Unveiling the Benzoic Acid Structure and Properties
Discover the significance of the benzoic acid structure in organic chemistry. Uncover its molecular composition, properties, and applications in this comprehensive article. Felton2 MIN READMay 17, 2024Benzoic acid, as an important organic compound, holds significant applications and research value in the field of chemistry. Understanding its molecular structure is fundamental to comprehend the properties and reaction mechanisms of benzoic acid. In this article, we will delve into what the structure of benzoic acid is, dissecting the features and significance within its molecular structure. Through interpreting the structure of benzoic acid, we can better grasp its role and applications in organic chemistry, laying the foundation for further learning and research.
What is Benzoic Acid?
Benzoic acid is an organic compound with the benzoic acid structure C6H5COOH or C7H6O2. It is a white or colorless crystalline solid belonging to the carboxylic acid family. It is used in the manufacture of various products, including perfumes, toothpaste, face wash, chemicals, dyes, and insect repellents. It is also used as a preservative in certain foods such as pickles, jams, etc. It has a pleasant fruity odor. Sodium benzoate is a salt used for food preservation and is a derivative of benzoic acid.
Benzoic acid was first discovered in the 16th century. It was initially extracted naturally from gum benzoin, hence the name benzoic acid. Gum benzoin was used earlier in traditional medicine. German chemist Adolf von Baeyer first synthesized benzoic acid in 1875. It was extracted from a compound called toluene, which comes from coal tar. Nowadays, benzoic acid is mainly synthesized in laboratories.
What is the Benzoic Acid Structure?
What is the format of benzoic acid? The molecular formula of benzoic acid is C6H5COOH or C7H6O2. The benzoic acid molecule consists of seven carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. Benzoic acid consists of a benzene (hexagonal) ring with six carbons. Each carbon in the benzene ring has an alternating single and double bond. Additionally, 5 out of the 6 carbons are singly bonded to hydrogen atoms. Furthermore, the ring is attached to a carboxyl functional group (-COOH), which imparts acidity to benzoic acid. The carboxyl group consists of a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group. The structure of benzoic acid is as follows:
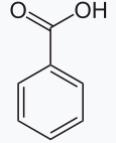
What is the Crystal Structure of Benzoic Acid?
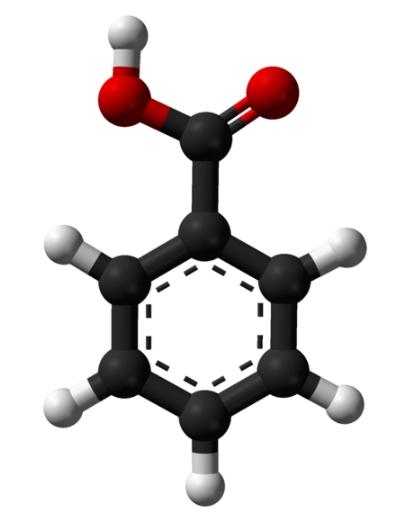
Benzoic acid crystallizes in a monoclinic crystal system. R. Feld et al. redetermined the crystal structure of benzoic acid C6H5CO2H at room temperature using X-ray diffraction. Extensive neutron diffraction measurements were also conducted: single crystal methods at room temperature and 130 K; powder profile analysis on C6D5CO2H at 130 K and 5 K.
The structure consists of centrosymmetric dimers where two molecules are connected by a pair of hydrogen bonds between their carboxyl groups. Better precision was attached to the X-ray results. The full-matrix refinement on 1011 independent reflections converged at R = 3.7%. For all atoms except the acidic hydrogen, this improvement is indeed based on a formally ordered model. C - O distances are 1.258, 1.268(2) Å, C - C - O angles are 118.7, 117.8(1)°; while the acidic hydrogen manifests as two "half-atoms" on the hydrogen bond with a distance of 0.9 Å to each oxygen atom. The simplest explanation for these findings is due to disorder: two configurations, appearing randomly, in almost equal proportions.
Properties of Benzoic Acid
Benzoic acid possesses many characteristics that make it widely useful across various industries. Its properties make it unique and contribute to its extensive use and applications. The physical and chemical properties of benzoic acid are as follows.
Physical Properties
State: Benzoic acid is a white or colorless crystalline solid.
Solubility: Benzoic acid is slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol.
Density: The density of benzoic acid is approximately 1.27 grams per cubic centimeter.
Odor: Benzoic acid typically has a pleasant fruity odor.
Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of benzoic acid is 122.12 g/mol.
Melting Point: 122°C.
Boiling Point: Approximately 249°C.
pKa: 4.19.
Density: 1.27 g/cm3.
Chemical Properties
Stability: Benzoic acid exhibits high stability under normal conditions and is not easily decomposed.
Acidity: It is a weak acid, thus capable of donating hydrogen ions (H+) to form benzoate ions.
pH Value: As a weak acid, its pH is approximately 2.8.
Antimicrobial Properties: Benzoic acid possesses antimicrobial properties, hence its salts are commonly used as preservatives in food and cosmetics.
Sublimation: Benzoic acid can sublime, meaning it can transition directly from solid to vapor without becoming a liquid.
Reactivity: Various chemical reactions can occur, such as nitration, oxidation, decarboxylation, etc.
What is benzoic acid functional group?
The functional group in benzoic acid is the carboxylic acid group. This group consists of a carbonyl (C=O) bonded to a hydroxyl (OH) group. The chemical formula for the carboxyl group is -COOH.
Benzoic acid is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is C6H5COOH, meaning it has a benzene ring (C6H6) attached to a carboxyl group. Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid, slightly soluble in water. It is a weak acid but stronger in acidity compared to most alcohols. This is because the benzene ring helps stabilize the negative charge on the carboxylic acid oxygen atom when the carboxyl loses a proton (H+).
Frequently Asked Questions About Benzoic Acid
(1) What does benzoic acid look like?
Benzoic acid appears as white crystalline solids. These crystals can be needle-like or flaky. See the image below:

(2) Is benzoic acid good for the body?
While the body shouldn't be overly exposed to benzoic acid, it can bring about many practical benefits. Benzoic acid can prevent the formation of bacteria, which applies to topical creams used for treating and curing insect bites, redness, swelling, burns, etc. Due to these antifungal and antibacterial uses, it may also be used to boost people's digestive functions. It is also used as a preservative in many foods.
(3) Does benzoic acid harm the environment?
When handling benzoic acid, it's important to know that, in controlled amounts, this acid won't have corresponding negative effects on anything. However, in laboratory environments, where the concentration of this substance is higher, spills and accidents may occur. In such cases, it's always important to ensure that everything is gloved up and shielded well.
Conclusion
Through this introduction, we have delved into the structure and molecular characteristics of benzoic acid. Benzoic acid, an organic acid, contains a benzene ring and a carboxyl group in its molecular structure, which gives it a range of specific chemical properties and reaction characteristics. Understanding the structure of benzoic acid helps us better comprehend its role in chemical reactions and its physical properties.
References:
[1]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benzoic_acid
[2]Feld R, Lehmann M S, Muir K W, et al. The crystal structure of benzoic acid: a redetermination with X-rays at room temperature; a summary of neutron-diffraction work at temperatures down to 5 K[J]. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie-Crystalline Materials, 1981, 157(3-4): 215-231.
[3]https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/benzoic-acid
[4]https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/benzoic-acid/?ref=header_search
-
 Decoding the Polarity of Benzoic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide Benzoic acid Unravel the mystery of benzoic acid polarity, exploring its structure and electrical properties. Is benzoic acid polar or nonpolar? Delve into the influence of its molecular structure and learn about its applications.
Decoding the Polarity of Benzoic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide Benzoic acid Unravel the mystery of benzoic acid polarity, exploring its structure and electrical properties. Is benzoic acid polar or nonpolar? Delve into the influence of its molecular structure and learn about its applications. -
 Understanding Benzoic Acid Solubility: A Comprehensive Guide Benzoic acid Discover the ins and outs of benzoic acid solubility in this comprehensive guide. Learn why it's vital in chemistry experiments and reactions.
Understanding Benzoic Acid Solubility: A Comprehensive Guide Benzoic acid Discover the ins and outs of benzoic acid solubility in this comprehensive guide. Learn why it's vital in chemistry experiments and reactions. -
 Unveiling the Benzoic Acid Structure and Properties Benzoic acid Discover the significance of the benzoic acid structure in organic chemistry. Uncover its molecular composition, properties, and applications in this comprehensive article.
Unveiling the Benzoic Acid Structure and Properties Benzoic acid Discover the significance of the benzoic acid structure in organic chemistry. Uncover its molecular composition, properties, and applications in this comprehensive article.
- Decoding the Polarity of Benzoic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Benzoic Acid Solubility: A Comprehensive Guide
- Unveiling the Benzoic Acid Structure and Properties
- The Ultimate Guide to Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
- Trans Resveratrol vs Resveratrol: Understanding the Key Differences
- Unraveling the Mysteries of Phthalic Anhydride: What is phthalic anhydride
- What is the Lewis Structure of Isopropyl alcohol?
- What is the Lewis Structure of Methane?





