What is Digital Revolution?
The digital revolution refers to the shift from analog electronic and mechanical devices to digital technology, beginning in the 1980s and continuing today. This era brought widespread use of computers, the Internet, smartphones, VoIP services, and digital ecosystems, integrating Internet-based communications and digital tools into our daily lives.
The digital revolution has transformed the way we live, work and communicate. Smartphones, social media, and e-commerce have made information and services more accessible, keeping us connected. In the workplace, tools like cloud computing, collaborative software, and artificial intelligence (AI) have boosted productivity and communication, making businesses more efficient and innovative. This shift also allows remote work, letting employees work from anywhere and breaking traditional office boundaries.
The digital revolution marks the beginning of the Information Era and is also called the Third Industrial Revolution.
Key Takeaways
- The digital revolution definition refers to the advancement of technology from analog devices to the digital technologies available today.
- It started during the 1980s and is ongoing, introducing us to the Internet, streaming, smartphones, digital ecosystems, and more.
- The digital revolution has transformed the way we live, work and communicate.
- Notable positive impacts include access to vast knowledge, instant global communications, convenience, innovation, and social empowerment.
- Key applications shaping the digital revolution today include 5G networks, AI, blockchain technology, IoT, and others.
History of Digital Revolution
The development and advancement of digital technologies started with one fundamental idea: The Internet.
Here is a brief timeline of how the digital revolution progressed:
The transistor, which was introduced in 1947, paved the way for the development of advanced digital computers. The government, military and other organizations used computer systems during the 1950s and 1960s. This research eventually led to the creation of the World Wide Web (WWW).
Computers became familiar machines, and by the end of the decade, being able to use one became necessary for many jobs. The first cellphone was also introduced during this decade.
By 1992, the World Wide Web had been introduced, and by 1996 the Internet became a normal part of most business operations. By the late 1990s, the Internet became a part of everyday life for almost half of the American population.
By this decade, the digital revolution had begun to spread all over the developing world. Mobile phones were commonly seen, the number of Internet users continued to grow, television transitioned from analog to digital signals.
By this decade, the Internet reached more than 25% of the world’s population. Mobile communication became crucial and the connection between websites and mobile gadgets was a standard. 2013 saw the rise of cloud computing services, allowing users to consume media and use business applications on mobile devices.
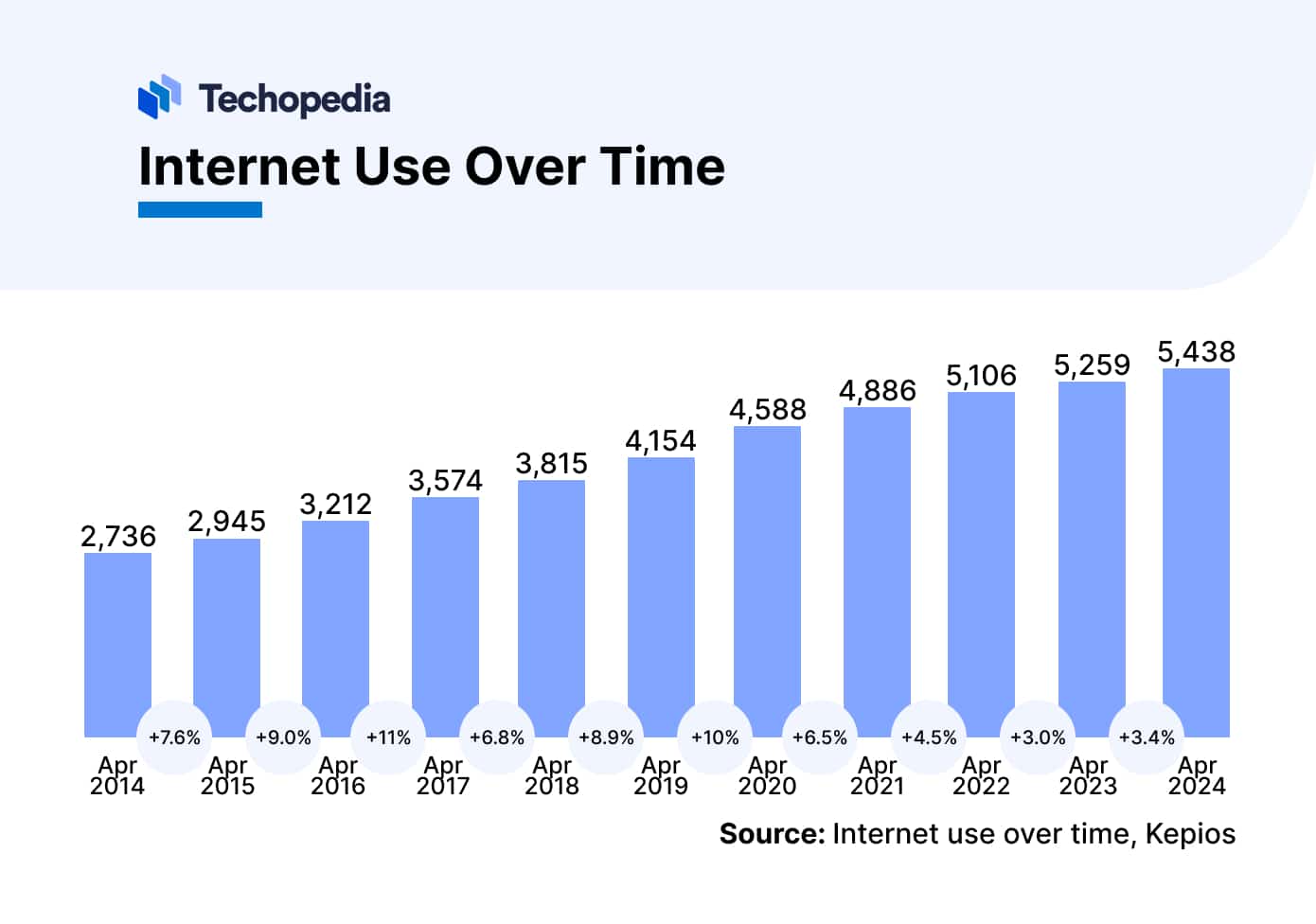
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work technologies. Artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) continued to innovate across many domains, such as healthcare, finance, and customer service. As of April 2024, there were 5.44 billion Internet users worldwide, or around 67% of the world’s total population.
The digital revolution is still evolving, with continuous advancements in technology and digital innovation shaping our world – how we learn, work, communicate, and complete tasks in our daily lives.
The Positive Impact of the Digital Revolution
- Access to information: Vast knowledge is readily available online.
- Connectivity: Global communications are instant, from anywhere.
- Convenience: Digital tools and services simplify daily tasks.
- Economic growth: The digital economy spurred new industries and jobs.
- Education: Online learning and digital resources make education more accessible.
- Social empowerment: Digital platforms amplify voices and facilitate social movements.
Negative Consequences of Digital Revolution
- Cybersecurity: Growing risks of hacking and cyberattacks.
- Digital divide: Unequal access to technology and the Internet.
- Environmental impact: Electronic waste (e-waste) and energy consumption.
- Information overload: Difficulty managing vast amounts of data.
- Job displacement: Automation leading to loss of traditional jobs.
- Privacy concerns: Increased data collection and surveillance.
Digital Revolution Challenges
The digital revolution offers numerous benefits, but it also presents challenges for consumers and businesses.
Challenges for consumers:
- Cybersecurity risks
- Digital divide
- Digital literacy & digital dexterity
- E-waste
- Job displacement
- Internet privacy concerns
Challenges for business:
- Cybersecurity threats
- Data privacy regulations
- Digital transformation costs
- Ethical use of technology
- Finding expertise in emerging technologies
- Regulation and compliance
- Remote work challenges
Digital Revolution Future
The future of the digital revolution promises even more changes through ongoing digital transformation. As technology advances, we will see further integration of digital tools and processes driving innovation, impacting many aspects of our daily lives – from work and communication to learning and entertainment.
Key technologies shaping the digital revolution today include:
The Bottom Line
The digital revolution meaning refers to the shift from electronic and mechanical devices to today’s digital technology. Beginning in the 1980s, this era has transformed how we live, work, and communicate. It offers easy access to information, instant communication, digital ecosystems, and more accessible education. However, these advancements also bring challenges, such as cybersecurity risks, privacy concerns, and potential job displacement.
The digital revolution is ongoing and will continue to reshape our lives, workplaces, and societies through continuous technological innovation.
FAQs
What is the Digital Revolution in simple terms?
What are the five phases of the digital revolution?
Who led the digital revolution?
What was the digital revolution in the 1970s?
What was the digital revolution in the 1990s?
References
- Digital Around the World (Datareportal)