The evolution of car engines is a captivating journey that stretches over a century of technological advancements, innovation, and adaptation to changing societal and environmental needs. Explore the remarkable journey of car engine evolution spanning over a century, from the inception of internal combustion engines to the rise of hybrid and electric technologies.
Here’s a concise overview of this evolution:
1. The inception of Internal Combustion Engines (Late 19th Century)
- Origins – A shift from steam-powered engines to more efficient and versatile internal combustion engines during the late 19th century
Establishment of Principles
- Inventors and engineers began experimenting with the concept of burning fuel inside a cylinder to produce mechanical energy.
- The idea was to harness the energy released from burning fuel to drive pistons and, ultimately, propel vehicles.
Pioneering Innovators
- Nikolaus Otto – Otto developed the first practical four-stroke internal combustion engine in 1875, known as the Otto cycle.
- Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach – Daimler and Maybach built the first high-speed petrol engine In the 1880s which was compact and lightweight, making it suitable for automotive applications.
Early Challenges
- Inefficient fuel consumption
- lack of proper cooling systems
- Reliability issues
2. Rise of the Four-Stroke Engine (Early 20th Century)
Introduction of the Four-Stroke Cycle
- Widespread adoption of the four-stroke cycle as the standard design for internal combustion engines.
- The four-stroke cycle consists of four distinct phases: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
- Otto Cycle Standardization – The four-stroke cycle, also known as the Otto cycle, was based on Nikolaus Otto’s 1876 design and became the benchmark for automotive engines and aided car engine evolution
- Technological Advancements – Innovations in materials, manufacturing techniques, and engine design allowed for more efficient and powerful four-stroke engines.
- Mass Production and Accessibility
- Henry Ford’s introduction of the assembly line and mass production techniques made automobiles more affordable and accessible to the general public.
- The standardization of four-stroke engines played a crucial role in this automotive revolution, driving the widespread adoption of cars powered by internal combustion engines.
3. Turbocharging and Supercharging (Mid-20th Century)
- Forced Induction Introduction: Turbocharging and supercharging were introduced in the mid-20th century to enhance engine performance by increasing air intake and fuel combustion.
- Turbocharging Explained: Turbochargers use exhaust gases to spin a turbine, driving a compressor to force more air into the engine, boosting power without increasing engine size.
- Supercharging Mechanism: Superchargers, either belt-driven or mechanically driven, compress air to higher pressures, delivering immediate power gains across a broader engine speed range.
Benefits:
- Increased Power and Torque: Both technologies enhance acceleration and overall performance.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Despite increased power, they can optimize fuel combustion and efficiency.
Challenges:
- Heat Management: Additional heat generated requires efficient cooling systems.
- Durability: Higher pressures and temperatures can impact long-term engine reliability.
- Adoption in Performance Cars: Synonymous with high-performance vehicles, these technologies also offer a balance of performance and efficiency in mainstream cars.
- Environmental Impact: While boosting performance, these systems can increase emissions, leading to stricter regulations and cleaner engine advancements.
4. Adoption of Fuel Injection (Late 20th Century)
- Transition from Carburetors: In the late 20th century, electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems began replacing traditional carburettors in automotive engines and helped the car engine evolution.
- EFI Systems Explained: Electronic fuel injection uses sensors and an electronic control unit (ECU) to precisely meter and deliver fuel to the engine, optimizing combustion and performance.
Benefits of Fuel Injection:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: EFI systems provide more accurate fuel delivery, enhancing combustion efficiency and reducing fuel consumption.
- Enhanced Performance: Precise control over fuel delivery leads to better engine responsiveness, smoother acceleration, and increased power output.
- Emissions Control: EFI systems play a vital role in reducing harmful emissions by optimizing the air-fuel mixture and combustion process, aiding compliance with stricter environmental regulations.
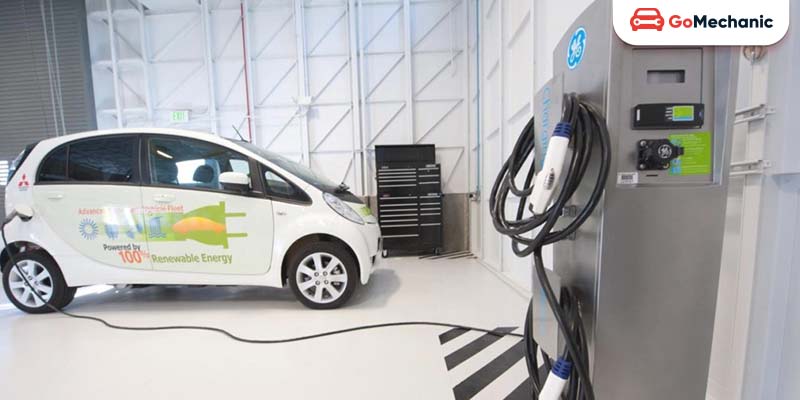
5. Hybrid and Electric Engines (21st Century)
- Environmental Focus: Growing environmental concerns drove the development and adoption of hybrid and electric engines in the 21st century and assisted car engine evolution.
- Hybrid Technology: Combines internal combustion engines with electric motors to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Powered solely by electric motors and batteries, eliminating tailpipe emissions and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Battery Innovations: Advances in lithium-ion battery technology have increased range, reduced charging times, and improved the overall performance of hybrid and electric vehicles.
6. Integration of Advanced Electronics (21st Century)
- Engine Management Systems: Advanced engine control units (ECUs) use sensors and algorithms to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
- Connectivity and Telematics: Integration of GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular technologies enable connected car features, real-time data monitoring, and remote diagnostics.
- Autonomous Driving Technologies: Advanced electronics, including radar, lidar, and cameras, support the development and deployment of autonomous driving features and self-driving capabilities.
- Safety Systems: Electronic stability control (ESC), anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and collision avoidance systems utilize advanced electronics to enhance vehicle safety and driver assistance.
7. Shift towards Alternative Fuels (21st Century)
- Environmental Concerns: Rising awareness of climate change drives the search for cleaner, sustainable fuel alternatives.
- Biofuels: Derived from renewable sources like corn and algae, biofuels offer a greener option than fossil fuels.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Producing only water as a byproduct, hydrogen-powered vehicles promise zero emissions.
- Natural Gas and Propane: CNG and propane provide cleaner-burning options with reduced emissions.
- Electric Vehicles: Advancements in battery tech and charging infrastructure support the rise of electric vehicles as a clean fuel alternative and towards the car engine evolution.
Conclusion
From the days of internal combustion engines to the era of hybrid and electric powertrains, the car engine evolution reflects a relentless journey of efficiency, performance, and environmental sustainability. As technology continues to advance, the automotive industry is moving towards further innovation and adaptation to meet the evolving needs of society and the planet.






