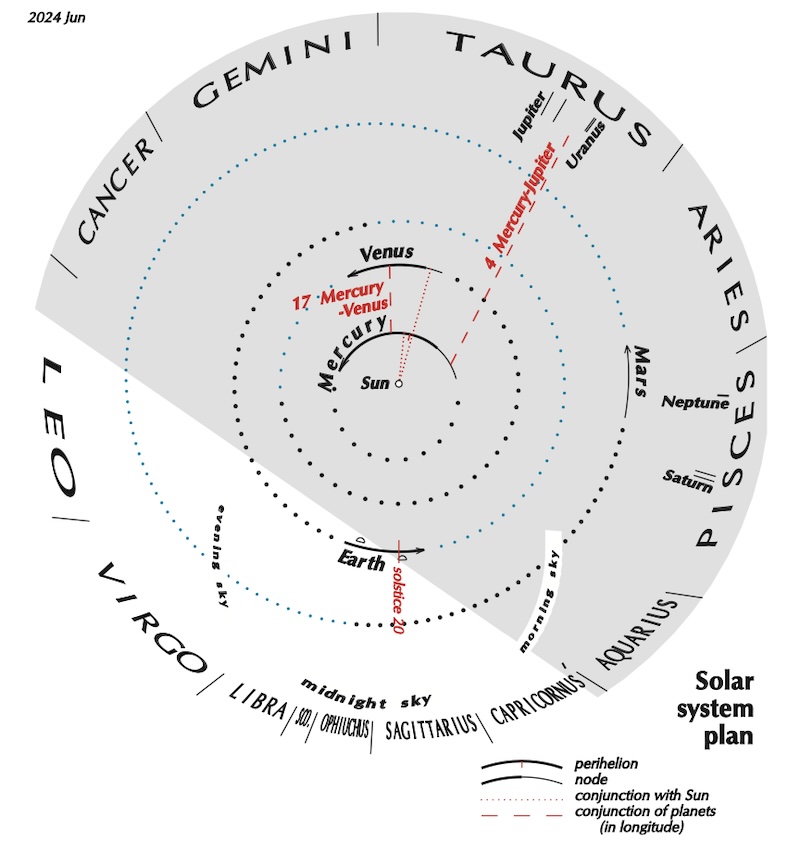
Heliocentric solar system visible planets and more
The sun-centered charts come from Guy Ottewell. You’ll find charts like these for every month of 2024 in his Astronomical Calendar.
Guy Ottewell explains heliocentric charts.
Some resources to enjoy
For more videos of great night sky events, visit EarthSky’s YouTube page.
Watch EarthSky’s video about Two Great Solar Eclipses Coming Up
Don’t miss anything. Subscribe to daily emails from EarthSky. It’s free!
Visit EarthSky’s Best Places to Stargaze to find a dark-sky location near you.
Post your own night sky photos at EarthSky Community Photos.
Translate Universal Time (UTC) to your time.
See the indispensable Observer’s Handbook, from the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada.
Visit Stellarium-Web.org for precise views from your location.
Almanac: Bright visible planets (rise and set times for your location).
Visit TheSkyLive for precise views from your location.

Bottom line: Visible planets and night sky guide for May 2024. Get ready for 6 planets to grace our skies in a line, starting from May 31. Plus, watch our livestream today at 12:15pm CDT.











