Ever wondered about the complex web of trade that shaped our world? Triangular trade refers to a historical trade system that connected three regions across the globe, creating a network of exchange that was as fascinating as it was impactful. But what exactly made this trade system so unique, and why does it still capture our imagination today? From the exchange of goods like sugar, tobacco, and cotton to the darker side of human history, the slave trade, this system was a cornerstone of the global economy for centuries. Ready to dive into a past filled with intrigue, economics, and transformation? Let's unravel the mysteries of triangular trade, revealing facts that bring to life the stories of people, products, and power dynamics that shaped the modern world.
Key Takeaways:
- The Triangular Trade connected Europe, Africa, and the Americas, shaping their economies and cultures. It led to the exchange of goods, enslaved people, and commodities, but also had devastating effects on African societies.
- The legacy of the Triangular Trade is still felt today, impacting racial inequality, economic systems, and cultural exchanges. Understanding its history is crucial for comprehending the complex effects of globalization.
What Is the Triangular Trade?
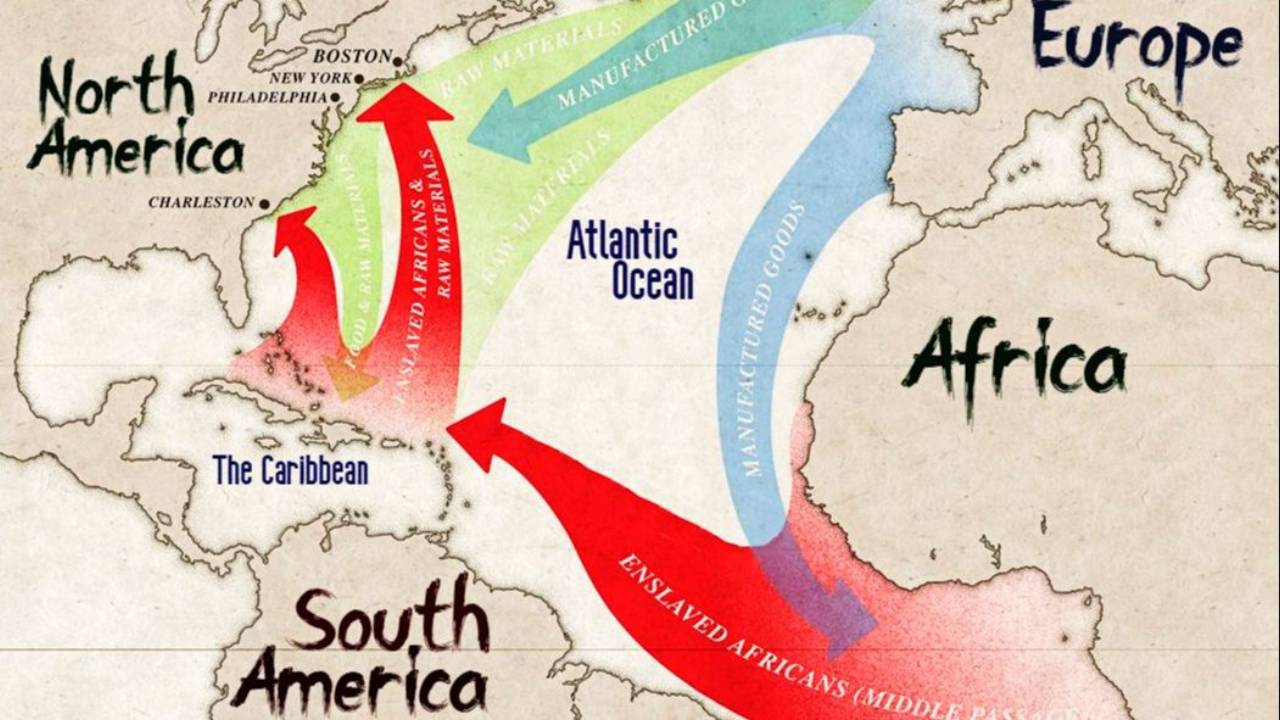
Triangular trade refers to a historical trade system that connected three regions across the Atlantic Ocean. This system allowed for the exchange of goods, enslaved people, and commodities between Europe, Africa, and the Americas. It played a significant role in the economy and development of these regions from the 16th to the 19th century.
Origins of the Triangular Trade
-
Triangular trade began in the late 16th century as European powers sought new sources of wealth. They discovered that by linking the continents, they could profit from the sale of goods and the forced labor of enslaved Africans.
-
Initially, European ships transported manufactured goods to Africa, where they were exchanged for enslaved people. These individuals were then taken across the Atlantic to the Americas, where they were sold. The ships would return to Europe with goods such as sugar, cotton, and tobacco, completing the triangle.
The Middle Passage
-
The journey of enslaved Africans to the Americas, known as the Middle Passage, was notoriously brutal. Conditions on board were horrific, with inadequate space, food, and sanitation.
-
It's estimated that around 12 million Africans were transported to the Americas during the triangular trade, with a significant number dying during the Middle Passage due to the inhumane conditions.
Economic Impact on Europe
-
European countries, especially Britain, Portugal, and the Netherlands, greatly benefited economically from the triangular trade. Profits from the trade funded industrial growth and the expansion of empires.
-
Wealth accumulated from the trade contributed to the financing of the Industrial Revolution in Britain, changing the global economic landscape forever.
Effects on Africa
-
The triangular trade had devastating effects on African societies. It led to increased warfare and instability as groups sought to capture others to sell into slavery.
-
Populations in some regions of Africa were significantly reduced, and the social fabric of many communities was destroyed, leading to long-term economic and social challenges.
The Role of the Americas
-
In the Americas, the labor of enslaved Africans was crucial for the development of colonies, especially in the production of cash crops like sugar, tobacco, and cotton.
-
The wealth generated from these crops, produced through forced labor, laid the foundation for the economic systems of many American states and contributed to their eventual independence and growth.
Abolition and Legacy
-
The triangular trade came to an end in the early 19th century as movements against slavery grew stronger, leading to the abolition of the slave trade and eventually slavery itself in most parts of the world.
-
The legacy of the triangular trade is still felt today, with its impacts on racial inequality, economic disparities, and cultural identities being subjects of ongoing study and discussion.
Cultural Exchanges
-
Despite its brutal nature, the triangular trade led to significant cultural exchanges among Europe, Africa, and the Americas. These included the spread of African music, food, and traditions, which have enriched cultures across the Americas.
-
Languages, religions, and other cultural practices were also blended, creating unique Afro-European and Afro-American cultures that continue to influence the world today.
Economic Systems
-
The triangular trade also played a role in the development of the modern capitalist economy. It introduced new commodities to global markets and established trade routes that are still in use.
-
Moreover, the wealth generated from this trade system helped to build financial institutions and commercial practices that underpin today's global economy.
Environmental Impact
-
The large-scale agricultural practices introduced in the Americas to produce cash crops for the triangular trade had significant environmental impacts, including deforestation and soil depletion.
-
These practices also led to the introduction of invasive species and the alteration of landscapes, some of which continue to affect biodiversity in the Americas.
Conclusion
-
Understanding the triangular trade is essential for comprehending the complex history of globalization and its effects on the world. It highlights the interconnectedness of economies and cultures, as well as the dark aspects of human history.
-
As we reflect on the triangular trade, it's crucial to acknowledge its role in shaping the modern world, while also learning from its injustices to prevent similar atrocities in the future.
Piecing Together the Triangular Trade Puzzle
We've journeyed through the complex web of triangular trade, uncovering its profound impact on history, economies, and societies across continents. This trade network wasn't just about the exchange of goods like sugar, tobacco, and cotton; it was deeply intertwined with the dark history of slavery, shaping the modern world in ways that are still felt today. Understanding these facts helps us grasp the interconnectedness of global history and the lasting legacies of colonialism. As we reflect on this knowledge, let's remember the human stories behind these transactions, the resilience of those who suffered, and the lessons they offer for today's world. Knowledge of the triangular trade is more than historical trivia; it's a lens through which we can view the complexities of global relations and human rights.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
