Ever wondered why the ocean tides rise and fall? What is the difference between a spring tide and a neap tide? The answer lies in the Moon’s gravitational pull on Earth’s waters. This post will explore how the Moon’s position and gravitational forces play a pivotal role in the rhythmic movement of tides. We’ll also review how tidal extremes affect the marine environment, human activities, and coastal life. By understanding this celestial influence, we gain insights into one of our planet’s most consistent and observable natural phenomena.
What We Review
The Moon’s Tidal Grip on Earth
At its core, the question “How does the moon affect the tides?” revolves around the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon on Earth’s oceans.
Moon’s Gravity: The Driver of Tides
The Moon’s gravitational pull on the Earth is not uniform. This is due to the varying distances of different parts of our planet from the Moon. This differential pull creates what are known as tidal forces. The side of Earth closest to the Moon experiences a stronger gravitational pull. As a result, the water bulges outwards, creating what is known as a high tide. Conversely, another high tide occurs on the opposite side of the Earth due to rotational forces.
In essence, at any given time, there are two high tides and two low tides around the Earth: one high tide where the Moon’s pull is strongest, another on the opposite side due to the rotational forces, and low tides in the areas perpendicular to these points.
The Bay of Fundy is known for having the highest tides in the world. This location experiences a natural phenomenon where water levels can rise by as much as 16 meters (52 feet) twice daily. This unique tidal range provides a dynamic and rich habitat for marine life. It also offers a spectacular view for visitors and showcases the powerful interplay between the Moon and Earth.
The Sun’s Subtle Tidal Influence
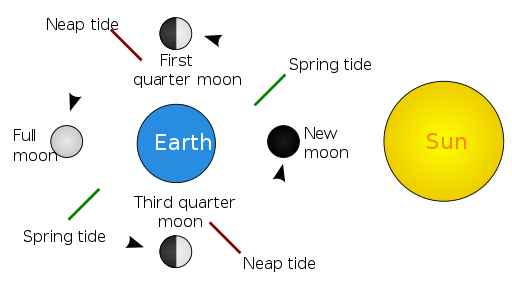
While the Moon is the primary influencer, the Sun also plays a significant role. Since the sun is much farther away, its effect is not as pronounced. When the Sun, Moon, and Earth align during the full and new moons, the Sun’s gravitational pull combines with the Moon’s, intensifying the tidal forces and resulting in even higher high tides and lower low tides. When this occurs, we call it a spring tide.
Conversely, when the Sun and Moon are at right angles relative to Earth, their gravitational forces partially cancel each other out. This scenario leads to neap tides, where the difference between high and low tides is less pronounced.
Exploring Spring Tides and Neap Tides
What is a Spring Tide?
A spring tide occurs when the Earth, Moon, and Sun align during new or full moons. This alignment means the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun combine to pull the Earth’s oceans more strongly, causing higher high tides and lower low tides. The term “spring” refers to the tide’s rise, not the season. The difference between high and low tides is more significant during spring tides, affecting coastal areas and marine life.
What is a Neap tide?
A neap tide occurs during the quarter moon phases when the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other. This angle makes their gravitational forces work against each other, leading to weaker tides. The ocean experiences the least difference between high and low tides during neap tides, creating milder tidal conditions.
Predicting Tides: How Often They Change
Frequency of Spring and Neap Tides
Spring and neap tides occur regularly due to the lunar cycle. Spring tides align with the new moon and full moon phases, happening approximately every 14 days, or twice a month. In contrast, neap tides align with the first and third quarters of the moon, also occurring twice a month. This regularity is dictated by the moon’s orbit around Earth, ensuring that these tides are predictable and follow a consistent schedule.
Comparing Spring and Neap Tides
The key difference between a spring and a neap tide is their strength and the extent of the tidal range. Spring tides bring the highest high tides and the lowest low tides, creating a significant difference between the two, known as the tidal range. These tides can lead to flooding in low-lying coastal areas and impact navigation and marine life.
Neap tides, on the other hand, present a much smaller tidal range, with less extreme high and low tides. These conditions can be favorable for activities that require more stable and predictable water levels, such as marine construction or coastal recreation that relies on calmer waters.
Tides in Action: Practical Impacts on Our World

Understanding the difference between a spring tide and a neap tide is important for various coastal activities and planning. For instance, shipping industries need to consider the larger tidal range during spring tides for docking and undocking ships, while beachgoers might prefer the milder conditions of neap tides for certain water activities. Similarly, coastal ecosystems adapt to these tidal changes, with different species thriving under the varying conditions brought by spring and neap tides.
Maritime Navigation: Tides are crucial in maritime navigation, particularly in coastal and estuarine waters. For instance, high tides provide the necessary water depth for large ships to enter or leave ports without running aground. Navigators must carefully plan their routes and timing based on tidal predictions to ensure safe and efficient passage, especially when navigating through narrow channels or over submerged hazards.

Coastal Wildlife: Tides also significantly influence coastal ecosystems. In tidal marshes, for example, the rise and fall of tides bring in nutrients that support a diverse range of organisms. Many species of birds, fish, and invertebrates rely on the tidal cycle for feeding and breeding. The horseshoe crab, a prehistoric species found along the East Coast of the United States, times its spawning to the high tides of spring and summer, ensuring that eggs are deposited in areas that will remain submerged and protected.
Beach Tourism: The tides affect beach tourism as well. Beachgoers’ experiences can vary significantly depending on whether it’s high or low tide. During low tide, more of the beach is exposed, revealing tide pools and extended shorelines that attract tourists for exploration and recreational activities. Conversely, high tides offer better conditions for swimming and water sports. Coastal businesses, such as tour operators and beach resorts, often schedule their activities around the tide to maximize the safety and enjoyment of their guests.
Examining these scenarios shows that tides have a far-reaching impact on human activities and natural habitats. This highlights the practical importance of understanding this dynamic natural force.
Wrapping Up: The Moon’s Mark on Earth’s Tides
The rise and fall of ocean tides, controlled by the Moon’s gravity, are a key component of Earth’s natural systems. These tidal cycles affect both marine life and human activities. This look at how the Moon influences tides, including the stronger spring tide and the weaker neap tide, shows how connected space and Earth are. Understanding these forces helps us learn more about Earth and improves how we move and work with the sea.